Abstract
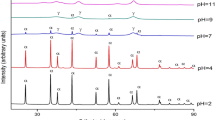
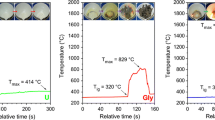
Fuel type and fuel/aluminium nitrate molar ratio proved to be of great importance during the preparation of α-Al2O3 powders. A stoichiometric amount of urea (U) enabled the formation of α-Al2O3 with a surface area of 24 m2/g directly from the combustion reaction. Monoethanolamine, triethylenetetramine, trishydroxymethylaminomethane, and triethanolamine yield amorphous powders. This behaviour was explained by the reaction mechanism, which requires the simultaneous decomposition of metal nitrate and fuel, as shown by thermal analysis. The use of 50% of the stoichiometric amount of U was unable to trigger a combustion reaction. The resulting powder was amorphous and had a surface area of 424 m2/g. A parabolic correlation between the surface area of combustion-synthesized powder and the U/aluminium nitrate molar ratio was found. Due to U consumption during the hydrolysis side-reaction, 50% of U excess above the stoichiometric ratio is required in order to maximize the exothermic effect of the combustion reaction. The use of U excess higher than 150% of the stoichiometric ratio not only increases the surface area of the powder, but also changes the phase composition: as the U excess increases the proportion of α-Al2O3 decreases and the amount of γ-Al2O3 increases.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volceanov E, Volceanov A, Stoleriu Ş (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27:759
Menecier S, Jarrige J, Labbe JC et al (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27:851
Gitknecht D, Chevalier J, Garnier V et al (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27:1547
Ul’yanova TM, Titova LV, Krut’ko NP (2002) Glass Ceram 59:279
Badmos AY, Ivey DG (2001) J Mater Sci 36:4995. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011885631876
Kiiko VS, Makurin YN, Safronov AA et al (2003) Refract Ind Ceram 44:94
Temuujin J, Jadambaa T, Mackenzie KJD et al (2000) Bull Mater Sci 23:301
Martin ST, Yu J, Han J et al (2000) J Aerosol Sci 31:1283
Hernandez T, Bautista MC (2005) J Eur Ceram Soc 25:663
Janbey A, Pati RK, Tahir S et al (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:2285
Patil KC, Aruna ST, Mimani T (2002) Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 6:507
Ianoş R (2009) J Mater Res. doi:https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2009.0019
Ianoş R, Lazău I, Păcurariu C et al (2008) Eur J Inorg Chem 2008:931
Bhaduri S, Zhou E, Bhaduri SB (1996) Nanostruct Mater 7:487
Mimani T (2000) Resonance 5:50
Mimani T, Patil KC (2001) Mater Phys Mech 4:134
Chen CC, Huang KT (2005) J Mater Res 20:424
Ozuna O, Hirata GA, McKittrick J (2004) J Phys Condens Matter 16:2585
Toniolo JC, Lima MD, Takimi AS et al (2005) Mater Res Bull 40:561
Peng T, Liu X, Dai K et al (2006) Mater Res Bull 41:1683
Pathak LC, Singh TB, Das S et al (2002) Mater Lett 57:380
Li J, Wu Y, Pan Y et al (2007) Ceram Int 33:361
Speight JG (2005) Lange’s handbook of chemistry, 16th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Pacewska B, Keshr M (2002) Thermochim Acta 385:73
Kakade MB, Ramanathan S, Ravindran PV (2003) J Alloys Compd 350:123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ianoş, R., Lazău, I. & Păcurariu, C. The influence of combustion synthesis conditions on the α-Al2O3 powder preparation. J Mater Sci 44, 1016–1023 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3226-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3226-5