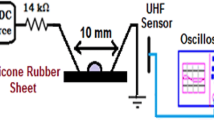
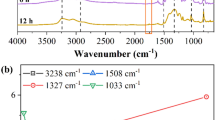
Abstract
Silicone rubber is widely used as the housing material of composite insulator for outdoor high-voltage insulation. However, corona-induced aging in silicone rubber contributes to the ingress of water or moisture, which finally leads to fracture of a composite insulator. To investigate water transportation in silicone rubber helps to shed light upon the insulator fracture mechanism. In this work, water transportation behaviors in silicone rubber treated by different applied voltages of corona discharge were systematically studied using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Low voltages (3, 4 kV) of corona treatments result in growing value of \(f_{\theta \mathrm{min}}\) in Bode phase angle, indicative of severer degree of surface delamination. After 5 kV of corona treatment, water can finally diffuse through the silicone rubber, and then induces double-layer capacitance (\(C_{\mathrm{dl}}\)) and the charge transfer resistance (\(R_{\mathrm{ct}}\)) in EIS spectra. For high-voltage (\(\ge 6\ \hbox {kV}\)) corona-exposed samples, great number of surface cracks are observed, and then Warburg impedance appears in EIS spectra on initial period of immersion, suggesting a direct water transportation process. The polar groups generated in silicone rubber during corona exposure also facilitate this water diffusion process. Calculated water diffusion coefficients show a sharp increase between 5 and 6 kV, which serves as an indicator for percolation of cracks or defects in bulk of silicone rubber.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hackam R (1999) Outdoor HV composite polymeric insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 6(5):557
Gorur RS, Orbeck T (1991) Surface dielectric behavior of polymeric insulation under HV outdoor conditions. IEEE Trans Electr Insul 26(5):1064
Ansorge S, Schmuck F, Papailiou KO (2012) Improved silicone rubbers for the use as housing material in composite insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19(1):209
Hillborg H, Gedde UW (1999) Hydrophobicity changes in silicone rubbers. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 6(5):703
Reddy BS, Prasad DS (2015) Effect of coldfog on the corona induced degradation of silicone rubber samples. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 22(3):1711
Reynders JP, Jandrell IR, Reynders SM (1999) Review of aging and recovery of silicone rubber insulation for outdoor use. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 6(5):620
Chang JS, Lawless PA, Yamamoto T (1991) Corona discharge processes. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 19(6):1152
Zhu Y, Otsubo M, Honda C, Tanaka S (2006) Loss and recovery in hydrophobicity of silicone rubber exposed to corona discharge. Polym Degrad Stab 91(7):1448
Hillborg H, Gedde UW (1998) Hydrophobicity recovery of polydimethylsiloxane after exposure to corona discharges. Polymer 39(10):1991
Kim J, Chaudhury MK, Owen MJ (2000) Hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane elastomer exposed to partial electrical discharge. J Colloid Interface Sci 226(2):231
Gorur RS, Karady GG, Jagota A, Shah M, Yates AM (1992) Aging in silicone rubber used for outdoor insulations. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 7(2):525
Gubanski SM (2005) Modern outdoor insulation—concerns and challenges. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 21(6):5
Wang J, Liang X, Gao Y (2014) Failure analysis of decay-like fracture of composite insulator. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 21(6):2503
Liang X, Dai J (2006) Analysis of the acid sources of a field brittle fractured composite insulator. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 13(4):870
Lutz B, Cheng L, Guan Z, Wang L, Zhang F (2012) Analysis of a fractured 500 kV composite insulator - identification of aging mechanisms and their causes. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19(5):1723
Montesinos J, Gorur RS, Mobasher B, Kingsbury D (2002) Mechanism of brittle fracture in nonceramic insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 9(2):236
Lutz B, Guan Z, Wang L, Zhang F, L Z 2012 In: 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Electrical Insulation, pp 478–482
Dai J, Yao XF, Yeh HY, Liang X (2006) Moisture absorption of filled silicone rubber under electrolyte. J Appl Polym Sci 99(5):2253
Gao Y, Wang J, Liang X, Yan Z, Liu Y, Cai Y (2014) Investigation on permeation properties of liquids into HTV silicone rubber materials. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 21(6):2428
