Abstract
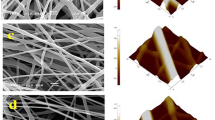
A novel nano-sized copolymer nanofilm provides a unique reinforcement to the mechanical properties of natural textiles. This study reveals that a nano-sized coating provides a strong healing effect to resist the crack propagation of natural fiber surfaces. As little as 0.15 wt% addition of the nanoparticles to the cotton surface improved the fabrics’ tearing resistance by 56% and abrasion resistance by 100%. Surface analyses (SEM and AFM) demonstrated that the nanoparticles formed a uniform monolayer and after heat treatment the monolayer nanofilm covalently bonded to the substrate. This nanofilm is reliable in repeated washes due to its covalent bonding. Using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy (TOF-SIMS), we studied the reactivity and phase-transition process of the nanoparticles as they transformed into the nanofilm. The study demonstrates the active role of the N-methylol group and the primary hydroxyl group toward the cotton surface, which modulate the rupture process of the fiber substrate; meanwhile, it demonstrates the positively charged nanoparticles have an excellent dispersibility on the negatively charged cotton surface. The result opens the possibility for various textiles to enhance their properties via an electrostatic affinity and covalent bonding of functional nanoparticles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahltig B, Bo¨ttcher H (2003) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 27:43
Mahltig B, Fiedler D, Böttcher H (2004) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 32:219
Vince J, Orel B, Vilcnik A, Fir M, Surca Vuk A, Jovanovski V, Simoncic B (2006) Langmuir 22:6489
Qian L, Sun G (2005) Ind Eng Chem Res 44:852
Hoefnagels HF, Wu D, de With G, Ming W (2007) Langmuir 23:13158
Service RF (2003) Science 301:909
Tiller JC, Liao CJ, Kim L, Klibanov AM (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:5981
Schramm C, Binder WH, Tessadri R (2004) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 29:155
Mahltig B, Haufe H, Bo¨ttcher H (2005) J Mater Chem 15:4385
Mahltig B, Audenaert F, Bo¨ttcher H (2005) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 34:103
Salon M-CB, Abdelmouleh M, Boufi S, Belgacem MN, Gandini A (2005) J Colloid Interface Sci 289:249
Soane DS, Offord DA, Linford MR, Millward DB, Ware W, Erskine L, Green E, Lau R (2003) US Pat Appl Publ US 2003013369, 2003
Alince B (2005) J Appl Polym Sci 98:1879
Alince B, Arnoldova P, Frolik R (2000) J Appl Polym Sci 76:1677
Zhang Y, Yang WL, Wang CC, Wu W, Fu SK (2006) J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6:2896
Yang C (2007) Explorations in the application of nanotechnology to improve the mechanical properties of composite materials, in “Chemistry”, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, p 161
PeulaGarcia JM, HidalgoAlvarez R, delasNieves FJ (1997) Colloid Surf A 127:19
Tsuruta LR, Lessa MM, Carmonaribeiro AM (1995) J Colloid Interface Sci 175:470
Goldfinger G (1969) Clean surfaces: their preparation and characterization for interfacial studies. Dekker, New York
Young RA, Rowell RM (1986) Cellulose: structure, modification, and hydrolysis. Wiley, New York
Pizarro GDC, Jeria M, Marambio OG, Huerta M, Rivas BL (2005) J Appl Polym Sci 98:1903
Isik B, Guenay Y (2004) Colloid Polym Sci 287:693
Kawaguchi H, Sugi Y, Ohtsuka Y (1981) J Appl Polym Sci 26:1649
Yan CE, Xu ZH, Cheng SY, Feng LX (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 68:969
Kim JH, Chainey M, El-Aasser MS, Vanderhoff JW (1989) J Polym Sci Polym Chem 27:3187
Kim JH, Chainey M, El-Aasser MS, Vanderhoff JW (1992) J Polym Sci Polym Chem 30:171
Frick JG, Kottes BH, Reid JD (1959) Text Res J 29:314
American Society for Testing and Materials (1969) Book of ASTM standards. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, p 1716
American Society for Testing and Materials (1969) Book of ASTM standards. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, p 539
Andersson M, Hietala S, Tenhu H, Maunu SL (2006) Colloid Polym Sci 284:1255
Hearle JWS (1963) J Appl Polym Sci 7:1207
Hearle JWS (1985) Cell Chem Appl 480
Hearle JWS, Sparrow JT (1971) Text Res J 41:736
Hearle JWS, Wilkins AH (2006) J Text Inst 97:1
Acknowledgements
This research work was partially supported by ITF (Hong Kong) grant No. 109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Preparation of other nanoparticles, SEM analyses on the nanoparticle treated cotton fabrics. This material is available free of charge via the internet at https://doi.org/www.springerlink.com/.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Gao, P. & Xu, B. Investigations of a controllable nanoscale coating on natural fiber system: effects of charge and bonding on the mechanical properties of textiles. J Mater Sci 44, 469–476 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3094-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3094-z