Abstract
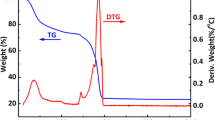
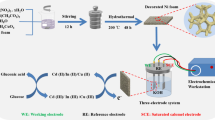
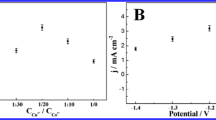
Amorphous copper cobalt carbonate hydroxide (CuCoCH) was prepared on copper foam (CF) by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. The binder-free approach facilitates the transfer of electrons in the CuCoCH/CF electrode, its hierarchical porous network structure promotes the diffusion of glucose and its large surface area provides abundant catalytic sites for electrocatalysis oxidation of glucose. Moreover, the easily controllable Cu/Co ratio and the synergistic effect of copper and cobalt in CuCoCH increase the electrocatalytic activity for glucose oxidation. As a result, the CuCoCH/CF electrode exhibits a linear range of 0.005–3.47 mM, a sensitivity of 1.5167 mA·mM−1·cm−2 and a detection limit of 2.3 μM (S/N = 3) for glucose detection. Meanwhile, it also demonstrates satisfactory selectivity, reproducibility, stability and practical applicability, indicating the CuCoCH/CF electrode prepared by this facile method is promising in non-enzymatic glucose sensing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA (2001) The hormone resist in links obesity to diabetes. Nature 409:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053000
Lee I, Loew N, Tsugaw W, Ikebukuro K, SodeK, (2019) Development of a third-generation glucose sensor based on the open circuit potential for continuous glucose monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 124:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.09.099
Bauer JA, Zámocká M, Majtán J, Bauerová-Hlinková V (2022) Glucose oxidase, an enzyme “Ferrari”: its structure, function, production and properties in the light of various industrial and biotechnological applications. Biomolecules 12:472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030472
Yan X, Gu Y, Li C, Zheng B, Li Y, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Yang M (2019) Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the CuS nanoflakes–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Anal methods 10:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY02290E
Ma D, Tang X, Guo M, Lu H, Xu X (2015) Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on bimetallic hollow Ag/Pt nanoparticles prepared by galvanic replacement reaction. Ionics 21:1417–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1290-1
Shim K, Lee WC, Park MS, Shahabuddin M, Yamauchi Y, Hossain MSA, Shim YB, Kim JH (2019) Au decorated core-shell structured Au@Pt for the glucose oxidation reaction. Sens Actuators B Chem 278:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.048
Li J, Yan L, Wang H, Wang H, Chen X, Wang L, Wu M (2017) Au NPs/ITO prepared by dopamine reduction and its application in glucose sensing. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:3067–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5894-2
ShervedaniRK KM, Amini A (2014) Prickly nickel nanowires grown on Cu substrate as a supersensitive enzyme-free electrochemical glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 204:783–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.08.033
Fallatah A, Almomtan M, Padalkar S (2019) Cerium oxide based glucose biosensors: influence of morphology and underlying substrate on biosensor performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:8083–8089. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02286
Wang Q, Chen Y, Zhu R, Luo M, Zou Z, Yu H, Jiang X, Xiong X (2020) One-step synthesis of Co(OH)F nanoflower based on micro-plasma: as an effective non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 304:127282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127282
Huang PC, Shen MY, Yu HH, Wei SC, Luo SC (2018) Surface engineering of phenylboronic acid-functionalized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for fast responsive and sensitive glucose monitoring. ACS Appl Bio Mater 1:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.8b00060
Quintero-Jaime AF, Quílez-Bermejo J, Cazorla-Amorós D, Morallón E (2021) Metal free electrochemical glucose biosensor based on N-doped porous carbon material. Electrochim Acta 367:137434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137434
Rahsepar M, Foroughi F, Kim H (2019) A new enzyme-free biosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene with high sensing performance for electrochemical detection of glucose at biological pH value. Sens Actuators B Chem 282:322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.078
Prasad R, Bhat BR (2015) Multi-wall carbon nanotube–NiO nanoparticle composite as enzyme-free electrochemical glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 220:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.065
