Abstract
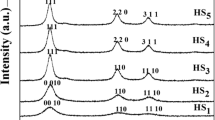
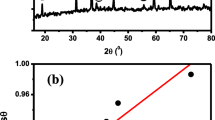
Antimony trioxide (Sb2O3) nanoparticles with particle sizes ranging from 2 to 12 nm, spherical in shape, and well-distributed were successfully synthesized by chemical reduction method. The nanoparticles were synthesized in the presence of hydrazine as a reduction agent in ethylene glycol through the reaction between antimony trichloride and sodium hydroxide. Effects of reaction temperature, reaction time, precursor concentration and boiling temperature on the particle size, shape, and distribution of the Sb2O3 nanoparticles were investigated. Morphology of the nanoparticles was examined by transmission electron microscope (TEM). It was revealed that the particle size increased when reaction temperature, reaction time and concentration of precursor were increased. Moreover, the mixture needed to be boiled prior to the addition of hydrazine as a reduction agent, in order to obtain an optimum reduction. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was employed to study the crystallinity and phase of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were determined as cubic phase of Sb2O3 (ICDD file no. 00-043-1071) by XRD. Interrelation between UV–vis absorption spectra of the nanoparticles and their particle size were obtained.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang D, Zhou Y, Song C, Shao M (2009) J Cryst Growth 311:3948
Ye CH, Wang GY, Kong MG, Zhang LD (2006) J Nanomater 2006:1
Xie XL, Li RKY, Liu QX, Mai YW (2004) Polymer 45:2793
Feng L, Wang J, Liu J, Wang B, Song S (2007) J Compos Mater 41:1487
Laachachi A, Cochez M, Ferriol M, Leroy E, Lopez Cuesta JM, Oget N (2004) Polym Degrad Stab 85:641
Duh B (2002) Polymer 43:3147
Nalin M, Messaddeq Y, Ribeiro SJL, Poulain M, Briois V (2001) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 3:553
Sahoo NK, Apparao KVSR (1997) Appl Phys A 63:195
Ozawa K, Sakka Y, Amano M (1998) J Mater Res 13:830
Dzimitrowicz DJ, Goodenough JB, Wiseman PJ (1982) Mater Res Bull 17:971
Zhang ZL, Guo L, Wang WD (2001) J Mater Res 16:803
Jha AK, Prasad K (2009) Biochem Eng J 43:303
Chen XY, Huh HS, Lee SW (2008) J Solid State Chem 181:2127
Liu YP, Zhang YH, Zhang MW, Zhang WH, Qian YT, Yang L, Wang CS, Chen ZW (1997) Mater Sci Eng B 49:42
Zeng DW, Zhu BL, Xie CS, Song WL, Wang AH (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 366:332
Zeng DW, Xie CS, Zhu BL, Song WL (2004) Mater Lett 58:312
Xu CH, Shi SQ, Surya C, Woo CH (2007) J Mater Sci 42:9855. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1799-z
Qiu KQ, Zhang RL (2006) Vacuum 80:1016
Chin HS, Cheong KY, Abdul Razak K (2010) J Mater Sci 45:5993. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4849-x
Wu SH, Chen DH (2003) J Colloid Interface Sci 259:282
Balela MDL (2008) Dissertation, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang
Lee YM, Qin GW, Lee CG, Koo BH, Moon KY, Shimada Y, Kitakami O (2007) Met Mater Int 13:207
Kim KD, Kim HT (2003) Mater Lett 2003:3211
Pattabi M, Saraswathi AB (2007) J New Mater Electrochem Syst 10:43
Yang M, Zhang Y, Pang G, Feng S (2007) Eur J Inorg Chem 2007:3841
Segets D, Tomalino LM, Gradl J, Peukert W (2009) J Phys Chem C 113:11995
Zhang G, Roy BK, Allard LF, Cho J (2008) J Am Ceram Soc 91:3875
Chin HS, Cheong KY, Abdul Razak K (2010) J Nanoparticle Res. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0169-y
Rautio J, Perämäki P, Honkamo J, Jantunen H (2009) Microchem J 91:272
Chang PR, Yu J, Ma X (2009) Macromol Mater Eng 294:762
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (H.S.C) would like to thank USM RU-PRGS grant and USM fellowship for the scholarship and financial support on this project. Another author (K.Y.C) would like to acknowledge the financial support given by Short Term Grant of Universiti Sains Malaysia (6039038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, H.S., Cheong, K.Y. & Abdul Razak, K. Effect of process parameters on size, shape, and distribution of Sb2O3 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 46, 5129–5139 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5444-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5444-5