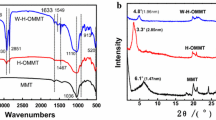
Abstract
In this study, a nanocomposite of poly[styrene–(ethylene-co-butylene)–styrene] triblock copolymer (SEBS) and poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) blend modified with an alkyl phosphonium salt-intercalated organic montmorillonite (OMMT) was prepared by melt mixing. The effect of OMMT and the compatibilizer SEBS-MA on structure, morphology, rheological behavior, and crystallization properties of the SEBS/PCL nanocomposites was studied. Better dispersion of PCL domains in SEBS matrix was achieved after adding 5 wt% SEBS-MA, with the crystallinity of the PCL increased considerably. Compared with pristine montmorillonite, the SEBS/PCL composite with OMMT showed a more uniform dispersion. Meanwhile, the OMMT platelets were preferentially dispersed at outer edge of the PCL domains with intercalated structure. Good interfacial interaction between the OMMT and the SEBS/PCL matrix was suggested, with occurrence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the PCL and the OMMT. The prepared SEBS/PCL/OMMT nanocomposite displayed significantly improved mechanical, anti-water-absorption, and anti-UV-irradiation properties, which can be attributed to its unique morphology. These superior properties of the SEBS/PCL/OMMT nanocomposite are important for both environmental and biomedical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calisi N, Giuliani A, Alderighi M, Schnorr JM, Swager TM, Francesco FD, Pucci A (2013) Factors affecting the dispersion of MWCNTs in electrically conducting SEBS nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 49:1471–1478
Jeong U, Lee HH, Yang H, Kim JK, Okamoto S (2003) Kinetics and mechanism of morpohological transition from Lamella to cylinder microdomain in polystyrene–block-poly(ethylene-co-but-l-ene)–block-polystyrene triblock copolymer. Macromolecules 36:1685–1693
Wang X, Pang SL, Yang JH, Yang F (2006) Structure and properties of SEBS/PP/OMMT nanocomposites. Trans Nonferr Metals Soc China 16:524–528
Fukushima F, Abbate C, Tabuani D, Gennari M, Rizzarelli P, Camino G (2010) Biodegradation trend of poly(ε-caprolactone) and nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng C 30:566–574
Singh RP, Pandey JK, Rutot D, Degee P, Dubois P (2003) Biodegradation of poly(ε-caprolactone)/starch blends and composites in composting and culture environments: the effect of compatibilization on the inherent biodegradability of the host polymer. Carbohyd Res 338:1759–1769
Huang MH, Li S, Vert M (2004) Synthesis and degradation of PLA–PCL–PLA triblock copolymer prepared by successive polymerization of ε-caprolactone and dl-lactide. Polymer 45:8675–8681
Zhang Y, Song PA, Liu HZ, Li Q, Fu SY (2016) Morphology, healing and mechanical performance of nanofibrillated cellulose reinforced poly(ε-caprolactone)/epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 125:62–70
Shadpour M, Nasrin N (2016) Modification of morphological, mechanical, optical and thermal properties in polycaprolactone-based nanocomposites by the incorporation of diacid-modified ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 51:6400–6410. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-9936-1
Labidi S, Azema N, Perrin D, Lopez-Cuesta JM (2010) Organo-modified montmorillonite/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) nanocomposites prepared by melt intercalation in a twin-screw extruder. Polym Degrad 95:382–388
Sun YC, Cai SY, Ren J, Naguib HE (2017) Room temperature deformable shape memory composite with fine-tuned crystallization induced via nanoclay particles. J Polym Sci Pol Phys 55:1197–1206
Kuester S, Merlini C, Barra GMO, Ferreira Jr JCF, Lucas A, Soares BG (2016) Processing and characterization of conductive composites based on poly (styrene-b-ethylene-ran-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS) and carbon additives: a comparative study of expanded graphite and carbon black. Compos Part B Eng 84:236–247