Ejaz A, Jeon S (2017) Synthesis and application of electrochemically reduced N–rGO–Co(OH)2 nanocomposite for concurrent detection of biomolecules. Electrochim Acta 235:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.036
Duan X, Liu K, Xu Y, Yuan M, Gao T, Wang J (2019) Nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor constructed by NiCo2O4@ Ppy nanowires on nickel foam substrate. Sens Actuators B Chem 292:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.107
Qiu R, Zhang XL, Qiao R, Li Y, Kim YI, KangYS, (2007) CuNi dendritic material:synthesis, mechanism discussion, and application as glucose sensor. Chem Mater 19:4174–4180. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm070638a
Noh HB, Lee KS, Chandra P, Won MS, Shim YB (2012) Application of a Cu–Co alloy dendrite on glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensors. Electrochim Acta 61:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.11.066
Suneesh PV,VargisVS, RamachandranT, Nair BG, Babu TGS (2015) Co–Cu alloy nanoparticles decorated TiO2 nanotube arrays for highly sensitive and selective nonenzymatic sensing of glucose. Sens Actuators B Chem 215: 337–344 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.073
Sedaghat S, PiepenburgCR ZA, Qi Z, Peana S, Wang H, Rahimi R (2020) Laser-induced mesoporous nickel oxide as a highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose densor. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:5260–5270. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c00659
Khan AY, Bandyopadhyaya R (2021) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor with copper oxide nanoparticle impregnated mesoporous silica. J Porous Mater 28:1097–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01064-6
Liu W, Chai G, Zhao X, Dai Y, Qi Y (2020) Effect of different copper sources on the morphology of cuprous oxide and its application as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 321:128485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128485
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Zeng T, Wan Q, Yang N (2021) Morphology-dependent sensing performance of CuO nanomaterials. Anal Chim Acta 1171:338663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338663
Tao Y, Liu Q, ChangQ DJ, Tao Z, Guan H, Chen G, Mao Y, Xie J, Dong C (2019) In situ fabrication of Co(OH)2 by hydrothermal treating Co foil in MOH (M ¼ H, Li, Na, K) for non-enzymatic glucose detection. J Alloy Compd 781:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.148
Wang S, Zhang L, Tian Y, Lin L, Zhuiykov S (2019) Fabrication of Ni(OH)2&NiOOH film/Ni electrode and the effect of NaOH concentration on its glucose detection. J Electrochem Soc 166:B1732–B1741. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0721916jes
Zhe T, Sun X, Liu Y, Wang Q, Li F, Bu T, Jia P, Lu Q, Wang J, Wang L (2019) An integrated anode based on porous Ni/Cu(OH)2 nanospheres for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Microchem J 151:104197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104197
Shi N, Sun S, Zhang B, Du Q, Liao Y, Liao X, Yin G, Huang Z, Pu X, Chen X (2020) Co(OH)2 nanosheets decorated Cu(OH)2 nanorods for highly sensitive nonenzymatic detection of glucose. Nanotechnology 31:325502. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab8c77
HuangW LF, Huang Y, YangW PJ (2021) Facile one-pot synthesis of hollow-structured CuS/Cu2S hybrid for enhanced electrochemical determination of glucose. Electrochemistry 89:340–347. https://doi.org/10.5796/electrochemistry.21-00027
Vilian ATE, Hwang SK, Ranjith KS, Cho Y, Huh YS, Han YK (2021) A facile method for the fabrication of hierarchically structured Ni2CoS4 nanopetals on carbon nanofibers to enhance non-enzymatic glucose oxidation. Microchim Acta 188:106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04749-6
Kim WB, Lee SH, Cho M, Lee Y (2017) Facile and cost-effective CuS dendrite electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 249:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.089
Keerthi M, Mutharani B, Chen SM, Ranganathan P (2019) Carbon fibers coated with urchin-like copper sulfide for nonenzymatic voltammetric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 186:807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3915-6
Pan W, Zheng WuX, Gao J, Liu Y, Yuan Q, Gan W (2021) Facile synthesis of 2D/3D hierarchical NiCu bimetallic MOF for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Microchem J 170:106652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106652
Kim SE, Muthurasu A (2020) Metal-organic framework–assisted bimetallic Ni@Cu microsphere for enzyme-free electrochemical sensing of glucose. J Electroanal Chem 873:114356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114356
DingJ ZL, Wang X, Chai L, Wang Y, Jiang M, Li TT, Hu Y, Qian J, Huang S (2020) General approach to MOF-derived core-shell bimetallic oxide nanowires for fast response to glucose oxidation. Sens Actuators B Chem 306:127551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127551
