Abstract
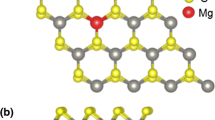
To pursue the advanced properties of 2D materials, we explore the single-layer WSe2, one of the most studied transitional metal chalcogenide-based magnetic structures. Based on the first-principle calculations, we predict the excellent ferromagnetic coupling between the doped Cu and its nearby Se and W atoms in the single-layer WSe2 (SL-WSe2). Our calculations point out that the Cu-d electrons and the interactions between the dopant and the nearby atoms are the major cause for the induced magnetism. The emerging electronic states around the Fermi level, arising from the doped Cu and its nearby W and Se atoms, not only introduce magnetism into SL-WSe2, but also low its energy gap largely. We also demonstrate a semiconducting–metallic transition in the Cu-doped SL-WSe2 caused by the applied compressive strain and a semiconducting–half metal transition under the applied tensile strain. Moreover, we show the feasibility of doping concentrations and external strain on manipulating the conductivity and magnetism of the Cu-doped SL-WSe2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler SZ, Hollen SM, Cao LY, Cui Y, Gupta JA, Gutierrez HR, Heinz TF, Hong SS, Huang JX, Ismach AF, Johnston-Halperin E, Kuno M, Plashnitsa VV, Robinson RD, Ruoff RS, Salahuddin S, Shan J, Shi L, Spencer MG, Terrones M, Windl W, Goldberger JE (2013) Progress, challenges, and opportunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano 7(4):2898–2926
Xu MS, Liang T, Shi MM, Chen HZ (2013) Graphene-like two-dimensional materials. Chem Rev 113(5):3766–3798
Li XL, Wang XR, Zhang L, Lee S, Dai HJ (2008) Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors. Science 319:1229–1232
Han MY, Özyilmaz B, Zhang YB, Kim P (2007) Electron transport in disordered graphene nanoribbons. Phys Rev Lett 104(5):056801
Schwierz F (2010) Graphene transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 5:487–496
Xf Qian, Liu J, Fu L, Li J (2014) Quantum spin hall effect in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Science 346:1344–1347
Wang QH, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kis A, Coleman JN, Strano MS (2012) Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat Nanotechnol 7:699–712
Fiori G, Bonaccorso F, Iannaccone G, Palacios T, Neumaier D, Seabaugh A, Banerjee SK, Colombo L (2014) Erratum: electronics based on two-dimensional materials. Nat Nanotechnol 9(12):768–779
Podzorov V, Gershenson ME, Kloc Ch, Zeis R, Bucher E (2004) High-mobility field-effect transistors based on transition metal dichalcogenides. Appl Phys Lett 84:3301–3303
Liu W, Kang JH, Sarkar D, Khatami Y, Jena D, Banerjee K (2013) Role of metal contacts in designing high-performance monolayer n-type WSe2 field effect transistors. Nano Lett 13(5):1983–1990
Clark G, Wu S, Rivera P, Finney J, Nguyen P, Cobden DH, Xu X (2014) Vapor-transport growth of high optical quality WSe2 monolayers. APL Mater 2(10):101101
Ryder CR, Wood JD, Wells SA, Hersam MC (2016) Chemically tailoring semiconducting two dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides and black phosphorus. ACS Nano 10:3900–3917
Wang HT, Yuan HT, Hong SS, Li YB, Cui Y (2015) Physical and chemical tuning of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem Soc Rev 44:2664–2680
Jariwala D, Sangwan VK, Lauhon LJ, Marks TJ, Hersam MC (2014) Emerging device applications for semiconducting two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. ACS Nano 8(2):1102–1120
Li H, Wu J, Yin Z, Zhang H (2014) Preparation and applications of mechanically exfoliated single-layer and multilayer MoS2 and WSe2 nanosheets. Acc Chem Res 47(4):1067–1075
Li H, Lu G, Wang YL, Yin ZY, Cong CX, He QY, Wang L, Ding F, Yu T, Zhang H (2013) Mechanical exfoliation and characterization of single and few-layer nanosheets of WSe2, TaS2, and TaSe2. Small 9(11):1974–1981
