Abstract
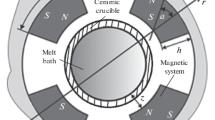
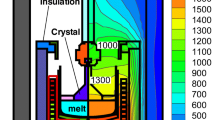
The radio frequency floating-zone growth of massive intermetallic single crystals is very often unsuccessful due to an unfavourable solid–liquid interface geometry enclosing concave fringes. This interface depends on the flow in the molten zone. A tailored magnetic two-phase stirrer system has been developed which enables the controlled influence on the melt flow ranging from intense inwards to outwards flows. Depending on the phase shift between the two induction coils, a transition from a double vortex structure to a single vortex structure is created at a preferable phase shift of 90°. This change in the flow field has a significant influence on the shape of the solid–liquid interface. Due to their attractive properties for high temperature applications such as high melting temperature, low density, high modulus and good oxidation resistance, the magnetic system was applied to the crystal growth of TiAl alloys.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dold P, Cröll A, Lichtensteiger M, Kaiser Th, Benz KW (2001) J Cryst Growth 231(1–2):95
Ma N, Walker JS, Lüdge A, Riemann H (2001) J Cryst Growth 230(1–2):118
Cröll A, Benz KW (1999) Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 38(1–4):133
Passerone A, Eustathopoulos N (2005) J Mater Sci 40(9–10):XV. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-2128-z
Morthland TE, Walker JS (1997) Int J Heat Mass Transf 40(14):3283
Munakata T, Tanasawa I (1999) J Growth 206(1–2):27
Tanaka T, Bannai E, Kawai S, Yamane T (1975) J Cryst Growth 30:193
Takeya H, Habuta E, Kawano-Furukawa H, Ooba T, Hirata K (2001) J Magn Magn Mater 226–230(Part 1):269
Behr G, Löser W, Graw G, Bitterlich H, Freudenberger J, Fink J, Schultz L (1999) J Cryst Growth 198–199(Part 1):642
Clemens H (1995) Z Metallkd 86(12):814
Dimiduk DM (1999) Mater Sci Eng A 263:281
Hermann R, Behr G, Gerbeth G, Priede J, Uhlemann H-J, Fischer F, Schultz L (2005) J Cryst Growth 275:e1533–e1538
Priede J, Gerbeth G (2006) IEEE Trans Magn 42(2):301–308
Krauze A, Priede J, Hermann R, Gerbeth G (2008) Proceedings of the 7th PAMIR international conference on fundamental and applied MHD, Giens, 8–12 September 2008, pp 851–855
Witusiewicz VT, Bondar AA, Hecht U, Rex S, Velikanova TYa (2008) J Alloys Compd 465:64
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the SFB 609 “Elektromagnetische Strömungsbeeinflussung in Metallurgie, Kristallzüchtung und Elektrochemie” is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermann, R., Gerbeth, G., Priede, J. et al. Convectional controlled crystal–melt interface using two-phase radio-frequency electromagnetic heating. J Mater Sci 45, 2228–2232 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4117-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4117-0