Abstract
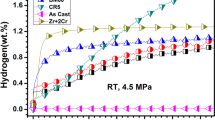
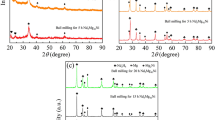
In this paper, we report the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of TiFe + 4 wt% (Zr + 2Mn) alloy before and after high-energy milling. The as-cast sample was made of a main TiFe phase with a Zr- and Mn-rich secondary phase. We found that ball milling can significantly reduce the crystallite size of TiFe + 4 wt% (Zr + 2Mn) alloy. First hydrogenation measurements showed that the sample milled for 15 min displayed a faster hydrogenation than the as-cast sample but with a slight loss of capacity. Further milling made the samples totally inert to hydrogen. It may be concluded that the as-cast alloy has a special microstructure that is possibly destroyed by milling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali W, Hao Z, Li Z, Chen G, Wu Z, Lu X et al (2017) Effects of Cu and Y substitution on hydrogen storage performance of TiFe0.86Mn0.1Y0.1 − xCux. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:16620–16631
Endo N, Saita I, Nakamura Y, Saitoh H, Machida A (2015) Hydrogenation of a TiFe-based alloy at high pressures and temperatures. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:3283–3287
Leng H, Yu Z, Yin J, Li Q, Wu Z, Chou K-C (2017) Effects of Ce on the hydrogen storage properties of TiFe0.9Mn0.1 alloy. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:23731–23736
Zadorozhnyy VY, Milovzorov GS, Klyamkin SN, Zadorozhnyy MY, Strugova DV, Gorshenkov MV et al (2017) Preparation and hydrogen storage properties of nanocrystalline TiFe synthesized by mechanical alloying. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 27:149–155
Schober T, Westlake D (1981) The activation of FeTi for hydrogen storage: a different view. Scr Metall 15:913–918
Khatamian D, Weatherly G, Manchester F (1983) Some effects of activation for hydrogen absorption in FeTi powder. Acta Metall 31:1771–1780
Reilly J, Wiswall R Jr (1974) Formation and properties of iron titanium hydride. Inorg Chem 13:218–222
Gosselin C, Huot J (2015) Hydrogenation properties of TiFe doped with zirconium. Materials 8:7864–7872
Jain P, Gosselin C, Huot J (2015) Effect of Zr, Ni and Zr 7 Ni 10 alloy on hydrogen storage characteristics of TiFe alloy. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:16921–16927
Lv P, Huot J (2016) Hydrogen storage properties of Ti 0.95 FeZr 0.05, TiFe 0.95 Zr 0.05 and TiFeZr 0.05 alloys. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:22128–22133
Lee S-M, Perng T-P (1994) Effect of the second phase on the initiation of hydrogenation of TiFe1 − xMx (M=Cr, Mn) alloys. Int J Hydrog Energy 19:259–263
Lv P, Huot J (2017) Hydrogenation improvement of TiFe by adding ZrMn2. Energy 138:375–382
Miller H, Murray J, Laury E, Reinhardt J, Goudy A (1995) The hydriding and dehydriding kinetics of FeTi and Fe0. 9TiMn0.1. J Alloy Compd 231:670–674
Nishimiya N, Wada T, Matsumoto A, Tsutsumi K (2000) Hydriding characteristics of zirconium-substituted FeTi. J Alloy Compd 313:53–58
Abe M, Kuji T (2007) Hydrogen absorption of TiFe alloy synthesized by ball milling and post-annealing. J Alloy Compd 446–447:200–203
Zadorozhnyy V, Klyamkin S, Zadorozhnyy M, Bermesheva O, Kaloshkin S (2012) Hydrogen storage nanocrystalline TiFe intermetallic compound: synthesis by mechanical alloying and compacting. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:17131–17136
Zadorozhnyy VY, Klyamkin SN, Zadorozhnyy MY, Gorshenkov MV, Kaloshkin SD (2014) Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped with sulfur and magnesium. J Alloy Compd 615:S569–S572
Zadorozhnyy VY, Klyamkin SN, Zadorozhnyy MY, Bermesheva OV, Kaloshkin SD (2014) Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped by aluminum and chromium. J Alloy Compd 586:S56–S60
Emami H, Edalati K, Matsuda J, Akiba E, Horita Z (2015) Hydrogen storage performance of TiFe after processing by ball milling. Acta Mater 88:190–195
Coelho AA (2004) A Computer programme for Rietveld analysis. Topas-Academic, Brisbane
Bruker A (2005) TOPAS V3: general profile and structure analysis software for powder diffraction data. User’s Manual. Bruker AXS, Karlsruhe
Patel AK, Sharma P, Huot J (2018) Effect of annealing on microstructure and hydrogenation properties of TiFe + X wt% Zr (X = 4, 8). Int J Hydrog Energy 43:6238–6243
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Fonds de recherche du Quebec-Nature et technologies (FRQNT) for a Ph.D. fellowship (P. L.) and MITACS for an internship fellowship (G. R.). We would also thank Mrs. A. Lejeune for SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero, G., Lv, P. & Huot, J. Effect of ball milling on the first hydrogenation of TiFe alloy doped with 4 wt% (Zr + 2Mn) additive. J Mater Sci 53, 13751–13757 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2301-9