Abstract
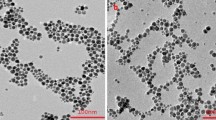
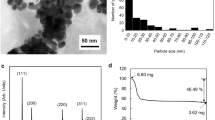
The temperature dependency and reversibility of the sheet resistance of silver nanoparticles covered by 3-mercaptopropionic acid (Ag-MPA) molecules, used in the printed temperature sensor, has been investigated. The microstructural evaluation, the FTIR spectra and thermal property analyses of the Ag-MPA films suggest co-existence of both weakly adsorbed as well as firmly adsorbed MPA molecules on the surface of Ag nanoparticles. The weakly adsorbed MPA molecules was to a great extent be desorbed and removed from the surfaces of silver nanoparticles when heated up to 180 °C for the first time. While the firmly adsorbed MPA molecules remain on the surfaces of silver nanoparticles even at higher temperature. Yet the firmly adsorbed MPA molecules are likely having gone through a transformation circle from/to the gauche and trans conformations in correspondence to a heating and cooling cycle, which results in temperature dependent and reversible sheet resistance. The MPA molecules in the gauche conformation are more densely packed on the surface of silver nanoparticles and can hinder the electron’s movability within the Ag-MPA film. While in the trans conformation with lower ‘surface space’ coverage by the MPA molecules, electrons move more freely within the film. Based on the temperature dependent nature, the fully printed temperature sensor using the Ag-MPA nanoparticles as the functional layer was made, of which the highest sensitivity is 5.12% °C−1 at 200 °C.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kamyshny, S. Magdassi, Conductive nanomaterials for printed electronics. Small 10, 3515–3535 (2014)
W. Yang, C. Liu, Z. Zhang, Y. Liu, S. Nie, Paper-based nanosilver conductive ink. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 628–634 (2013)
B.Y. Ahn, E.B. Duoss, M.J. Motala, X.Y. Guo, S.I. Park, Y.J. Xiong, J. Yoon, R.G. Nuzzo, J.A. Rogers, J.A. Lewis, Omnidirectional printing of flexible, stretchable, and spanning silver microelectrodes. Science 323, 1590–1593 (2009)
J. Perelaer, P.J. Smith, D. Mager, D. Soltman, S.K. Volkman, V. Subramanian, J.G. Korvink, U.S. Schubert, Printed electronics: the challenges involved in printing devices, interconnects, and contacts based on inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 8446–8453 (2010)
T. Yamada, K. Fukuhara, K. Matsuoka, H. Minemawari, J. Tsutsumi, N. Fukuda, K. Aoshima, S. Arai, Y. Makita, H. Kubo, T. Enomoto, T. Togashi, M. Kurihara, T. Hasegawa, Nanoparticle chemisorption printing technique for conductive silver patterning with submicron resolution. Nat. Commun. 7, 9 (2016)
J.K. Jiang, B. Bao, M.Z. Li, J.Z. Sun, C. Zhang, Y. Li, F.Y. Li, X. Yao, Y.L. Song, Fabrication of transparent multilayer circuits by inkjet printing. Adv. Mater. 28, 1420–1426 (2016)
X.Q. Zhou, W. Li, M.L. Wu, S. Tang, D.Z. Liu, Enhanced dispersibility and dispersion stability of dodecylamine-protected silver nanoparticles by dodecanethiol for ink-jet conductive inks. Appl. Surf. Sci. 292, 537–543 (2014)
P. Kanninen, C. Johans, J. Merta, K. Kontturi, Influence of ligand structure on the stability and oxidation of copper nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 318, 88–95 (2008)
J. Natsuki, T. Abe, Synthesis of pure colloidal silver nanoparticles with high electroconductivity for printed electronic circuits: the effect of amines on their formation in aqueous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 359, 19–23 (2011)
A.J. Lovinger, Development of electrical conduction in silver-filled epoxy adhesives. J. Adhes. 10, 1–15 (2008)
G.R. Ruschau, S. Yoshikawa, R.E. Newnham, Resistivities of conductive composites. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 953–959 (1992)
L.X. Mo, D.Z. Liu, W. Li, L.H. Li, L.C. Wang, X.Q. Zhou, Effects of dodecylamine and dodecanethiol on the conductive properties of nano-Ag films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 5746–5753 (2011)
F.C. Wu, D.Z. Liu, T.Y. Wang, W. Li, X.Q. Zhou, Different surface properties of l-arginine functionalized silver nanoparticles and their influence on the conductive and adhesive properties of nanosilver films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 6781–6786 (2015)
J. Liu, H. Ji, S. Wang, M. Li, The low temperature exothermic sintering of formic acid treated Cu nanoparticles for conductive ink. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-5476-3
P. Pulkkinen, J. Shan, K. Leppanen, A. Kansakoski, A. Laiho, M. Jarn, H. Tenhu, Poly(ethylene imine) and tetraethylenepentamine as protecting agents for metallic copper nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 519–525 (2009)
L.X. Mo, D.Z. Liu, X.Q. Zhou, L.H. Li, Preparation and conductive mechanism of the ink-jet printed nanosilver films for flexible display, in: 2009 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, CISP’09, October 17, 2009–October 19, 2009, (IEEE Computer Society, Tianjin University of Technology, Tianjin, 2009)
Y.Q. Yong, T. Yonezawa, M. Matsubara, H. Tsukamoto, The mechanism of alkylamine-stabilized copper fine particles towards improving the electrical conductivity of copper films at low sintering temperature. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 5890–5895 (2015)
S. Magdassi, M. Grouchko, O. Berezin, A. Kamyshny, Triggering the sintering of silver nanoparticles at room temperature. ACS Nano 4, 1943–1948 (2010)
