Abstract
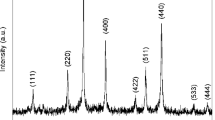
The face centered cubic phase of NiO nanostructures were successfully synthesized from microwave and hydrothermal methods. The structural properties of the synthesized material were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. The thermal analysis revealed the transformation of Ni(OH)2 into NiO at about 380 °C. The obtained scanning electron microscopy images exhibited less agglomerated flowers for hydrothermal reacted NiO than the microwave processed samples. The sheet like morphologies of NiO nanostructures were confirmed by transmission electron microscope and the obtained particles sizes were comparable to the calculated values from XRD data. The UV–Vis and photoluminescence spectra results showed that the absorption edges of the NiO nanoflowers have a blue-shift due to quantum confinement effect. The Raman spectrum exhibited the transformation of antiferromagnetic to superparamagnetic transition confirmed from the absence of magnon peak. The XPS spectrum presented the observation of Ni 2p and O 1s levels with higher intense peak nature for hydrothermal treated NiO than microwave. The hysteresis loops of the NiO samples prepared by both hydrothermal and microwave heating methods revealed the weak ferromagnetic behaviors at room temperature. Based on the experimental observations and analysis, a possible hydrothermal reaction mechanism is proposed to synthesize flower shaped NiO nanostructured materials with improved structural, optical, morphological and magnetic properties compared to microwave synthesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.A. Harraz, R.M. Mohamed, A. Shawky, I.A. Ibrahim, Composition and phase control of Ni/NiO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of EDTA. J. Alloys Compd. 508, 133–140 (2010)
Q. Dong, S. Yin, C. Guo, X. Wu, N. Kumada, T. Takei, A. Miura, Y. Yonesaki, T. Sato, Single-crystalline porous NiO nanosheets prepared from β-Ni(OH)2 nanosheets: magnetic property and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 147, 741–747 (2014)
C. Xia, X. Yanjun, W. Ning, Facile synthesis of NiO nanoflowers and their electrocatalytic performance. Sens. Actuators B 153, 434–438 (2011)
G. Bai, H. Dai, J. Deng, Y. Liu, W. Qiu, Z. Zhao, X. Li, H. Yang, The microemulsion preparation and high catalytic performance of mesoporous NiO nanorods and nanocubes for toluene combustion. Chem. Eng. J. 219, 200–208 (2013)
S. Das, J.B. Seol, Y.C. Kim, C.G. Park, Formation of NiO nanowires on the surface of nickel strips. J. Alloys Compd. 505, L19–L21 (2010)
L. Hu, B. Qu, L. Chen, Q. Li, Low-temperature preparation of ultrathin nanoflakes assembled tremella-like NiO hierarchical nanostructures for high-performance lithium–ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 108, 92–95 (2013)
C. Yuan, L. Hou, Y. Feng, S. Xiong, X. Zhang, Sacrificial template synthesis of short mesoporous NiO nanotubes and their application in electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 88, 507–512 (2013)
B. Cheng, Y. Le, W. Cai, J. Yu, Synthesis of hierarchical Ni(OH)2 and NiO nanosheets and their adsorption kinetics and isotherms to Congo red in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 185, 889–897 (2011)
C.Y. Cao, W. Guo, Z.M. Cui, W.G. Song, W. Cai, Microwave-assisted gas/liquid interfacial synthesis of flowerlike NiO hollow nanosphere precursors and their application as supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3204–3209 (2011)
Y. Luo, G. Duan, G. Li, Synthesis and characterization of flower-like β-Ni(OH)2 nanoarchitectures. J. Solid State Chem. 180, 2149–2153 (2007)
G. Bai, H. Dai, J. Deng, Y. Liu, K. Ji, Porous NiO nanoflowers and nanourchins: highly active catalysts for toluene combustion. Catal. Commun. 27, 148–153 (2012)
A. Wei, B. Liu, H. Zhao, Y. Chen, W. Wang, Y. Ma, H. Yang, S. Liu, Synthesis and formation mechanism of flowerlike architectures assembled from ultrathin NiO nanoflakes and their adsorption to malachite green and acid red in water. Chem. Eng. J. 239, 141–148 (2014)
