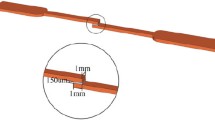
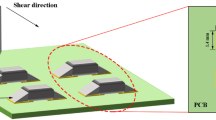
Abstract
Currently, one of the serious challenges in microelectronic devices is the miniaturization trend of packaging. As the decrease of joint dimension, electromigration (EM) and thermomechanical fatigue become critical issues for fine pitch packaging. The independent mechanisms of EM and thermomechanical fatigue are widely investigated and understood. However, the coupling effect of both conditions needs further exploration. The current study established the correlation between resistance and microstructure evolution of solder joint under the combination effect of thermal cycling and high current density and illustrated the different contributions of these two factors to the reliability of the joint through the comparison monopoly tests. The results revealed that cracks had more impact on resistance increase than phase segregation. The resistance evolution could be divided into three stages. First, the resistance mitigated due to the phase coarsening. Second, Joule heating effect made the resistance increase slowly. Third, EM led to the resistance increase rapidly. The high current density can help to improve the reliability of the solder joint under the coupling effect of thermal cycling and EM at the initial stage, but harmful to the consequence process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plumbridge WJ (1996) J Mater Sci 31(10):2501. doi:10.1007/BF00687275
Lee JG, Subramanian KN (2003) J Electron Mater 32(6):523
Liu J, Salmela O, Sarkka J, Morris JE, Tegehall PE, Andersson C (2011) Reliability of microtechnology: interconnects, devices and systems. Springer, New York
Miao HW, Duh JG, Chiou BS (2000) J Mater Sci 11(8):609. doi:10.1023/A:1008928729212
Pang HLJ, Tan KH, Shi XQ, Wang ZP (2001) Mater Sci Eng A Struct 307(1–2):42
Pang JHL, Low TH, Xiong BS, Luhua X, Neo CC (2004) Thin Solid Films 462:370
Chen C, Tong HM, Tu KN (2010) Annu Rev Mater Res 40(1):531
Ma LM, Xu GC, Sun J, Guo F, Wang XT (2011) J Mater Sci 46(14):4896. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5401-3
Lee A, Liu W, Ho CE, Subramanian KN (2007) J Appl Phys 102(5):053507
Ho CE, Lee A, Subramanian KN, Liu W (2007) Appl Phys Lett 91(2):021906
Chen C, Liang SW (2007) J Mater Sci 18(1–3):259. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-48433-4_17
Ma LM, Guo F, Xu GC, Wang XT, He HW, Zhao HY (2012) J Electron Mater 41(2):425
Zhou W, Liu L, Li B, Wu P (2010) Thin Solid Films 518(20):5875
He HW, Xu GC, Guo F (2010) J Mater Sci 45(4):929. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-4022-6
Liu HY, Zhu QS, Wang ZG, Shang JK (2011) Mater Sci Eng Struct 528(3):1467
Choi WJ, Yeh ECC, Tu KN (2003) J Appl Phys 94(9):5665
Cook B, Anderson I, Harringa J, Kang S (2003) J Electron Mater 32(12):1384
Sun J, Xu GC, Guo F (2011) J Mater Sci 46(10):3544. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5265-6
He HW, Xu GC, Guo F (2010) J Mater Sci 45(2):334. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3939-0
Agarwal R, Ou SE, Tu KN (2006) J Appl Phys 100(2):024909
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of this work from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51071006) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation Program and Scientific Research Key Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KZ200910005004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, Y., Ma, L., Liu, S. et al. The coupling effects of thermal cycling and high current density on Sn58Bi solder joints. J Mater Sci 48, 2318–2325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-7011-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-7011-0