Abstract
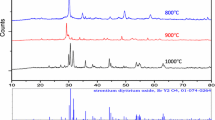
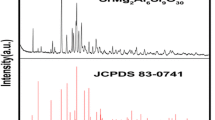
SrAl2O4 phosphor nano-powders activated with heavy elements such as Eu and Dy were prepared by microwave synthesis method. Using this method led to the reduction of processing time. Various calcinations times have been employed to produce pure SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor materials. It was found out that microwave synthesis technique led to reduction of optimum calcinations time to 9 min. XRD analysis showed that the powders were nearly pure SrAl2O4 phase, in which the SrAl2O4 host phase has the maximum fraction of monoclinic SrAl2O4 phase. The critical pH to achieve pure SrAl2O4 phase determined to be equal to 4. For the synthesized SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+, the properties of photoluminescence such as emission, excitation and decay time were examined. Fluorescent spectrophotometer results revealed that two excitation peaks are appeared at 280 and 339 nm and an emission peak at 515 nm. The crystallite size of these pigments is about 58.22 nm after calcinations for 9 min in microwave as determined by Scherrer’s formula. SEM was used to study the morphology and shape of powders.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Blasse, B.C. Grabmaier, Luminescent Materials (Springer, Berlin, 1994)
T. Matsuzawa, Y. Aoki, N. Takeuchi, Y. Murayama, Rare Earths 29, 79 (1996)
D. Haranath, V. Shanker, H. Chander, Mater. Chem. Phys. 78, 6–10 (2002)
T. Peng, L. Huajun, H. Yang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 85, 68–72 (2004)
W.Y. Jia, H.B. Yuan, W.M. Yen, J. Lumin. 76, 424 (1998)
G. Groppi, C. Cristiani, P. Forzatti, J. Mater. Sci. 29, 3441 (1994)
J. Sikkim, J. Cer. Proc. Res. 10, 443–447 (2009)
Y. Lin et al., Mater. Chem. Phys. 70, 156 (2001)
A. Nag, T.R.N. Kutty, J. Alloys Comp. 354, 221 (2003)
T. Aitasalo et al., J. Alloys Comp. 341, 76 (2002)
E. Shafia, A. Aghaei, M. Bodaghi, M. Tahriri, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2010). doi:10.1007/s10854-010-0273-x
I. Bilecka, M. Niederberger, Nanoscale 2, 1269–1528 (2010)
B. L. Hayes, Matthews. (2002)
B.L. Cushing, V.L. Kolesnichenko, C.J. O’Connor , Chem. Rev. 104, 3893–3946 (2004)
C.A. Mirkin, The beginning of the small rev. Small 1, 14–16 (2005)
G.D. Wilk, R.M. Wallace, J.M. Anthony, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5243–5275 (2001)
H. Kacirek, H. Lechert, J. Phys. Chem. 79, 1589–1593 (1975)
H. Li, M. Eddaoudi, M. O’Keeffe, O.M. Yaghi, Nature 402, 276–279 (1999)
R.J. Helmich, Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Inorganic Materials. Literature Seminar. October 12, (2006)
Shafia et al., Ceram. Inter. (2013). doi:10.1016/J.ceramint.2013.09.011
X. Yu, C. Zhou, X. He, Z. Peng, S. Yang, Mater. Lett. 58, 1087–1091 (2004)
W.S. Shi, H. Yamada, K. Nishikubo, H. Kusaba, C.N. Xu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, H97–H100 (2004)
J. Sanchez-Benitez, A. de Andres, M. Marchal, E. Cordoncillo, M. ValletRegi, P. Escribano, J. Solid Chem. 171, 273–277 (2003)
T. Peng, H. Yang, X. Pu, B. Hu, Z. Jiang, C. Yan, Mater. Lett. 58, 352–356 (2004)
C.F. Bacalski, M.A. Cherry, G.A. Hiralla, J.M. Mckittrick, J. Mourant, J. Soc. Inf. Display (Suppl 1), 93–98 (2000)
L.E. Shea, J. Mckittrick, O.A. Lopez, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 3257–3265 (1996)
T. Mimani, Resonance 5, 50–57 (2000)
S.D. Ham, K.C. Singh, T.Y. Cho, J. Lumin. 128, 301–305 (2008)
Y. Lin, Z. Zhang, F. Zhang, Z. Tang, Q. Chen, Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 103–106 (2000)
S. Hongzhi, G. Zhifeng, D. Jinxiu, J. Rare, Met. Mater. Eng. 32(5), 370 (2003)
A.J. Lenus, K.G. Rajan, M. Yousuf, D. Sornadurai, B. Purniah, Mater. Lett. 54, 70–74 (2002)
T. Aitasalo, P. Deren, J. Holsa, H. Jungner, J.C. Krupa, M. Lastusaari, J. Legendziewicz, J. Niittykoski, W. Strek, J. Solid State Chem. 171, 114–121 (2003)
T. Matsuzawa, Y. Aoki, N. Takeuchi, T. Murayama, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 2670–2673 (1996)
Z. Zhou, W. Luo, B. Lü, X. Wu, Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 5(2), 125–127 (2011)
Y. Lin, Z. Zhang, F. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 103–106 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank INSF of Iran (contract number of 91/sad/23410, in 16/1/2012) for complete financial support provided for this research work. Also authors greatly appreciate Mr. Ehsan Shafia (PhD student at Department of Applied Science and Technology, Politecnicodi Torino, Torino, ITALY) for fruitful help during this research period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsagh, M., Rajabi, M. & Amini, E. Characterization of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor nano-powders produced by microwave synthesis route. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 1612–1619 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1773-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1773-x