H. Chai, X. Chen, D. Jia, S. Bao, W. Zhou, Flower-like NiO structures: controlled hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical characteristic. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 3947–3951 (2012)
Y. Cui, C. Wang, S. Wu, G. Liu, F. Zhang, T. Wang, Lotus-root-like NiO nanosheets and flower-like NiO microspheres: synthesis and magnetic properties. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 13, 4930–4934 (2011)
S.K. Meher, P. Justin, G. Ranga Rao, Sumanta Kumar Meher, Microwave-mediated synthesis for improved morphology and pseudocapacitance performance of nickel oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 2063–2073 (2011)
Q. Yang, J. Sha, X. Ma, D. Yang, Synthesis of NiO nanowires by a sol–gel process. Mater. Lett. 59, 1967–1970 (2005)
V. Verma, M. Katiyar, Effect of the deposition parameters on the structural and magnetic properties of pulsed laser ablated NiO thin films. Thin Solid Films 527, 369–376 (2013)
A. Aslani, V. Oroojpour, M. Fallahi, Sonochemical synthesis, size controlling and gas sensing properties of NiO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 4056–4061 (2011)
K. Chen, Z. Lü, X. Chen, N. Ai, X. Huang, B. Wei, J. Hu, W. Su, Characteristics of NiO-YSZ anode based on NiO particles synthesized by the precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 454, 447–453 (2008)
A.G. Al-Sehemi, A.S. Al-Shihri, A. Kalam, G. Du, T. Ahmad, Microwave synthesis, optical properties and surface area studies of NiO nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1058, 56–61 (2014)
M. Liu, J. Chang, J. Sun, L. Gao, A facile preparation of NiO/Ni composites as high-performance pseudocapacitor materials. RSC Adv. 3, 8000–8008 (2013)
S.D.G. Ram, M.A. Kulandainathan, G. Ravi, On the study of pH effects in the microwave enhanced rapid synthesis of nano-ZnO. Appl. Phys. A 99, 197–203 (2010)
Z. Zhu, N. Wei, H. Liu, Z. He, Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Ni(OH)2 architectures and their in situ thermal convention to NiO. Adv. Powder. Technol. 22, 422–426 (2011)
X. Tian, C. Cheng, L. Qian, B. Zheng, H. Yuan, S. Xie, D. Xiao, M.M.F. Choi, Microwave-assisted non-aqueous homogenous precipitation of nanoball-like mesoporous α-Ni(OH)2 as a precursor for NiOx and its application as a pseudocapacitor. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 8029–8035 (2012)
Z. Wei, H. Qiao, H. Yang, C. Zhang, X. Yan, Characterization of NiO nanoparticles by anodic arc plasma method. J. Alloys Compd. 479, 855–858 (2009)
E.R. Beach, K. Shqau, S.E. Brown, S.J. Rozeveld, P.A. Morris, Solvothermal synthesis of crystalline nickel oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 371–377 (2009)
S. Mohseni Meybodi, S.A. Hosseini, M. Razaee, S.K. Sadrnezhaad, D. Mohammadyani, Synthesis of wide band gap nanocrystalline NiO powder via a sonochemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19, 841–845 (2012)
Y. Wang, J. Zhu, X. Yang, L. Lu, X. Wang, Preparation of NiO nanoparticles and their catalytic activity in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Thermochim. Acta 437, 106–109 (2005)
L. Wang, Y. Zhao, Q. Lai, Y. Hao, Preparation of 3D rose-like NiO complex structure and its electrochemical property. J. Alloys Compd. 495, 82–87 (2010)
X. Song, L. Gao, Facile synthesis of polycrystalline NiO nanorods assisted by microwave heating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91(10), 3465–3468 (2008)
A.P. LaGrow, B. Ingham, S. Cheong, G.V.M. Williams, C. Dotzler, M.F. Toney, D.A. Jefferson, E.C. Corbos, P.T. Bishop, J. Cookson, R.D. Tilley, Synthesis, alignment, and magnetic properties of monodisperse nickel nanocubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 855–858 (2012)
Y. Ren, L. Gao, From three-dimensional flower-like α-Ni(OH)2 nanostructures to hierarchical porous NiO nanoflowers: microwave-assisted fabrication and supercapacitor properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(11), 3560–3564 (2010)
S. Rakshit, S. Chall, S.S. Mati, A. Roychowdhury, S.P. Moulika, S.C. Bhattacharya, Morphology control of nickel oxalate by soft chemistry and conversion to nickel oxide for application in photocatalysis. RSC Adv. 3, 6106–6116 (2013)
