Abstract
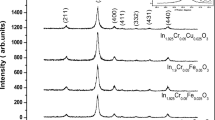
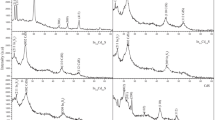
The (In1−xCrx)2O3 powders as well as thin films of x = 0.03, 0.05 and 0.07 were synthesized using a solid state reaction and an electron beam evaporation technique (on glass substrate), respectively. The influence of Cr doping concentration on structural, optical and magnetic properties of the In2O3 samples was systematically studied. The X-ray diffraction results confirmed that all the Cr doped In2O3 samples exist cubic structure of In2O3 without any secondary phases presence. The chemical composition analyses showed that all the Cr doped In2O3 compounds were nearly stoichiometric. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of the Cr doped In2O3 thin films showed an increase of oxygen vacancies with Cr concentration and the existence of Cr as Cr3+ state in the host In2O3 lattice. A small blue shift in the optical band gap was observed in the powder compounds, when the dopant concentration increased from x = 0.03 to x = 0.07. In thin films, the band gap found to increase from 3.63 to 3.74 eV, with an increase of Cr concentration. The magnetic measurements show that the undoped In2O3 bulk powder sample has the diamagnetic property at room temperature. And a trace of paramagnetism was observed in Cr doped In2O3 powders. However (In1−xCrx)2O3 thin films (x = 0.00, 0.03, 0.05 and 0.07) samples shows soft ferromagnetism. The observed ferromagnetism in thin films are attributed to oxygen vacancies created during film prepared in vacuum conditions. The ferromagnetic exchange interactions are established between metal cations via free electrons trapped in oxygen vacancies (F-centers).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ohno, A window on future of spintronics. Nat. Mater. 9, 952–954 (2010)
J.K. Furdyna, J. Kossut, Diluted magnetic semiconductors, in Semiconductors and Semimetals, vol. 25, ed. by R.K. Willardson, A.C. Beer (Academic Press, London, 1988), pp. 1–462
E.L. Nagaev, Physics of Magnetic Semiconductors (Mir, Moscow, 1986)
H. Ohno, A. Shen, F. Matsukura, A. Oiwa, A. Endo, S. Katsumoto, Y. Iye, (Ga, Mn)As: a new diluted magnetic semiconductor based on GaAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 363–365 (1996)
M. Zhong, S. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Hu, M. Zhu, H. Jin, Y. Li, H. Zhang, H. Zhao, Room temperature ferromagnetic Cr–Ni codoped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors synthesized by hydrothermal method under high pulsed magnetic field. Ceram. Int. 41, 451–457 (2015)
S. Mehraj, M.S. Ansari, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of (Fe, Co) co-doped SnO2 diluted magnetic semiconductor nanostructures. Phys. E 65, 84–92 (2015)
A.A. Faisal, E. Al-Arfaj, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, B.D. Stein, Y. Losovyj, L.M. Bronstein, F.S. Shokr, W.E. Mahmoud, Structure and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic metal oxides based on Cu-doped CeO2 nanopowders. Ceram. Int. 41, 1115–1119 (2015)
N. Sai Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, G. Amarendra, N. Madhusudhana Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, M. Kuppan, M. Rigana Begam, D. Sreekantha Reddy, I. Omkaram, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Fe doped In2O3 powders. Mater. Res. Bull. 61, 486–491 (2015)
A.V. Singh, R.M. Mehra, N. Buthrath, A. Wakahara, A. Yoshida, Highly conductive and transparent aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition in oxygen ambient. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 5661–5665 (2001)
P. Kharel, C. Sudakar, M.B. Sahana, G. Lawes, R. Suryanarayanan, R. Naik, V.M. Naik, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Cr-doped In2O3 on high vacuum annealing of thin films and bulk samples. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 09H117 (2007)
H. Kim, M. Osofsky, M.M. Miller, S.B. Qadri, R.C.Y. Auyeung, A. Pique, Room temperature ferromagnetism in transparent Fe-doped In2O3 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 032404 (2012)
N.H. Hong, J. Sakai, N.T. Huong, V. Brizé, Co-doped In2O3 thin films: room temperature ferromagnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 228–231 (2006)
V. Olmos, R. America, J.I.G. Peralta, R.Y.S. Berru, A.L.F. Osorio, Diluted magnetic semiconductors based on Mn-doped In2O3 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S522–S525 (2014)
