Abstract
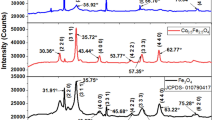
This article reports the structural, optical and magnetic properties of transition metal (Ni, Co, Mn and Fe) doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by modified Pechini sol–gel method. From the X-ray diffraction studies, it is obvious that all the synthesized samples show a phase purity of rutile tetragonal crystal structure of SnO2. The morphology was studied and the particle sizes were estimated from the field emission scanning electron microscopy. From photoluminescence spectra, we observed emission due to the presence of singly ionized oxygen vacancies. Raman spectroscopy shows dominant peaks at 644 and 782 cm−1 which were ascribed to A1g and B2g modes of the rutile structure. Isomer shifting due to dopant addition and large quadrupole splitting due to surface defects were observed in Mössbauer spectra. All the samples show ferromagnetic ordering up to 1 T. The relatively stronger ferromagnetic nature in Fe and Co doped SnO2 is due to the strong p–d exchange interaction. In case of Ni and Mn doped SnO2 samples, the lack of carrier-mediated interaction due to its inherent semiconducting nature reduces the total magnetic moment observed in these samples. The exchange coupling depends on the dopant type and its concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Sharma, M. Varshney, S. Kumar, K.D. Verma, R. Kumar, Magnetic properties of Fe and Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 1, 29 (2011)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019 (2000)
A.L. Schoenhalz, J.T. Arantes, A. Fazzio, G.M. Dalpian, Surface magnetization in non-doped ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 162503 (2009)
Y.C. Cho, S.J. Kim, S. Lee, S.J. Kim, C.R. Cho, H.H. Nahm, C.H. Park, I.K. Jeong, S. Park, T.E. Hong, S. Kuroda, S.Y. Jeong, Reversible ferromagnetic spin ordering governed by hydrogen in Co-doped ZnO semiconductor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 172514 (2009)
J. Hays, A. Punnoose, R. Baldner, M.H. Engelhard, J. Peloquin, K.M. Reddy, Relationship between the structural and magnetic properties of Co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 72, 075203 (2005)
H. Peng, J. Li, S.S. Li, J.B. Xia, Possible origin of ferromagnetism in undoped anatase TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 79, 092411 (2009)
R.C. Pawar, D.H. Choi, J.S. Lee, C.S. Lee, Formation of polar surfaces in microstructured ZnO by doping with Cu and applications in photocatalysis using visible light. Mater. Chem. Phys. 151, 167e180 (2015)
S.B. Ogale, R.J. Choudhary, J.P. Bhuban, S.E. Lofland, S.R. Shinde, S.N. Kale, V.N. Kulkarni, J. Higgins, C. Lanci, J.R. Simpson, N.D. Browning, S.D. Sarma, H.D. Drew, R.L. Greene, T. Venkatesan, High temperature ferromagnetism with a giant magnetic moment in transparent Co-doped SnO2−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 077205 (2003)
P. Venkateswara Reddy, S. Venkatramana Reddy, B. Sankara Reddy, Synthesis and properties of (Ni, Al) co-doped nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-5172-3
J.Y. Patil, A.V. Rajgure, L.K. Bagal, R.C. Pawar, I.S. Mulla, S.S. Suryavanshi, Structural, morphological, and gas response properties of citrate gel synthesized nanocrystalline ZnO and Zn0.9Cd0.10 materials. Ceram. Int. 39, 4383 (2013)
G.D. Khuspe, R.D. Sakhare, S.T. Navale, M.A. Chougule, Y.D. Kolekar, R.N. Mulik, R.C. Pawar, C.S. Lee, V.B. Patil, Nanostructured SnO2 thin films for NO2 gas sensing applications. Ceram. Int. 39, 8673 (2013)
A.V. Chichagov et al., Kristallographiya 35, 610 (1990)
A.A. Bolzan, C. Fong, B.J. Kennedy, C.J. Howard, Structural studies of rutile-type metal dioxides. Acta Crystallogr. B 53, 373 (1997)
