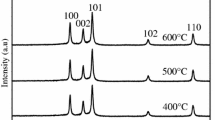
Abstract
ZnO–Co2O3–Bi2O3 nanocomposites were synthesized by sol–gel method with the aid of xanthan gum as a polymerization agent instead of any organic additives. Xanthan gum was polymerization agent to terminate the growth of doped nanocrystalline ZnO powders and then stabilize them. Spherical and hexagonal doped nanocrystalline ZnO powders with particle size of about 20–45 nm were easily obtained in the presence of xanthan gum. The results showed that ZnO nanopowders were doped in additional metal oxides and Bi7.5Co0.47O11.92 phase was observed at the as-prepared ZnO nanopowders after calcined at 500 and 600 °C. The varistor ceramics sintered at 1150 °C for 2 h in air have a density of 5.52 g/cm3 corresponding to 95.5 % of the theoretical density with breakdown voltage of 3100.91 V/cm and nonlinear coefficient of ~27.19. The experimental results showed the advantage of addition of the xanthan gum for avoiding hard agglomeration and improving electrical performance of the varistors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Janotti, C.G. Van der Walle, Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 1–29 (2009)
S. Benramache, H.B. Temam, A. Arif, A. Guettaf, Optik 125, 1816–1820 (2014)
Q. Zhang, C. Dandeneau, X. Zhou, G. Cao, Adv. Mater. 21, 1–22 (2009)
C.K. Srikanth, P. Jeevanandam, J. Alloys Compd. 486, 677–684 (2009)
K.C. Barick, M. Aslam, V.P. Dravid, D. Bahadur, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 349, 19–26 (2010)
C.W. Nahm, Ceram. Int. 35, 2679–2685 (2009)
Z. Xu, S. Ma, R. Chu, J. Hao, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 4997–5000 (2015)
K. Hembram, D. Sivaprahasam, T.N. Rao, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 1905–1913 (2011)
P. Duran, F. Capel, J. Tartaj, C. Moure, Adv. Mater. 14(2), 137–141 (2002)
S.Y. Chu, T.M. Yan, S.L. Chen, Ceram. Int. 26, 733–737 (2000)
M. Singhal, V. Chhabra, P. Kang, D.O. Shah, Mater. Res. Bull. 32, 239–247 (1997)
H. Toplan, Y. Karakas, Ceram. Int. 27, 761–765 (2001)
P. Duran, F. Capel, J. Tartaj, C. Moure, Adv. Mater. 14(2), 137–141 (2002)
K.Y. Cheong, N. Muti, S.R. Ramanan, Thin Solid Films 410, 142–146 (2002)
E.G. Lori, D.Y. Benjamin, L. Matt, Z. David, Y. Peidong, Inorg. Chem. 45, 7535–7543 (2006)
M. Darroudi, Z. Sabouri, R.K. Oskuee et al., Ceram. Int. 40, 4827–4831 (2014)
A.K. Zak, W.H.A. Majid, Mater. Lett. 65, 70–73 (2011)
K. Hembram, D. Sivaprahasam, T.N. Rao, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 1905–1913 (2011)
M. Darroudi, Z. Sabouri et al., Ceram. Int. 40, 4827–4831 (2014)
A.J. Reddy, M.K. Kokila et al., J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5349–5355 (2011)
G.P. Singh, P. Kaur, S. Kaur, D.P. Singh, Phys. B 407, 4168–4172 (2012)
R.Y. Hong, J.H. Li, L.L. Chen et al., Powder Technol. 189, 426–432 (2009)
S. Maensiri, J. Sreesongmuang et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 301, 422–432 (2006)
S. Desplanques, M. Grisel et al., Food Hydrocoll. 35, 181–188 (2014)
C.W. Nahm, Ceram. Int. 39, 2121–2177 (2013)
M. Zunic, Z. Brankovic, S. Bernik, M.S. Goes et al., J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3897–3900 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Changzhou Science and Technology Innovation Project (CC20140048, CC20130204) and 2014 Research and Innovation Project for College Graduates of Jiangsu Province and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51273027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, TT., Wang, MH., Zhang, HP. et al. Sol–gel synthesis of doped nanocrystalline ZnO powders using xanthan gum and varistor properties study. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 9056–9062 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3590-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3590-2