Abstract
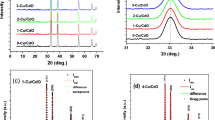
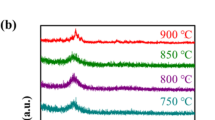
Silicon carbide (SiC) is regarded as a semiconductor and thus characterized mainly for its electrical conductivity. However, SiC does exhibit significant electrical resistance at low ambient temperatures and represents a possible dielectric insulator. In this paper, the dielectric properties of the β-SiC nanopowders were examined by X-ray diffraction and dielectric spectroscopy within the humid Malaysian environment. Research emphasis is placed on the stable dielectric behavior of the nanopowder itself as the nanopowder phase is susceptible to hydroxyl oxidization as mentioned by the nanopowder manufacturer. The XRD results identified the presence of β-SiC peaks whereas EDX detected minor oxygen presence in the nanopowder. Dielectric permittivity response of the nanopowder pellet indicated stable Quasi-DC dielectric behavior from 30 to 400 °C with minor increments of the initial relative dielectric permittivity at the lower temperatures. The relative dielectric permittivity of the SiC nanoparticles was determined to be 44 (30 °C) to 31 (400 °C) at 1 MHz. Arrhenius plot of the dielectric data resulted in a two linear energy activation plots due to possible hopping mechanisms within the SiC nanoparticles covalent structure. Overall, the β-SiC nanopowder exhibited a stable Quasi-DC behavior at the measured temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.D. Kingery, H.K. Bowen, D.R. Uhlmann, Introduction to Ceramics, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1976), pp. 44–45
A.A. Sagues, J.T. Wolan, A. De Fex, T.J. Fawcett, Electrochim. Acta 51(8–9), 1656–1663 (2006)
Y. Li, J. Yin, H. Wu, H. Deng, J. Chen, Y. Yan, X. Liu, Z. Huang, D. Jiang, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc. 35, 1647–1652 (2015)
J.G. Lee, S.P. Lee, Sensor Actuat. B 117, 437–441 (2006)
E. Arslan, Y. Safak, I. Tascioglu, H. Uslu, E. Ozbay, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1997–2001 (2010)
T. Sugino, T. Tai, Y. Etou, Diam. Relat. Mater. 10, 1375–1379 (2001)
H. Aoki, H. Shima, C. Kimura, T. Sugino, Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 1300–1303 (2007)
D. Hofman, J.A. Lely, J. Volger, The dielectric constant of SiC. Physica 23, 236 (1967)
L. Patrick, W.J. Choyke, Static dielectric constant of SiC. Phys. Rev. B. 2, 2255 (1970)
O. Chuvert, T. Stoto, L. Zuppiroli, Phys. Rev. B. 46, 8139 (1992)
D. Zhao, H. Zhao, W. Zhou, Phys. E 9, 679–685 (2001)
J. Sun, J. Li, G. Sun, B. Zhang, S. Zhang, H. Zhai, Ceram. Int. 28, 741–745 (2002)
X. Su, W. Zhou, J. Xu, Z. Li, F. Luo, D. Zhu, J. Alloys Compd. 402, L16–L19 (2010)
X. Su, W. Zhou, J. Xu, Z. Li, F. Luo, D. Zhu, Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 880–883 (2009)
H. Liu, H. Tian, J. Eur, Ceram. Soc. 32, 2505–2512 (2012)
S. Kasahara, Y. Katano, S. Shimanuki, K. Nakata, H. Ohno, J. Nucl. Mater. 191–194, 579–582 (1992)
J.S. Gonzalez, A.L. Ortiz, F. Guiberteau, C. Pascual, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3935–3939 (2007)
S. Li, N. Wang, H. Zhao, L. Du, Mater. Lett. 126, 217–219 (2014)
K.J. Kim, K. Lim, Y. Kim, M. Lee, W. Seo, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1695–1701 (2014)
K.J. Kim, K. Lim, Y. Kim, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 4401–4406 (2012)
D.K. Das-Gupta, P.C.N. Scarpa, Handbook of low and high dielectric constant materials and their applications, vol. 2, in Phenomena, Properties and Applications, ed. by H.S. Nalwa (Academic Press, San Diego, 1999), pp. 289–316
S. Agathopoulos, Ceram. Int. 38, 3309–3315 (2012)
O. Chauvet, I. Solomon, L. Zuppiroli, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 11, 303–306 (1992)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Malaysian Ministry of Education for providing financial aid for this research under the Research University Grant Scheme Project Code 05-01-12-1635RU. We also thank the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, UPM and the Institute of Advanced Material (ITMA), UPM for assistance in the technical and sample preparation stages.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
See, A., Hassan, J., Hashim, M. et al. Dielectric behavior of β-SiC nanopowders in air between 30 and 400 °C. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 6623–6629 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4608-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4608-0