Abstract
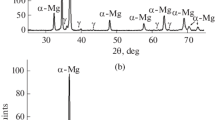
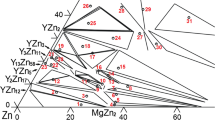
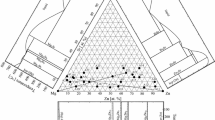
The Mg–Y–Zr system was studied via experimental investigation and thermodynamic modeling. Four diffusion couples and four key alloys of the Mg–Y–Zr system at 500 °C were prepared. The phase relations of the Mg–Y–Zr system were investigated by means of X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and electron probe microanalysis. No ternary compound was found at 500 °C. The solubility of (αZr) in the Mg–Y intermetallics, i.e., Mg24Y5, Mg2Y and MgY, was determined to be negligible. The differential scanning calorimetry measurement was performed on the Mg–Y–Zr alloys to obtain the phase transition temperature. The present thermodynamic calculations of the Mg–Y–Zr system matched well with the experimental data. The presently established Mg–Y–Zr phase diagram can offer a better understanding of the recent processing technique of creep-resistant magnesium alloys.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mordike BL, Ebert T (2001) Magnesium: properties–applications-potential. Mater Sci Eng A 302:37–45
Nie JF (2003) Preface to viewpoint set on: phase transformations and deformation in magnesium alloys. Scr Mater 48:981–984
Nie JF, Muddle BC (2000) Characterisation of strengthening precipitate phases in a Mg–Y–Nd alloy. Acta Mater 48:1691–1703
Apps PJ, Karimzadeh H, King JF, Lorimer GW (2003) Precipitation reactions in magnesium–rare earth alloys containing yttrium, gadolinium or dysprosium. Scr Mater 48:1023–1028
Anthony I, Kamado S, Kojima Y (2001) Aging characteristics and high temperature tensile properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys. Mater Trans 42:1206–1211
Anthony I, Kamado S, Kojima Y (2001) Creep properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys. Mater Trans 42:1212–1218
Nie JF, Muddle BC (1999) Precipitation in magnesium alloy WE54 during isothermal ageing at 250 °C. Scr Mater 40:1089–1094
Nie JF (2012) Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 43A:3891–3939
Riontino G, Massazza M, Lussana D, Mengucci P, Barucca G, Ferragut R (2008) A novel thermal treatment on a Mg–4.2Y–2.3Nd–0.6Zr (WE43) alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 494:445–448
Mengucci P, Barucca G, Riontino G et al (2008) Structure evolution of a WE43 Mg alloy submitted to different thermal treatments. Mater Sci Eng A 479:37–44
Zheng KY, Dong J, Zeng XQ, Ding WJ (2008) Effect of pre-deformation on aging characteristics and mechanical properties of a Mg–Gd–Nd–Zr alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 491:103–109
Barucca G, Ferragut R, Fiori F et al (2011) Formation and evolution of the hardening precipitates in a Mg–Y–Nd alloy. Acta Mater 59:4151–4158
Agnew SR, Mulay RP, Polesak FJ, Calhoun CA, Bhattacharyya JJ, Clausen B (2013) In situ neutron diffraction and poly plasticity modeling of a Mg–Y–Nd–Zr alloy: effects of precipitation on individual deformation mechanisms. Acta Mater 61:3769–3780
Liu H, Gao Y, Liu JZ, Zhu YM, Wang Y, Nie JF (2013) A simulation study of the shape of beta’ precipitates in Mg–Y and Mg–Gd alloys. Acta Mater 61:453–466
Berche A, Benigni P, Rogez J, Record MC (2014) Thremodynamic investigations in the solid state of the lanthanum–magnesium–zinc system. Intermetallics 45:46–52
Gröbner J, Harmpl M, Schmid-Fetzer R et al (2012) Phase analysis of Mg–La–Nd and Mg–La–Ce alloys. Intermetallics 28:92–101
Zhang C, Luo AA, Peng LM, Stone DS, Chang YA (2011) Thermodynamic modeling and experimental investigation of the magnesium–neodymium–zinc alloys. Intermetallics 19:1720–1726
Cheng KM, Zhou H, Hu B et al (2014) Experimental investigation and thermodynamic modeling of the Nd–Zr and the Mg–Nd–Zr systems. Metall Mater Trans A 45:2708–2718
Kim YD, Kang NH, Jo IG, Kim KH, Kim IB (2008) Aging behavior of Mg–Y–Zr and Mg–Nd–Zr cast alloys. J Mater Sci Technol 24:80–84
Drits ME, Padezhnova EM, Guzey LS (1977) Investigation of the phase equilibria and properties of Mg–Y–Zr magnesium alloys. Russ Metall 3:188–191
He CY, Du Y, Chen HL, Ouyang H (2008) Measurement of the isothermal sections at 700 and 427 °C in the Al–Mg–Ni system. Int J Mater Res 99:907–911
Ran Q, Lukas HL, Effenberg G, Petzow G (1988) Thermodynamic optimization of the Mg–Y system. CALPHAD 12:375–381
Fabrichnaya OB, Lukas HL, Effenberg G, Aldinger F (2003) Thermodynamic optimization in the Mg–Y system. Intermetallics 11:1183–1188
Shakhshir SA, Medraj M (2006) Computational thermodynamic model for the Mg–Al–Y system. J Phase Equilibria Diffus 27:231–244
Guo C, Du Z, Li C (2007) A thermodynamic description of the Gd–Mg–Y system. Calphad 31:75–88
Meng FG, Wang J, Liu HS, Liu LB, Jin ZP (2007) Experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation of phase relations in the Mg–Nd–Y ternary system. Mater Sci Eng A 454–455:266–273
Hämäläinen M, Zeng K (1998) Thermodynamic evaluation of the Mg–Zr system. CALPHAD 22:375–380
Arroyave R, Shin D, Liu ZK (2005) Modification of the thermodynamic model for the Mg–Zr system. CALPHAD 29:230–238
Flandorfer H, Gröbner J, Stamou A (1997) Experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation of the ternary system Mn–Y–Zr. Z Metallkd 88:529–538
He HX, Liu HS (2009) Determination of the isothermal section of the Cu–Zr–Y ternary system at 978 K. J Alloy Compd 475:245–251
Sundman B, Jansson B, Andersson JO (1985) The thermo-calc databank system. CALPHAD 9:153–190
Friedrich HE, Mordike BL (2006) Magnesium technology. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2011CB610401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51371199 and 51101172), and Thermo-Calc Software AB under the Mg Alloy Database Project is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, K., Zhou, H., Du, Y. et al. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic description of the Mg–Y–Zr system. J Mater Sci 49, 7124–7132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8420-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8420-z