Coleman JN, Lotya M, O’Neill A, Bergin SD, King PJ, Khan U, Young K, Gaucher A, De S, Smith RJ, Shvets IV, Arora SK, Stanton G, Kim HY, Lee K, Kim GT, Duesberg GS, Hallam T, Boland JJ, Wang JJ, Donegan JF, Grunlan JC, Moriarty G, Shmeliov A, Nicholls RJ, Perkins JM, Grieveson EM, Theuwissen K, McComb DW, Nellist PD, Nicolosi V (2011) Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science 331:568–571
Liu BL, Fathi M, Chen L, Abbas A, Ma YQ, Zhou CW (2015) Chemical vapor deposition growth of monolayer WSe2 with tunable device characteristics and growth mechanism study. ACS Nano 9(6):6119–6127
Gerchman D, Alves AK (2016) Solution-processable exfoliation and suspension of atomically thin WSe2. J Colloid Interace Sci 468:247–252
Chiritescu C, Cahill DG, Nguyen N, Johnson D, Bodapati A, Keblinski P, Zschack P (2007) Ultralow thermal conductivity in disordered, layered WSe2 crystals. Science 315:351–353
Zhuang HL, Henning RG (2013) Computational search for single-layer transition-metal dichalcogenide photocatalysts. J Phys Chem C 117:20440–20445
Mishra R, Zhou W, Pennycook SJ, Pantelides ST, Idrobo JC (2013) Long-range ferromagnetic ordering in manganese-doped two-dimensional dichalcogenides. Phys Rev B 88(14):144409
Dong L, Namburu RR, O’Regan TP, Dubey M, Dongare AM (2014) Theoretical study on strain-induced variations in electronic properties of monolayer MoS2. J Mater Sci 49:6762–6771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8370-5
Yun WS, Lee JD (2014) Unexpected strong magnetism of Cu doped single-layer MoS2 and its origin. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8990–8996
Andriotis AN, Menon M (2014) Tunable magnetic properties of transition metal doped MoS2. Phys Rev B 90:125304
Kafi F, Shahri RP, Benam MR, Akhtar A (2017) Tuning optical properties of MoS2 bulk and monolayer under compressive and tensile strain: a first principles study. J Mater Sci 46(10):6158–6166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5643-1
Pan H, Zhang YW (2012) Edge-dependent structural, electronic and magnetic properties of MoS2 nanoribbons. J Phys Chem C 116:11752–11757
Kresse G, Furthmu¨ller J, Hafner J (1994) Theory of the crystal structures of selenium and tellurium: the effect of generalized-gradient corrections to the local-density approximation. Phys Rev B Condens Mater Mater Phys 50(18):13181–13185
Cristol S, Paul J, Payen E, Bougeard D, Clemendot S, Hutschka F (2000) Theoretical study of the MoS2 (100) surface: a chemical potential analysis of sulfur and hydrogen coverage. J Phys Chem B 104:11220–11229
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77(18):3865–3868
Blöchl PE (1994) Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 50:17953–17979
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Monkhorst HJ, Pack JD (1976) Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys Rev B 13(12):5188
Salehi S, Saffarzadeh A (2016) Atomic defect states in monolayers of MoS2 and WS2. Surf Sci 651:215–221
Qiu H, Xu T, Wang ZL, Ren W, Nan HY, Ni ZH, Chen Q, Yuan SJ (2013) Hopping transport through defect-induced localized states in molybdenum disulphide. Nat Commun 4(4):2642
Ma X, Zhao X, Wang TX (2016) Effect of strain on the electronic and magnetic properties of an Fe-doped WSe2 monolayer. RSC Adv 6:69758–69763
Seixas L, Carvalho A, Neto AHC (2015) Atomically thin dilute magnetism in Co-doped phosphorene. Phys Rev B 91:155138
Cheng YC, Zhu ZY, Mi WB, Guo ZB, Schwingenschlogl U (2013) Prediction of two-dimensional diluted magnetic semiconductors: doped monolayer MoS2 systems. Phys Rev B 87:100401(R)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NNSFC) (21273172). This work was also supported by the 111 Project (B08040) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3102015BJ(II)JGZ005, 3102015BJ023) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Fan, X., Hu, Y. et al. Magnetic semiconducting and strain-induced semiconducting–metallic transition in Cu-doped single-layer WSe2. J Mater Sci 54, 529–539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2815-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2815-1