Wang Z, Zhao LH, Jia ZD, Guan ZC (2017) Water and moisture permeability of high-temperature vulcanized silicone rubber. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 24(4):2440
Wang Z, Jia ZD, Fang MH, Guan ZC (2015) Absorption and permeation of water and aqueous solutions of high-temperature vulcanized silicone rubber. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 22(6):3357
Perez C, Collazo A, Izquierdo M, Merino P, Novoa XR (1999) Characterisation of the barrier properties of different paint systems : part I. Experimental set-up and ideal fickian diffusion. Prog Org Coat 36(1):102
Fárnandez-Sánchez C, Mcneil CJ, Rawson K (2005) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy studies of polymer degradation: application to biosensor development. Trends Anal Chem 24(1):37
Liu F, Yin M, Xiong B, Zheng F, Mao W, Chen Z, He C, Zhao X, Fang P (2014) Evolution of microstructure of epoxy coating during UV degradation progress studied by slow positron annihilation spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 133:283
Hu JM, Zhang JT, Zhang JQ, Cao CN (2004) A novel method for determination of diffusion coefficient of corrosive species in organic coatings by EIS. J Mater Sci 39(14):4475. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000034140.96862.1a
Larson BJ, Gillmor SD, Braun JM, Cruz-Barba LE, Savage DE, Denes FS, Lagally MG (2013) Long-term reduction in poly (dimethylsiloxane) surface hydrophobicity via cold-plasma treatments. Langmuir 29(42):12990
Hollahan JR, Carlson GL (1970) Hydroxylation of polymethylsiloxane surfaces by oxidizing plasmas. J Appl Polym Sci 14(10):2499
Hillborg H, Sandelin M, Gedde UW (2001) Hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsioxane after exposure to partial discharges as a function of crosslink density. Polymer 42(17):7349
Zhang JT, Hu JM, Zhang JQ, Cao CN (2004) Studies of water transport behavior and impedance models of epoxy-coated metals in NaCl solution by EIS. Prog Org Coat 51(2):145
Zhang JT, Hu JM, Zhang JQ, Cao CN (2004) Studies of impedance models and water transport behaviors of polypropylene coated metals in NaCl solution. Prog Org Coat 49(4):293
Amirudin A, Thieny D (1995) Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to study the degradation of polymer-coated metals. Prog Org Coat 26(1):1
Mansfeld F, Tsai CH (1991) Determination of coating deterioration with EIS: I. Basic relationships. Corrosion 47(12):958
Murray JN (1997) Electrochemical test methods for evaluating organic coatings on metals: an update. Part III: multiple test parameter measurements. Prog Org Coat 31(3):255
Cano E, Lafuente D, Bastidas DM (2010) Use of EIS for the evaluation of the protective properties of coatings for metallic cultural heritage: a review. J Solid State Electrochem 14(3):381
Senkevich JJ (2000) Degradation of an alkyd polymer coating characterized by AC impedance. J Mater Sci 35(6):1359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004730006941
Kolek Z (1997) Characterization of water penetration inside organic coatings by capacitance measurements. Prog Org Coat 30(4):287
Hsu CH, Mansfeld F (2001) Technical note: concerning the conversion of the constant phase element parameter \(\text{ Y }_{0}\) into a capacitance. Corrosion 57(9):747
Castela AS, Simoes AM, Ferreira MGS (2000) EIS evaluation of attached and free polymer films. Prog Org Coat 38(1):1
Deflorian F, Fedrizzi L, Bonora P (1996) Influence of the photo-oxidative degradation on the water barrier and corrosion protection properties of polyester paints. Corros Sci 38(10):1697
Liu B, Li Y, Lin H, Cao C (2002) Effect of PVC on the diffusion behaviour of water through alkyd coatings. Corros Sci 44(12):2657
Bellucci F, Nicodemo L, Monetta T, Kloppers MJ, Latanision RM (1992) A study of corrosion initiation on polyimide coatings. Corros Sci 33(8):1203
Deflorian F, Fedrizzi L, Bonora PL (1996) Influence of the photo-oxidative degradation on the water barrier and corrosion protection properties of polyester paints. Corros Sci 38(10):1697
Zhang H, Zheng W, Yan Q, Yang Y, Wang J, Lu Z, Ji G, Yu Z (2010) Electrically conductive polyethylene terephthalate/graphene nanocomposites prepared by melt compounding. Polymer 51(5):1191
Saberi AA (2015) Recent advances in percolation theory and its applications. Phys Rep 578:1
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21174108) and the Large-scale Instrument and Equipment Sharing Foundation of Wuhan University (No. LF20170857).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yin, C., Li, J. et al. Electrochemical impedance study of water transportation in corona-aged silicone rubber: effect of applied voltage. J Mater Sci 53, 12871–12884 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2523-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2523-x