M. Grouchko, A. Kamyshny, C.F. Mihailescu, D.F. Anghel, S. Magdassi, Conductive inks with a “built-in” mechanism that enables sintering at room temperature. ACS Nano 5, 3354–3359 (2011)
L.X. Mo, J. Ran, L. Yang, Y. Fang, Q.B. Zhai, L.H. Li, Flexible transparent conductive films combining flexographic printed silver grids with CNT coating. Nanotechnology 27, 065202 (2016)
H. Shirai, M.T. Nguyen, Y. Ishida, T. Yonezawa, A new approach for additive-free room temperature sintering of conductive patterns using polymer-stabilized Sn nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 2228–2234 (2016)
B. Reiser, L. Gonzalez-Garcia, I. Kanelidis, J.H.M. Maurer, T. Kraus, Gold nanorods with conjugated polymer ligands: sintering-free conductive inks for printed electronics. Chem. Sci. 7, 4190–4196 (2016)
I. Jung, K. Shin, N.R. Kim, H.M. Lee, Synthesis of low-temperature-processable and highly conductive Ag ink by a simple ligand modification: the role of adsorption energy. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 1855–1862 (2013)
W. Yang, C. Liu, Z. Zhang, Y. Liu, S. Nie, Preparation and conductive mechanism of copper nanoparticles ink. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 5175–5182 (2013)
S. Bhanushali, P. Ghosh, A. Ganesh, W.L. Cheng, 1D copper nanostructures: progress, challenges and opportunities. Small 11, 1232–1252 (2015)
W.F. Shen, X.P. Zhang, Q.J. Huang, Q.S. Xu, W.J. Song, Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 6, 1622–1628 (2014)
Z.L. Zhang, X.Y. Zhang, Z.Q. Xin, M.M. Deng, Y.Q. Wen, Y.L. Song, Synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for ink-jet printed flexible electronics. Nanotechnology 22, 425601 (2011)
A. Ulman, Formation and structure of self-assembled monolayers. Chem. Rev. 96, 1533–1554 (1996)
J.C. Love, L.A. Estroff, J.K. Kriebel, R.G. Nuzzo, G.M. Whitesides, Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 105, 1103–1169 (2005)
L.L. Rouhana, M.D. Moussallem, J.B. Schlenoff, Adsorption of short-chain thiols and disulfides onto gold under defined mass transport conditions: coverage, kinetics, and mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 16080–16091 (2011)
Y. Taniguchi, T. Takishita, T. Kawai, T. Nakashima, End-to-end self-assembly of semiconductor nanorods in water by using an amphiphilic surface design. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 55, 2083–2086 (2016)
R.K. Mendes, R.F. Carvalhal, L.T. Kubota, Effects of different self-assembled monolayers on enzyme immobilization procedures in peroxidase-based biosensor development. J. Electroanal. Chem. 612, 164–172 (2008)
J.B. Shein, L.M.H. Lai, P.K. Eggers, M.N. Paddon-Row, J.J. Gooding, Formation of efficient electron transfer pathways by adsorbing gold nanoparticles to self-assembled monolayer modified electrodes. Langmuir 25, 11121–11128 (2009)
Y. Li, Y. Wu, B.S. Ong, Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles useful for fabrication of high-conductivity elements for printed electronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 3266–3267 (2005)
N.R. Jana, X. Peng, Single-phase and gram-scale routes toward nearly monodisperse Au and other noble metal nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 14280–14281 (2003)
C.N. Chen, C.P. Chen, T.Y. Dong, T.C. Chang, M.C. Chen, H.T. Chen, I.G. Chen, Using nanoparticles as direct-injection printing ink to fabricate conductive silver features on a transparent flexible PET substrate at room temperature. Acta Mater. 60, 5914–5924 (2012)
S.Y. Kang, K. Kim, Comparative study of dodecanethiol-derivatized silver nanoparticles prepared in one-phase and two-phase systems. Langmuir 14, 226–230 (1998)
H. Hiramatsu, F.E. Osterloh, A simple large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold and silver nanoparticles with adjustable sizes and with exchangeable surfactants. Chem. Mat. 16, 2509–2511 (2004)
A. Kudelski, Structures of monolayers formed from different HS-(CH2)2-X thiols on gold, silver and copper: comparative studies by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 34, 853–862 (2003)
K.S. Moon, H. Dong, R. Maric, S. Pothukuchi, Y. Li, C.P. Wong, Thermal behavior of silver nanoparticles for low-temperature interconnect applications. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 168–175 (2005)
D.S. Sidhaye, B.L.V. Prasad, Melting characteristics of superlattices of alkanethiol-capped gold nanoparticles: the “excluded” story of excess thiol. Chem. Mat. 22, 1680–1685 (2010)
N. Sandhyarani, M.P. Antony, G.P. Selvam, T. Pradeep, Melting of monolayer protected cluster superlattices. J. Chem. Phys. 113, 9794–9803 (2000)
A. Kudelski, Raman and electrochemical characterization of 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate monolayers on silver: a comparison with monolayers of 3-mercaptopropionic acid. Langmuir 18, 4741–4747 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61474144), Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KZ201510015001), 2011 Collaborative innovation centre (04190116008/002) and Beijing Innovation Ability Improving Program (TJSHG201310015016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, L., Yang, L., Wang, Z. et al. On the temperature dependency and reversibility of sheet resistance of silver nanoparticles covered by 3-mercaptopropionic acid. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 4035–4043 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6017-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6017-9