N. Sai Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, G. Amarendra, N. Madhusudhana Rao, M. Kuppan, M. Rigana Begam, D. Sreekantha Reddy, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of (In1−xNix)2O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.09) powders synthesized by solid state reaction. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 18, 22–27 (2014)
D.J. Craik, Magnetic Oxides (Wiley, New York, 1975)
G. Peleckis, X.L. Wang, S.X. Dou, Ferromagnetism in Mn-doped In2O3 oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 301, 308–311 (2006)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Wesley, California, 1978)
T. Mega, K. Tokao, J. Shimomura, State analysis of electrolytic chromate film by XPS and SXS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 121(122), 120–124 (1997)
N. Sai Krishna, S. Kaleemulla, G. Amarendra, N. Madhusudhana Rao, C. Krishnamoorthi, M. Rigana Begam, I. Omkaram, D. Sreekantha Reddy, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Cu-doped In2O3 thin films. J. Supercond. Novel Mag. 28, 2089–2095 (2015)
H. Baqiah, N.B. Ibrahim, M.H. Abdi, S.A. Halim, Electrical transport, microstructure and optical properties of Cr-doped In2O3 thin film prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 575, 198–206 (2013)
P. Kubelka, F. Munk, Ein Beitrag Zur Optik Der Farbanstriche. Z. Techn. Phys. 12, 593–601 (1931)
J. Tauc, Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors (Plenum Press, New York, 1974)
S. Sambasivam, B.C. Choi, J.G. Lin, Intrinsic magnetism in Fe doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 184, 199–203 (2011)
A. Caricato, M. Cesaria, A. Luches, M. Martino, G. Maruccio, D. Valerini, M. Catalano, A. Cola, M. Manera, M. Lomascolo, A. Taurino, R. Rella, Electrical and optical properties of ITO and ITO/Cr-doped ITO films. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 101, 753–758 (2010)
N.B. Ukah, R.K. Gupta, P.K. Kahol, K. Ghosh, Influence of oxygen growth pressure on laser ablated Cr-doped In2O3 thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9420–9424 (2009)
Y. Guo, S.J. Clark, J. Robertson, Electronic and magnetic properties of Ti2O3, Cr2O3, and Fe2O3 calculated by the screened exchange hybrid density functional. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 24, 325504 (2012)
S.M. Watts, S. Wirth, S. Von Molnar, A. Barry, J.M.D. Coey, Evidence for two-band magnetotransport in half-metallic chromium dioxide. Phys. Rev. B 61, 9621–9628 (2000)
A.P.S. Gaur, S. Sahoo, R.K. Katiyar, C. Rinaldi, J.F. Scott, R.S. Katiyar, Absence of magnetism in Cr-doped In2O3: a case study of phase separation versus phase formation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 49–53 (2011)
G. Peleckis, X.L. Wang, S.X. Dou, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Mn and Fe codoped In2O3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 132507 (2006)
A. Paola, M. Cesaria, V. Fiorentini, Impurity–vacancy complexes and ferromagnetism in doped sesquioxides. Phys. Rev. B 89, 134423 (1–5) (2014)
N.H. Hong, J. Sakai, F. Gervais, Magnetism due to oxygen vacancies and/or defects in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 214–217 (2007)
L.M. Huang, C. Århammar, C.M. Araújo, F. Silvearv, R. Ahuja, Tuning magnetic properties of In2O3 by control of intrinsic defects. EPL 89, 47005 (1–5) (2010)
J.M.D. Coey, M. Venkatesan, C.B. Fitzgerald, Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4, 173–179 (2005)
Q. Wang, Q. Sun, G. Chen, Y. Kawazoe, P. Jena, Vacancy-induced magnetism in ZnO thin films and nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 77, 205411 (1–7) (2008)
H. Peng, J. Li, S.S. Li, J.B. Xia, Possible origin of ferromagnetism in undoped anatase TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 79, 092411 (1–4) (2009)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to UGC-DAE-CSR, IGCAR, Kalpakkam, 603102, Tamilnadu, India, for providing financial (Grant No. CSR-KN/CRS-17/2011-12/589) support to carry out the present work. The authors are highly thankful to Pondicherry central university for providing the vibrating sample magnetometer facilities. Authors also thank VIT-SIF for providing XRD and UV–Vis–NIR spectrophotometer facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sai Krishna, N., Kaleemulla, S., Amarendra, G. et al. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Cr doped In2O3 powders and thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 8635–8643 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3538-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3538-6