Abstract
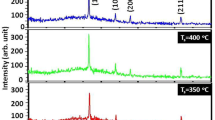
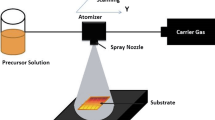
Nebulized spray pyrolysis is a simple and cost effective technique for the preparation of In2S3 thin films. In2S3 compound thin films were deposited on glass substrates at substrate temperatures from 200 to 350 °C in steps of 50 °C by nebulized spray pyrolysis technique. These films were shiny, thin and uniform, which were evidenced by specular reflections of white light due to multiple internal reflections of coherent rays. They were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), optical transmittance, scanning electron microscope imaging (SEM), energy dispersive analysis by X-rays and electrical conductivity. Cubic structure with preferential orientation along (111) plane was observed from XRD analysis. SEM analysis revealed that all the films have no voids and cracks. Direct band gap values were found to decrease up to 2.69 eV with increase in substrate temperature from 200 to 300 °C, but increased further, whereas the indirect band gap values were found to increase up to 2.14 eV with increase in substrate temperature from 200 to 300 °C, and decreased further. All the films were found as n-type semiconductors. The resistivity of all the samples decreased with increase in substrate temperature. A maximum carrier concentration value of 7.36 × 1018 cm−3 was obtained for the film grown at substrate temperature of 300 °C. The carrier mobility was increased up to 86.2 cm2/Vs by increasing the substrate temperature from 200 to 300 °C and then it decreased to 17.6 cm2/Vs at a substrate temperature of 350 °C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Naghavi, S. Spering, M. Powalla, B. Canava, D. Lincot, High-efficiency copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) solar cells with indium sulfide buffer layers deposited by atomic layer chemical vapour deposition (ALCVD). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 11, 437–443 (2003)
S. Gall, N. Barreau, S. Harel, J.C. Bernede, J. Kessler, Material analysis of PVD-grown indium sulphide buffer layers for Cu(In, Ga)Se2-based solar cells. Thin Solid Films 480–481, 138–141 (2005)
N. Barreau, Indium sulfide and relatives in the world of photovoltaics. Sol. Energy 83, 363–371 (2009)
S. Spiering, A. Eicke, D. Hariskos, M. Powalla, N. Naghavi, D. Lincot, Large-area Cd-free CIGS solar modules with In2S3 buffer layer deposited by ALCVD. Thin Solid Films 451–452, 562–566 (2004)
I. Repins, M.A. Contreras, B. Egaas, C. Deltart, J. Scharf, C.L. Perkins, B.T.R. Noufi, 19.9 % efficient ZnO/CdO/CuInGaSe2 Solar Cell with 81.2 % fill factor. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appln. 16, 235–239 (2008)
D. Hariskos, M. Ruckh, U. Riihle, T. Walter, H.W. Schock, J. Hedstrom, L. Stolt, A novel cadmium free buffer layer for Cu (In, Ga)Se2 based solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C. 41(42), 345–353 (1996)
N. Barreau, R. Bayon, J.C. Bernede, L. Assmann, 203rd Meeting of the Electrochemical Society., Paris, France, April 27–May 2, 2003
X. Meng, Y. Lu, X. Zhang, B. Yang, G. Yi, J. Jia, Fabrication and characterization of indium sulfide thin films deposited on SAMs modified substrates surfaces by chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 649–656 (2011)
B. Yahmadi, N. Kamoun, C. Guasch, R. Bennaceur, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystallized In2S3 thin films via CBD technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 127, 239–247 (2011)
Z. Gao, J. Liu, H. Wang, Investigation on growth of In2S3 thin films by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 15, 187–193 (2012)
D. Abou-Ras, G. Kostroz, A. Strohm, H.M. Schock, A.N. Tiwari, Interfacial layer formations between Cu (In, Ga)Se2 and InxSy layers. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 123512-1–123512-7 (2005)
Y. Yasaki, N. Sonoyama, T. Sakata, Semiconductor sensitization of colloidal In2S3 on wide gap semiconductors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 469, 116–122 (1999)
M. Kundakci, A. Ates, A. Astam, M. Yildirim, Structural, optical and electrical properties of CdS, Cd0.5In0.5S and In2S3 thin films grown by SILAR method. Phys. E 40, 600–605 (2008)
M. Calixto-Rodriguez, A. Tiburcio-Silver, A. Ortiz, A. Sanchez-Juarez, Optoelectronical properties of indium sulfide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 480–481, 133–137 (2005)
S. Buecheler, D. Corica, D. Guettler, A. Chirila, R. Verma, U. Muller, T.P. Niesan, J. Palm, A.N. Tiwari, Ultrasonically sprayed indium sulfide buffer layers for Cu (In, Ga)(S, Se)2 thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 517, 2312–2315 (2009)
A.S. Cherian, M. Mathew, C.S. Kartha, K.P. Vijayakumar, Role of chlorine on the opto-electronic properties of β-In2S3 thin films. Thin Solid Films 518, 1779–1783 (2010)
K. Otto, A. Katerski, O. Volobujeva, A. Mere, M. Krunks, Indium sulfide thin films deposited by chemical spray of aqueous and alcoholic solutions. Energy Procedia 3, 63–69 (2011)
C.S. Huang, C.S. Tao, C.H. Lee, Nebulized spray deposition of Pb(Zr, Ti)O thin films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144, 3556–3561 (1997)
S.P.S. Arya, H.E. Hintermann, Growth of Y-Ca-Ba-O superconducting thin films by ultrasonic nebulized spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 193(194), 841–846 (1990)
