Abstract
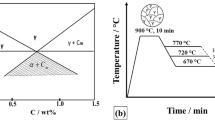
Multiphase (MP) steels have complex microstructures containing polygonal ferrite, martensite, bainite, carbide, and small amounts of retained austenite. This mixture of phases and constituents is responsible for a good combination of strength and ductility in this class of steels. The present work shows how different annealing parameters can be used to create the suitable microstructure to improve mechanical properties of MP steels. Samples were first heated to 740, 760, or 780 °C, held for 300 s, and then quickly cooled to 600 or 500 °C. They were then soaked for another 300 s and finally accelerated cooled in the range of 10–30 °C s−1. The microstructures were examined at the end of each processing route using optical, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy. Hardness values were determined for all conditions. Analysis of the available data allowed to establish the simple and yet useful quantitative relationship between the microstructural parameters, cooling rates, and hardness of the steel.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fekete JR (2005) In: Proc niobium microalloyed steel for automotive applications. Araxá, Brazil, TMS, p 107
DeArdo AJ (2003) Mater Sci Forum 426–432:49
Mesplont C, De Cooman BC (2002) Iron Steel 23:39
Lewellyn DT, Hillis DJ (1996) Iron Steelm 23:471
Pichler A, Traint S, Arnoldner G, Werner E, Pippan R, Stiaszny P (2000) In: Proc ‘42° mechanical working and steel processing’, Toronto, Canada, October 22–25, p 573
Cota AB, Barbosa R, Santos DB (2000) J Mater Process Tech 100:156. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00467-7
Silva F, Lopes NIA, Santos DB (2006) Mater Charact 56:3. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2005.07.008
Honeycombe RWK, Bhadeshia HKDH (1995) Steels, microstructure and properties, 2nd edn. Edward Arnold, London, England
Huang J, Poole WJ, Militzer M (2004) Metall Mater Trans A 35:3363. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0173-x
Ramos LF, Matlock DK, Krauss G (1979) Metall Trans A 10:259. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02817636
Speich GR, Demarest VA, Miller ML (1981) Metall Trans A 12:1419. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02643686
Bunge H-J, Vlad CM, Kopp H-H (1984) Arch Eisenh 55:163
Estay S, Cheng L, Purdy GR (1984) Can Metall Q 23:121
Demir B, Erdoðan M (2008) J Mater Process Tech. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.094
Rao BVN, Rashid MS (1983) Metallography 16:19. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0800(83)90042-3
Qu J, Dabboussi W, Hassani F, Yue S (2005) ISIJ Int 45:1741. doi:https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.45.1741
Verdeja JI, PeroSanz JA, Asensio J (2005) Mater Sci Forum 500–501:429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neves, É.G., Barbosa, R.N., Pereloma, E.V. et al. Effect of thermomechanical processing on mechanical behavior and microstructure evolution of C–Mn multiphase high strength cold rolled steel. J Mater Sci 43, 5705–5711 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2902-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2902-9