Arslan M, Tasdelen MA, Uyar T, Yagci Y (2015) Poly (epsilon caprolactone)/clay nanocomposites via host-guest chemistry. Eur Polym J 71:259–267
Anirban G, Anil KB (2009) Effect of polar modification on morphology and properties of styrene–(ethylene-co-butylene)–styrene triblock copolymer and its montmorillonite clay-based nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 44:903–918. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3183-z
Nofar M, Heuzey MC, Carreau PJ, Kamal MR (2016) Effects of nanoclay and its localization on the morphology stabilization of PLA/PBAT blends under shear flow. Polymer 98:353–364
Chiu FC (2017) Halloysite nanotube- and organoclay-filled biodegradable poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate)/maleated polyethylene blend-based nanocomposites with enhanced rigidity. Compos Part B Eng 110:193–203
Rajendra KS, Saurindra NM, Anup KG (2016) Mechanical, morphological, and solid-state viscoelastic responses of poly (lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate super-tough blend reinforced with halloysite nanotubes. J Mater Sci 51:10278–10292. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0255-3
Jing Q, Jia YL, Tan LP, Silberschmidt VV, Li L, Dong ZL (2015) Preparation, characterization and properties of polycaprolactone diol-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube/thermoplastic polyurethane composite. Compos Part A Appl S 70:8–15
Liu HL, Bai HW, Bai DY, Liu ZW, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2017) Design of high-performance poly(l-lactide)/elastomer blends through anchoring carbon nanotubes at the interface with the aid of stereocomplex crystallization. Polymer 108:38–49
Yahiaoui F, Benhacine F, Ferfera-Harrar H, Habi A, Hadj-Hamou AS, Grohens Y (2015) Development of antimicrobial PCL/nanoclay nanocomposite films with enhanced mechanical and water vapor barrier properties for packaging applications. Polym Bull 72:235–254
Lu X, Qiao X, Watanabe H, Gong X, Yang T, Li W, Sun K, Li M, Yang K, Xie H, Yin Q, Wang D, Chen X (2012) Mechanical and structural investigation of isotropic and anisotropic thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Rheol Acta 51:37–50
Horst MF, Quinzani LM, Failla MD (2014) Rheological and barrier properties of nanocomposites of HDPE and exfoliated montmorillonite. J Thermoplast Compos 27:106–125
Avagimova N, Pulyalina A, Toikka A, Suvorova O, Vilesov A, Polotskaya G (2013) Controlling the barrier properties of polymer composites containing montmorillonite. Petrol Chem 53:559–563
Mittal V (2013) Modelling and prediction of barrier properties of polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Polym Compos 21:509–518
Okada A, Usuki A (2006) Twenty years of polymer–clay nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng 291:1449–1476
Paul DR, Robeson LM (2008) Polymer nanotechnology: nanocomposites. Polymer 49:3187–3204
Duncan TV (2011) Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensors. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:1–24
Kotal M, Bhowmick AK (2015) Polymer nanocomposites from modified clays: recent advances and challenges. Prog Polym Sci 51:127–187
Onal M, Sarıkaya Y (2008) The effect of organic cation content on the interlayer spacing, surface area and porosity of methyltributylammonium-smectite. Colloids Surf A 317:323–327
Filippi S, Mameli E, Marazzato C, Magagnini P (2007) Comparison of solution-blending and melt intercalation for the preparation of poly(ethylene-co-acrylicacid)/organoclay nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 43:1645–1659
Chiu CW, Huang TK, Wang YC, Alamani BG, Lin JJ (2013) Intercalation strategies in clay/polymer hybrids. Prog Polym Sci 39:443–485
Tsai TY, Wen CK, Chuang HJ, Lin MJ, Ray U (2009) Effect of clay with different cation exchange capacity on the morphology and properties of poly (methyl methacrylate)/clay nanocomposites. Polym Compos 30:1552–1561
