Abstract
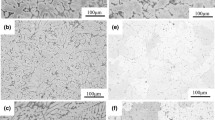
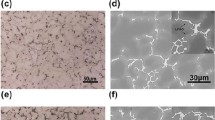
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–4Y–xSm–0.5Zr (x = 1, 4, 8) alloys during thermo-mechanical treatments were investigated in this study. Mg–4Y–4Sm–0.5Zr alloy exhibits higher tensile strength but lower elongation than Mg–4Y–1Sm–0.5Zr alloy during the thermo-mechanical treatments. Large amount of intermetallic phases still remained at grain boundaries in Mg–4Y–8Sm–0.5Zr alloy after solution. These undissolved phases can strengthen the grain boundaries at temperatures higher than 573 K. But the room temperature mechanical properties of Mg–4Y–8Sm–0.5Zr alloy during the thermo-mechanical treatments were greatly weakened for the brittleness of these undissolved intermetallic phases.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mordike BL, Ebert T (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 302:37
Aghion E, Gueta Y, Moscovitch N, Bronfin B (2008) J Mater Sci 43:4870. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2708-9
Wang JG, Hsiung LM, Nieh TG, Mabuchi M (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 315:81
Li ZC, Zhang H, Liu L, Xu YB (2004) Mater Lett 58:3021
Peng Q, Wu Y, Fang D, Meng J, Wang L (2007) J Mater Sci 42:3908. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0451-7
Mohri T, Mabuchi M, Satio N, Nakamura M (1998) Mater Sci Eng A 257:287
Weiss D, Kaya AA, Aghion E, Eliezer D (2002) J Mater Sci 37:5371. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:10210018138675371-5379
Song YL, Liu YH, Yu SR, Zhu XY, Wang SH (2007) J Mater Sci 42:4435. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0661-z
Rokhlin LL, Dobatkina TV, Tarytina IE, Timofeev VN, Balakhchi EE (2004) J Alloy Compd 367:17
Nie JF, Muddle BC (1999) Scri Mater 40:1089
Nie JF, Xiao XL, Luo CP, Muddle BC (2001) Micron 32:857
Smola B, Stulikova I (2004) J Alloy Compd 381:L1
Ping DH, Hono K, Nie JF (2003) Scri Mater 48:1017
Nie JF, Muddle BC (2000) Acta Mater 48:1691
Nakashima K, Iwasaki H, Mori T, Mabuchi M, Nakamura M, Asahina T (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 293:15
Rokhlin LL (2003) In: Magnesium alloys containing rare earth meals. Taylor and Francis Inc., London
Li D, Wang Q, Ding W (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 428:295
Li D, Wang Q, Ding W (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 448:165
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by International Cooperation Fond of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee, Shanghai/Rhone-Alpes Science and Technology cooperation fund (No. 06SR07104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wang, Q. & Ding, W. Effects of samarium on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Y–Sm–Zr alloys during thermo-mechanical treatments. J Mater Sci 44, 3049–3056 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3403-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3403-1