Abstract
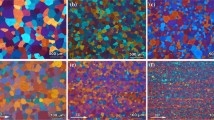
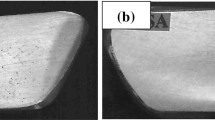
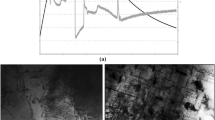
Two cast noncombustible Mg–9Al–1Zn–1Ca alloys (composition in mass%) with coarse and fine initial microstructures were hot forged by compression at temperatures of 523–603 K and a true strain rate of 1–10−2 s−1. The compressive stress–strain curves for the two alloys were similar and typical of metals undergoing dynamic recrystallization (DRX). The alloy with the coarse initial microstructure suffered from edge crack formation during hot forging, while the alloy with the fine initial microstructure exhibited smooth peripheral surfaces after hot forging at temperatures of 573 K and above. The reduction of grain size by DRX was similar in the two hot-forged alloys, but the recrystallized volume fraction was lower in the alloy with the coarse initial microstructure. Insoluble second phases (seemingly Al2Ca) provide additional DRX sites, and thus it is expected that the finer initial cast microstructure will improve the microstructure in the resulting hot-forged Mg parts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebert T, Mordike BL (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 302:37
Chino Y, Mabuchi M, Shimojima K, Yamada Y, Wen C, Miwa K, Nakamura M, Asahina T, Higashi K, Aizawa T (2001) Mater Trans 42:414
Takigawa Y, Honda M, Uesugi T, Higashi K (2008) Mater Trans 49:1979
Yang X, Miura H, Sakai T (2003) Mater Trans 44:197
Ding H, Liu L, Kamado S, Ding W, Kojima Y (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 452–453:503
Helis L, Okayasu K, Fukutomi H (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 430:98
StJohn DH, Qian M, Easton MA, Cao P, Hildebrand Z (2005) Metall Mater Trans A 36:1669
Li M, Tamura T, Miwa K (2009) J Mater Res 24:145
Akiyama S, Ueno H, Sakamoto M, Hirai H, Kitahara A (2000) Materia Japan 39:72–74 (in Japanese)
Watanabe H, Yamaguchi M, Takigawa Y, Higashi K (2008) Mater Trans 49:1262
Watanabe H, Yamaguchi M, Takigawa Y, Higashi K (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 454–455:384
Chino Y, Jae-Seol L, Nakaura Y, Ohori K, Mabuchi M (2005) Mater Trans 46:2592
Chino Y, Nakaura Y, Ohori K, Kamiya A, Mabuchi M (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 452–453:31
Hakamada M, Watazu A, Saito N, Iwasaki H (2008) Mater Trans 49:554
Humphreys FJ (1991) Mater Sci Eng A 135:267
Hakamada M, Watazu A, Saito N, Iwasaki H (2008) Mater Trans 49:1032
Hakamada M, Watazu A, Saito N, Iwasaki H (2009) Mater Trans 50:711
Thompson AW (1972) Metallography 5:366
Barnett MR (2003) Mater Trans 44:571
Watanabe H, Tsutsui H, Mukai T, Ishikawa K, Okanda Y, Kohzu M, Higashi K (2001) Mater Trans 42:1200
Dehghan-Manshadi A, Hodgson PD (2008) Metall Mater Trans A 39:2830
Tsuzaki K, Huang X, Maki T (1996) Acta Mater 44:4491
Frost HJ, Ashby MF (1982) Deformation-mechanism maps. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Hakamada M, Watazu A, Saito N, Iwasaki H (2008) J Mater Sci 43:2066. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2474-8
Acknowledgement
This study was conducted with the financial support of the Forged Magnesium Parts Technological Development Project, which is organized by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakamada, M., Shimizu, K., Yamashita, T. et al. Effect of initial microstructures on hot forging of Ca-containing cast Mg alloys. J Mater Sci 45, 719–724 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3990-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3990-x