Abstract
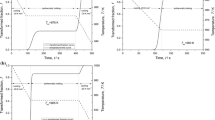
In this paper, a simultaneous thermal analyzer carried out isothermal eutectoid transformation experiments of Fe–0.4Mn, Fe–1.2Mn, and Fe–1.2Mn–0.2Si alloys. The kinetic model of the isothermal phase transformation of FeO was established using the Johnson–Mehl–Avrami–Kolmogorov (JMAK) equation combined with the experimental data. The kinetic model of the eutectoid transformation of FeO in a non-isothermal process was also established based on Scheil's additivity rule and the mapped-out FeO. The CCT diagram shows that increasing the Mn content and adding Si elements during the continuous cooling process cause the phase zone where the FeO layer undergoes eutectoid transformation to shift to the right. Due to the similarity of crystal structures, the (Fe, Mn)O solid solution formed by FeO and MnO improves the stability of FeO. Mn2+ widens the spacing between oxide ions, and with the increase in Mn content, the Gibbs energy of the formation of (Fe, Mn)O becomes too small to compensate for that of the formation of α-Fe from (Fe, Mn)O. In addition, the temperature point at which the phase transformation of FeO occurs decreases with the increase in Mn content, resulting in the decrease in phase transformation supercooling, so the increase in Mn content will inhibit the eutectoid transformation. The addition of elemental Si resulted in the formation of a cation-deficient FeO with higher O content and lower Fe content, and the time for the Fe2+ concentration to reach supersaturation was prolonged, thus further inhibiting the onset of the eutectoid transformation.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
Not applicable.
References
Li ZF, Cao GM, Lin F, Cui CY, Wang H, Liu ZY (2018) Phase transformation behavior of oxide scale on plain carbon steel containing 0.4 wt% Cr during continuous cooling. ISIJ Int 58(12):2338–2347. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-365
Xing LD, Gu C, Lv ZY, Bao YP (2022) High-temperature internal oxidation behavior of surface cracks in low alloy steel bloom. Corros Sci 197:110076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.110076
Chen RY, Yuen WYD (2001) Oxide-scale structures formed on commercial hot-rolled steel strip and their formation mechanisms. Oxid Met 56(1–2):89–118. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010395419981
Cao GM, Wu TZ, Xu R, Li ZF, Wang FX, Liu ZY (2015) Effects of coiling temperature and cooling condition on transformation behavior of tertiary oxide scale. J Iron Steel Res Int 22(10):892–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30086-8
Hayashi S, Yoneda S, Kondo Y, Tanei H (2020) Phase transformation of thermally grown FeO formed on high-purity Fe at low oxygen potential. Oxid Met 94(1–2):81–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-020-09979-2
Hayashi S, Mizumoto K, Yoneda S, Kondo Y, Tanei H, Ukai S (2014) The mechanism of phase transformation in thermally-grown FeO scale formed on pure-Fe in air. Oxid Met 81(3–4):357–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-013-9442-7
Gleeson B, Hadavi SMM, Young DJ (2000) Isothermal transformation behavior of thermally-grown wüstite. Mater High Temp 17(2):311–318. https://doi.org/10.3184/096034000783640776
Zhou CH, Ma HT, Li Y, Wang L (2012) Eutectoid magnetite in wüstite under conditions of compressive stress and cooling. Oxid Met 78(1–2):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-012-9296-4
Zhang YD, Jin SB, Jiang CL, Yang JJ, Sha G (2022) Formation of high-temperature inner oxide scale on low alloy steels: segregation, partitioning and transformation reactions. Corros Sci 195:109980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109980
Shizukawa Y, Hayashi S, Yoneda S, Kondo Y, Tanei H, Ukai S (2016) Mechanism of magnetite seam formation and its role for FeO scale transformation. Oxid Met 86(3–4):315–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9638-8
Avrami M (1939) Kinetics of phase change I general theory. J Chem Phys 7(12):1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1750380
Avrami M (1940) Kinetics of phase change II transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J Chem Phys 8(2):212–224. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1750631
Kumar V, Dixit US (2018) A model for the estimation of hardness of laser bent strips. Opt Laser Technol 107:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.06.029
Rezaei J, Parsa MH, Mirzadeh H (2023) Phase transformation kinetics of high-carbon steel during continuous heating. J Market Res 27:2524–2537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.10.089
Pohjonen A, Somani M, Porter D (2018) Modelling of austenite transformation along arbitrary cooling paths. Comp Mater Sci 150:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.03.052
Cao GM, Shan WC, Wang CY, Zhou ZX, Liu ZY (2023) Isothermal structure transformation and kinetics behavior of oxide scale on low carbon steel. ISIJ Int 63(2):366–374. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2022-179
