Abstract
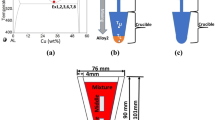
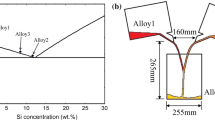
Controlled diffusion solidification is a novel and promising process wherein near-net-shaped cast product of a desired Al wrought alloy is obtained by mixing two precursor alloys at specific individual composition, mass, and temperature each to obtain a non-dendritic morphology of the primary Al phase in the solidified microstructure. This study is devoted to quantify the effect of the rate of mixing of the two precursor alloys on the morphology of the primary Al phase in the cast component. The results show that the lower mixing rate with a higher mixing velocity is more favorable for the CDS process.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
SCXI-1100 is a trademark of National Instruments, Vaudreuil-Dorion, PQ, Canada.
Eberbach Corporation, ANN Michigan, USA.
JEOL, INCA Oxford, England.
ImageJ, Image processing and Analysis in Java, 1.42q Java 1.6.0 (32 bit).
Abbreviations
- Alloy1:
-
Precursor alloy with higher thermal mass
- Alloy2:
-
Precursor alloy with lower thermal mass
- Alloy3:
-
Desired resultant alloy
- C :
-
Specific heat
- C o :
-
Average concentration of Alloy3
- k L :
-
Thermal conductivity of liquid pure Al
- m 1 :
-
Mass of Alloy1
- m 2 :
-
Mass of Alloy2
- mr:
-
Mass ratio (m1:m2)
- m T :
-
Total mass of Alloy3
- T 1 :
-
Initial temperature of liquid Alloy1
- T 2 :
-
Initial temperature of liquid Alloy2
- T 3 :
-
Initial temperature of liquid Alloy3
- T L1 :
-
Liquidus temperature of Alloy1
- T L2 :
-
Liquidus temperature of Alloy2
- T L3 :
-
Liquidus temperature of Alloy3
- ∆T :
-
Undercooling below the liquidus temperature of the respective alloy
- t :
-
Time
- D :
-
Solute diffusion coefficient
- L :
-
Characteristic length
- u :
-
Velocity
- ρ :
-
Density
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- α:
-
Thermal diffusivity
- σ :
-
Surface tension
- (N Pe)T :
-
Peclet number for thermal field
- (N Pe)S :
-
Peclet number for solute field
- N We :
-
Weber number
References
Saha D, Shankar S, Apelian D, Makhlouf MM (2004) Metall Mater Trans A 35A:2174
Goetzl CG, Ellis JL (1952) US Patent 2,611,443, September 30, 1952
Langford G, Cunningham RE (1978) Metall Trans B 9B:5
Apelian D, Langford G (1980) J Met 32(9):28
Wang J et al. (2002) Mater Sci Eng A338
Ashtari P, Birsan G, Khalaf A, Shankar S (2011) Int J Met Cast 2011(Spring):43
Symeonidis K (2009) PhD thesis, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, April
Saha D, Shankar S, Apelian D, Makhlouf M (2004) In: Crepeau P, Tiryakioglu M (eds) Proceedings of the John Campbell Honorary symposium. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS), Warrendale
Birsan G (2009) Master Thesis, Mechanical Engineering, McMaster University
Ashtari P, Birsan G, Shankar S (2009) In: Campbell J, Crepeau PN, Tiryakioglu M (eds) Shape casting: the 3rd international symposium. The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Warrendale, pp 223–230
Khalaf AA, Ashtari P, Shankar S (2009) In: Campbell J, Crepeau PN, Tiryakioglu M (eds) Shaped casting: the 3rd international symposium. The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Warrendale, pp. 215–222
Khalaf A, Ashtari P, Shankar S (2009) Metall Mater Trans B 40B:843
Khalaf AA (2010) PhD Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, pp. 72–90
Vishan V, Narlikar AV (1976) Mater Res Bull II:I257
ASM Handbook Committee (1973) Metals handbook, metallographic, structure and phase diagram, vol 8, 8th edn. American Society for Metals, Materials Park, OH
Kirkwood DH et al (2009) Springer Ser Mater Sci 124:22
Khalaf AA, Shankar S (2011) Metal Mater Trans A 42A:2456
Smallman RE, Bishop RJ (1999) Modern physical metallurgy and materials engineering, 6th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, p 41
Bruus H (2008) Theoretical microfluidics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kurz W, Fisher DJ (1989) Fundamentals of solidification, 3rd edn. Trans Tech Publications, Enfield
Apelian D, Makhlouf MM, Saha D (2006) Mater Sci Forum 519–521:1771
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalaf, A.A., Shankar, S. Effect of mixing rate on the morphology of primary Al phase in the controlled diffusion solidification (CDS) process. J Mater Sci 47, 8153–8166 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6711-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6711-9