Xie W, Gao Z, Liu K, Pan WP, Vaia R, Hunter D, Singh A (2001) Thermal characterization of organically modified montmorillonite. Thermochim Acta 367:339–350
Bellucci F, Camino G, Frache A, Sarra A (2007) Catalytic charring-volatilization competition in organoclay nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stabil 92:425–436
Rishi S, Saurindra NM (2015) Effects of SEBS-g-MA copolymer on non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of polypropylene. J Mater Sci 50:447–456. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8604-6
Li X, Zhou X, Shi,C, Xu J, Li Y, Tang S, Huang K, Wang X (2017) Preparation of a long-alkyl-chain silane grafted organic montmorillonite and its nanocomposite with SEBS. Polym Bull 74:107–120
Chatani Y, Okita Y, Tadokoro H, Yamashita Y (1970) Structural studies of polyesters. III. Crystal structure of poly-ε-caprolactone. Polym J 1:555–562
Hu H, Dorset DL (1990) Crystal structure of poly(ε-caprolactone). Macromolecules 23:4604–4607
Kaganer VM, Jenichen B, Ploog KH (2000) Bragg diffraction in a coherent X-ray scattering experiment. Physica B 283:268–272
Loos J, Katzenberg F, Petermann J (1997) Epitaxial crystallization of linear low-density polyethylene on high-density polyethylene. J Mater Sci 32:1551–1554. doi:10.1023/A:1018578606510
Jahromi AE, Jahromi HRE, Hemmati F, Saeb MR, Goodarzi V, Formela K (2016) Morphology and mechanical properties of polyamide/clay nanocomposites toughened with NBR/NBR-g-GMA: a comparative study. Compos Part B Eng 90:478–484
Nekhlaoui S, Essabir H, Bensalah MO, Fassi-Fehri O, Qaiss A, Bouhfid R (2014) Fracture study of the composite using essential work of fracture method: PP-SEBS-g-MA/E1 clay. Mater Design 53:741–748
Jancar J, Douglas JF, Starr FW (2010) Current issues in research on structure–property relationships in polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 51:3321–3343
Aghjeh MR, Asadi V, Mehdijabbar P, Khonakdar HA, Jafari SH (2016) Application of linear rheology in determination of nanoclay localization in PLA/EVA/Clay nanocomposites: correlation with microstructure and thermal properties. Compos Part B Eng 86:273–284
Bendict V, Cook WJ, Jarret P, Cameron JA, Huang SJ, Bell JP (1983) Fungal degradation of polycaprolactones. J Appl Polym Sci 28:327–334
Chen H, Chen J, Chen J, Yang J, Huang T, Zhang N (2012) Effect of organic montmorillonite on cold crystallization and hydrolytic degradation of poly(l-lactide). Polym Degrad Stab 97:2273–2283
Wu T, Wu CY (2006) Biodegradable polylactic acid)/chitosan-modified montmorillonite nanocomposites: preparation and characterization. Polym Degrad Stab 91:2198–2204
Luo S, Netravali AN (2003) A study of physical and mechanical properties of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) during composting. Polym Degrad Stab 80:59–66
Tsuji H, Echizen Y, Nishimura Y (2006) Photodegradation of biodegradable polyesters: a comprehensive study on poly(l-lactide) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polym Degrad Stab 91:1128–1137
Mosnacek J, Borska K, Danko M, Janigova I (2013) Photochemically promoted degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone) film. Mater Chem Phys 140:191–199
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51403128 and 51373100).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL and XW designed the experiments, whereas XW and KH conducted the experiments. Meanwhile, WS and XZ and HL assisted in the experimentation. JX and XW revised the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Huang, K., Wang, X. et al. Effect of montmorillonite on morphology, rheology, and properties of a poly[styrene–(ethylene-co-butylene)–styrene]/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) nanocomposite. J Mater Sci 53, 1191–1203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1606-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1606-4