Cao GM, Wang CY, Jiang YC, Li SL, Gao XY, Liu ZY (2022) Effect of Cr on isothermal structure transformation of iron oxide scale. Steel Res Int 94(5):2200512. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202200512
Chen RY, Yuen WYD (2000) A study of the scale structure of hot-rolled steel strip by simulated coiling and cooling. Oxid Met 53(5–6):539–560. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004637127231
Lin SN, Huang CC, Wu MT, Wang WL, Hsieh KC (2017) Crucial mechanism to the eutectoid transformation of wüstite scale on low carbon steel. Steel Res Int 88(11):1700045. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201700045
Yu XL, Jiang ZY, Zhao JW, Wei DB, Zhou CL (2013) Effect of cooling rate on oxidation behaviour of micro-alloyed steel. Appl Mech Mater 395–396:273–278. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.395-396.273
Scheil E (1935) Anlaufzeit der austenitumwandlung. Steel Res 8(12):565–567. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.193500186
Zhang YT, Mo CL, Li DZ, Li YY (2003) Modelling of phase transformation of plain carbon steels during continuous cooling. J Mater Sci Technol 19(3):262–264
Zhang YT, Li DZ, Li YY (2006) Modeling of austenite decomposition in plain carbon steels during hot rolling. J Mater Process Tech 171(2):175–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.07.003
Li HJ, Lin YC, Xiao N, Ning XY, Wang GD (2022) Softening behavior of deformed metals during continuous cooling and its relation to isothermal reactions. Mech Mater 167:104242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2022.104242
Polmear IJ (1959) Fatigue properties of ternary aluminium-zinc-magnesium alloys. Nature 183:1388–1389. https://doi.org/10.1038/1831388a0
Ben Fredj E, Nanesa HG, Jahazi M, Morin JB (2018) Influence of initial microstructure and grain size on transformation of bainite to austenite in large size forgings. J Iron Steel Res Int 25(5):554–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0070-y
López-Martínez E, Vázquez-Gómez O, Vergara-Hernández HJ, Campillo B (2015) Effect of initial microstructure on austenite formation kinetics in high-strength experimental microalloyed steels. Int J Min Met Mater 22(12):1304–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1198-4
Etesami SA, Enayati MH, Kalashami AG (2017) Austenite formation and mechanical properties of a cold rolled ferrite-martensite structure during intercritical annealing. Mat Sci Eng A Struct 682:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.112
Kirkaldy JS, Baganis EA (1978) Thermodynamic prediction of the ae3 temperature of steels with additions of Mn, Si, Ni, Cr, Mo. Cu Metall Trans A 9(4):495–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646405
Liu F, Yang C, Yang G, Zhou Y (2007) Additivity rule, isothermal and non-isothermal transformations on the basis of an analytical transformation model. Acta Mater 55(15):5255–5267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.05.041
Martin H, Amoako-Yirenkyi P, Pohjonen A, Frempong NK, Komi J, Somani M (2021) Statistical modeling for prediction of CCT diagrams of steels involving interaction of alloying elements. Metall Mater Trans B 52(1):223–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01991-w
Chen XJ, Xiao NM, Cai MH, Li DZ, Li GY, Sun GY, Rolfe BF (2016) A modified approach to modeling of diffusive transformation kinetics from nonisothermal data and experimental verification. Metall Mater Trans A 47(9):4732–4740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3608-2
Sano T, Tsuji M, Tamaura Y (1997) Effect of foreign cation of Zn(II) or Mn(II) ion in FeO-wüstite on its disproportionation reaction below 575 °C. Solid State Ionics 104(3–4):311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(97)00432-3
Mayer P, Smeltzer WW (1972) Kinetics of manganeseo-wustite scale formation on iron-manganese alloys. J Electrochem Soc 119(5):626. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2404275
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No.2022YFB3304800), the Reviving-Liaoning Excellence Plan (XLYC2203186), Science and Technology Special Projects of Liaoning Province, China (Grant No. 2022JH25/10200001), and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2021M701167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guangming Cao was contributed to investigation, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. Wencong Zhao and Wentao Song were contributed to conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft and editing. Hengxiang Yu and Silin Li was contributed to investigation. Zhenyu Liu was contributed to conceptualization, methodology, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest or competing interests exist.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Zhao Shen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, G., Zhao, W., Song, W. et al. Influence of Mn–Si elements on the kinetics of oxidative phase transformation under continuous cooling conditions and modeling study. J Mater Sci 59, 9593–9609 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09746-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09746-7