T. Sall, B.M. Soucase, M. Mollar, B. Hartitti, M. Fahoume, Chemical spray pyrolysis of β-In2S3 thin films deposited at different temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 76, 100–104 (2015)
X. Fu, G. Wu, S. Song, Z. Song, X. Duo, C. Lin, Preparation and characterization of MgO thin films by a simple nebulized spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 148, 223–228 (1999)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, P. Suresh, Effect of doping concentration on the structural and optical properties of pure and tin-doped zinc oxide thin films by nebulizer spray pyrolysis (NSP) technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 500–513 (2012)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, P. Suresh, R. Suresh, M. Ragavendar, C. Sankar, Depositon and characterization of pure and Cd doped SnO2 thin films by the nebulizer spray pyrolysis (NSP) technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 825–832 (2013)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, P. Suresh, R. Suresh, M. Ragavendar, Nanostructured GdxZn1−xO thin films by nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique: role of doping concentration on the structural and optical properties. Superlattices Microstruct. 59, 47–59 (2013)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, R. Suresh, P. Suresh, A. Chandra Bose, M. Ragavendar, Role of substrate temperature on the properties of Na-doped ZnO thin film nanorods and performance of ammonia gas sensors using nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 387–391 (2014)
E.E. Ebsenso, K. Sardar, M. Chandrasekhar, A.R. Raju, C.N.R. Raju, Thin films of Ln1−xSrxCoO3 (Ln = La, Nd and Gd) and SrRuO3 by nebulized spray pyrolysis. Solid State Sci. 2, 833–839 (2000)
S.R.C. Vivekchand, L.M. Cele, F.L. Deepak, A.R. Raju, A. Govindaraj, Carbon nanotubes by nebulized spray pyrolysis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 386, 313–318 (2004)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswami, M. Ragavendar, Effects of substrate temperature on the properties of CdSnSe thin films deposited by nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 15, 199–205 (2012)
V. Gowthami, P. Perumal, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, Structural and optical studies on nickel oxide thin film prepared by nebulizer spray technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter Phys. 452, 1–6 (2014)
JCPDS diffraction data, file No. 65-0459
M. Kraini, N. Bouguila, I. Halidou, A. Timoumi, S. Alaya, Properties of In2O3 films obtained by thermal oxidation of sprayed In2S3. Mat. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1388–1396 (2013)
T.T. John, C.S. Kartha, K.P. Vijayakumar, T. Abe, Y. Kashiwaba, Preparation of indium sulfide thin films by spray pyrolysis using a new precursor indium nitrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 1360–1367 (2005)
V.G. Rajeshmon, N. Poornima, C.S. Kartha, K.P. Vijaya Kumar, Modification of the optoelectronic properties of sprayed In2S3 thin films by indium diffusion for application as buffer layer in CZTS based solar cell. J. Alloys Compd. 553, 239–244 (2013)
K. Otto, A. Katerski, A. Mere, O. Volobujera, M. Krunks, Spray pyrolysis deposition of indium sulphide thin films. Thin Solid Films 519, 3055–3060 (2011)
L. Zhang, W. Zhang, H. Yang, W. Zhao, W. Fu, H. Zhao, J. Ma, Growth studies and characterization of In2S3 films prepared by hydrothermal method and their conversion to In2O3 films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 932–936 (2011)
A. Khorsand Zak, W.H.A. Majid, M.E. Abrishami, R. Yousefi, X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson–Hall and size–strain plot Methods. Solid State Sci. 13, 251–256 (2011)
L. Amalraj, C. Sanjeeviraja, M. Jayachandran, Spray pyrolysised tin disulphide thin film and characterization. J. Cryst. Growth 234, 683–689 (2002)
T.T. John, C.S. Kartha, K.P. Vijayakumar, T. Abe, Y. Kashiwaba, Spray pyrolyzed β-In2S3 thin fillm: effect of postdeposition annealing. Vacuum 80, 870–875 (2006)
M.G. Sandoval-Paz, M. Sotelo-Lerma, J.J. Valenzuela-Jauregui, M. Flores-Acosta, R. Ramirez-Bon, Structural and optical studies on thermal-annealed In2S3 films prepared by the chemical bath deposition technique. Thin Solid Films 472, 5–10 (2005)
S. Lugo-Loredo, Y. Pena-Mendez, M. Calixto-Rodriguez, S. Messina-Fernandez, Indium sulfide thin films as window layer in chemically deposited solar cells. Thin Solid Films 550, 110–113 (2014)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. N. Gopalakrishnan, Associate Professor, Department of Physics, NIT, Tiruchirappalli, India for analyzing the electrical characterization using Hall measurement instrument. One of the authors, Prof. C. Sanjeeviraja would like to thank CSIR, New Delhi, India for releasing Emeritus Scientist Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj Mohamed, J., Sanjeeviraja, C. & Amalraj, L. Effect of substrate temperature on nebulized spray pyrolysised In2S3 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 4437–4446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4315-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4315-x