S. Liu, J. Jia, J. Wang, S. Liu, X. Wang, H. Song, X. Hu, Synthesis of Fe-doped NiO nanofibers using electrospinning method and their ferromagnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2070–2074 (2012)
G. Zhu, C. Xi, H. Xu, D. Zheng, Y. Liu, X. Xu, X. Shen, Hierarchical NiO hollow microspheres assembled from nanosheet-stacked nanoparticles and their application in a gas sensor. RSC Adv. 2, 4236–4241 (2012)
T. Kavitha, H Yuvaraj (2011) A facile approach to the synthesis of high-quality NiO nanorods: electrochemical and antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 15686–15691 (2011)
K. Liang, X. Tang, W. Hu, High-performance three-dimensional nanoporous NiO film as a supercapacitor electrode. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 11062–11067 (2012)
B. Varghese, M.V. Reddy, Z. Yanwu, C.S. Lit, T.C. Hoong, G.V. Subba Rao, B.V.R. Chowdari, A.T.S. Wee, C.T. Lim, C.H. Sow, Fabrication of NiO nanowall electrodes for high performance lithium ion battery. Chem. Mater. 20, 3360–3367 (2008)
S.D. Tiwari, K.P. Rajeev, Signatures of spin-glass freezing in NiO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 72, 104433 (2005)
E. Winkler, R.D. Zysler, M.V. Mansilla, D. Fiorani, D. Rinaldi, M. Vasilakaki, K.N. Trohidou, Surface spin-glass freezing in interacting core–shell NiO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19, 185702–185710 (2008)
M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Mohandes, F. Davar, M. Mazaheri, M. Monemzadeh, N. Yavarinia, Preparation of NiO nanoparticles from metal-organic frameworks via a solid-state decomposition route. Inorg. Chim. Acta 362, 3691–3697 (2009)
F. Davar, Z. Fereshteh, M. Salavati-Niasari, Nanoparticles Ni and NiO: synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 476, 797–801 (2009)
M. Salavati-Niasari, N. Mir, F. Davar, Synthesis and characterization of NiO nanoclusters via thermal decomposition. Polyhedron 28, 1111–1114 (2009)
M.A. Khadar, V. Biju, A. Inoue, Effect of finite size on the magnetization behavior of nanostructured nickel oxide. J. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 1341–1349 (2003)
V. Ranga Rao Pulimi, P. Jeevanandam, The effect of anion on the magnetic properties of nanocrystalline NiO synthesized by homogeneous precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2556–2562 (2009)
S. Farhadi, Z. Roostaei-Zaniyani, Simple and low-temperature synthesis of NiO nanoparticles through solid-state thermal decomposition of the hexa(ammine)Ni(II) nitrate, [Ni(NH3)6](NO3)2, complex. Poyhedron 30, 1244–1249 (2011)
M. Tadic, M. Panjan, D. Markovic, B. Stanojevic, D. Jovanovic, I. Milosevic, V Spasojevic (2014) NiO core–shell nanostructure with ferromagnetic-like behavior at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 586, S322–S325 (2014)
Q. Li, L.S. Wang, B.Y. Hu, C. Yang, L. Zhou, L. Zhang, Preparation and characterization of NiO nanoparticles through calcination of malate gel. Mater. Lett. 61, 1615–1618 (2007)
S. Chander, S. Kumar, A. Krishnamurthy, B.K. Srivastava, V.K. Aswal, Magnetic behavior of nanoparticles of Fe2.9Zn0.1O4, Pram. J. Phys. 61(3), 617–624 (2003)
A.J. Rondinone, A.C.S. Samia, Z.J. Zhang, Superparamagnetic relaxation and magnetic anisotropy energy distribution in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 6876–6880 (1999)
S.N. Dolia, S. Chander, M.P. Sharma, S. Kumar, Superparamagnetic behavior of nanoparticles of Ni–Cu ferrite. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 44, 169–172 (2006)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors G. Anandha babu gratefully acknowledges DST, India for the financial support under the scheme of INSPIRE Fellowship (Grant No. IF110040) to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anandha Babu, G., Ravi, G., Navaneethan, M. et al. An investigation of flower shaped NiO nanostructures by microwave and hydrothermal route. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 5231–5240 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2293-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2293-4