Li M, Liu L, Xiong Y, Liu X, Nsabimana A, Bo X, Guo L (2015) Bimetallic MCo (M = Cu, Fe, Ni, and Mn) nanoparticles doped-carbon nanofibers synthetized by electrospinning for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 207:614–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.10.092
Guo SH, Yuan PW, Wang J, Chen WQ, Ma KY, Liu F, Cheng JP (2017) One-step synthesis of copper-cobalt carbonate hydroxide microsphere for electrochemical capacitors with superior stability. J Electroanal Chem 807:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.11.009
Wan L, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Du C, Chen J, Tian Z, Xie M (2021) FeCoP nanosheets@Ni-Co carbonate hydroxide nanoneedles as free-standing electrode material for hybrid supercapacitors. Chem Eng J 415:128995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128995
KangJ SJ, Xie J, Ye H, Chen J, Fu XZ, Du G, Sun R, Wong CP (2018) Tubular Cu(OH)2 arrays decorated with nanothorny Co–Ni bimetallic carbonate hydroxide supported on Cu foam: a 3D hierarchical core–shell efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 6:10064–10073. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA02492H
Zhao Z, Sun Y, Song J, Li Y, Xie Y, Cui H, Gong W, Hu J, Chen Y (2021) Highly sensitive nonenzymetic glucose sensing based on multicomponent hierarchical NiCo-LDH/CCCH/CuF nanostructures. Sens Actuators B Chem 326:128811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128811
Liu S, Hui KS, Hui KN, Jadhav VV, Xia QX, Yun JM, Cho YR, Mane RS, Kim KH (2016) Facile synthesis of microsphere copper cobalt carbonate hydroxides electrode for asymmetric supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 188:898–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.12.018
Vassileva DSK (2002) Infrared study of some synthetic phases of malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3)–hydrozincite (Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2) series. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 58:2051–2059. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-1425(01)00677-1
Zhou H, Wu D, Cai W (2022) Carbon nanotubes coated with hybrid nanocarbon layers for electrochemical sensing of psychoactive drug. Electrochim Acta 430:141001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141001
Wei H, Xu Q, Li A, Wan T, Huang Y, Cui D, Pan D, Dong B, Wei R, Naik N, Guo Z (2021) Dendritic core-shell copper-nickel alloy@metal oxide for efficient non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 337:129687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129687
Ni G, Wang F, Pan Z, Zhang R (2021) Bimetallic CuCo derived from prussian blue analogue for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Electroanalysis 33:845–853. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060402
Li W, Lv S, Wang Y, Zhang L, Cui X (2019) Nanoporous gold induced vertically standing 2D NiCo bimetal-organic framework nanosheets for non-enzymatic glucose biosensing. Sensors Actuators: B Chem 281:652–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.150
Luo X, Huang M, Bie L, He D, Zhang Y, Jiang P (2017) CuCo2O4 nanowire arrays supported on carbon cloth as an efficient 3D binder-free electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. RSC Adv 7:23093–23101. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra01840a
Babu KJ, Sheet S, Lee YS, kumar GG, (2018) Three-dimensional dendrite Cu–Co/reduced graphene oxide architectures on a disposable pencil graphite electrode as an electrochemical sensor for nonenzymatic glucose detection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:1909–1918. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03314
DingY SH, Ren C, Zhang M, Sun K (2020) A nonenzymatic glucose sensor platform based on specific recognition and conductive polymer-decorated CuCo2O4 carbon nanofibers. Materials 13:2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122874
Tsai PJ, Chuang KL, Yang CJ, Lee HT, Lu FH (2019) Synthesis of Cu–Co bimetallic nanoparticles using TiN-coated electrodes for glucose-sensing applications. J Alloy Compd 785:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.141
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21804035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared they have no conflict of interest to declare in this work.
Ethical approval
Not involved.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Catalin Croitoru.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Xu, W., Zeng, D. et al. Amorphous copper cobalt carbonate hydroxide prepared by SILAR on copper foam for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J Mater Sci 58, 199–210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08064-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08064-0