M. Parthibavarman, B. Renganathan, D. Sastikumar, Development of high sensitivity ethanol gas sensor based on Co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles by microwave irradiation technique. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 1537–1544 (2013)
F. Gu, S.F. Wang, M.K. Leu, Y.X. Qi, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu, D.R. Yuan, Luminescent properties of Mn2+-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 6, 882 (2003)
A. DiéGuez, A. Romano-Rodríguez, A. Vilà, J.R. Morante, The complete Raman spectrum of nanometric SnO2 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1550 (2001)
S. Thansanvarkan, P. Mangkortang, S. Choopun, N. Mangkorntong, Characterization of SnO2 nanowires synthesized from SnO by carbothermal reduction process. Ceram. Int. 34, 1127 (2008)
F.H. Aragón, J.A.H. Coaquira, P. Hidalgo, S.W. da Silva, S.L.M. Brito, D. Gouvêa, P.C. Morais, Evidences of the evolution from solid solution to surface segregation in Ni-doped SnO2 nanoparticles using Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 42, 2011 (1081)
A. Bouaine, N. Brihi, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, S. Colis, A. Dinia, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Co-doped SnO2 powders synthesized by the coprecipitation technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 2924 (2007)
S. Das, S. Kar, S. Chaudhuri, Optical properties of SnO2 nanoparticles and nanorods synthesized by solvothermal process. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 114303 (2006)
K.C. Verma, R.K. Kotnala, Realizing ferromagnetic ordering in SnO2 and ZnO nanostructures with Fe Co, Ce ions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 17565 (2016)
K. Nomura, E. Kuzmann, C.A. Barrero, S. Stichleutner, Z. Homonnay, 57Fe Mössbauer study of sol–gel synthesized Sn1−x−y FexSbyO2−δ powders. Hyperfine Interact. 184, 57 (2008)
R.H.R. Castro, P. Hidalgo, J.A.H. Coaquira, J. Bettini, D. Zanchet, D. Gouvêa, Surface segregation in SnO2–Fe2O3 nanopowders and effects in Mössbauer spectroscopy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 11, 2134 (2005)
B. Gržta, E. Tkalčec, C. Gobbert, M. Takeda, M. Takahashi, K. Nomura, M. Jakšič, Structural studies of nanocrystalline SnO2 doped with antimony: XRD and Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 63, 765 (2002)
F.H. Aragón, J.A.H. Coaquira, R. Cohen, L.C.C.M. Nagamine, P. Hidalgo, S.L.M. Brito, D. Gouvêa, Structural and hyperfine properties of Ni-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 211, 77 (2012)
J.J. Beltran, L.C. Sanchez, J. Osorio, L. Tirado, E.M. Baggio-Saitovitch, C.A. Barrero, Crystallographic and magnetic properties of Fe-doped SnO2 nanopowders obtained by a sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 5002 (2010)
J.M.D. Coey, M. Venkatesan, C.B. Fitzgerald, Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4, 173 (2005)
X.L. Wang, Z.X. Dai, Z. Zeng, Search for ferromagnetism in SnO2 doped with transition metals (V, Mn, Fe, and Co). J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20, 045214 (2008)
R. Janisch, N.A. Spaldin, Understanding ferromagnetism in Co-doped TiO2 anatase from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 73, 035201 (2006)
J.M.D. Coey, A.P. Douvalis, C.B. Fitzgerald, M. Venkatesan, Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1332 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by UGC Govt. of India. The authors want to thank Sastra University for FESEM data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inpasalini, M.S., Sharma, L.K., Roychowdhury, A. et al. Influence of magnetic ion doping on structural, optical, magnetic and hyperfine properties of nanocrystalline SnO2 based dilute magnetic semiconductors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 3285–3292 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5921-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5921-3