Abstract
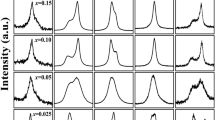
The widely used piezoelectric Pb(Zr1−xTix)O3 ceramics have been known to have Zr4+ and Ti4+ randomly distributed on the B-site lattice in the ABO3 perovskite structure. In this study, we attempted to develop long range 1:1 B-site cation order by forming the solid solution of (1 − x)Pb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3 − xPb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 (x ≥ 0.60). High temperature X-ray diffraction tests indicate that the cation order is embedded in the structural order. The solid solution ceramics appear to have a non-cubic paraelectric phase above their Curie temperatures. The competition between the antiferroelectric order in Pb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3 and the ferroelectric order in Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 leads to the relaxor ferroelectric behavior in the solid solution. Since the temperature at dielectric maximum, T m, is significantly above room temperature, regular polarization versus electric field hysteresis loops are recorded in these compositions at room temperature. In addition, these ceramics show very good piezoelectric properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell RH (2002) Perovskite: modern and ancient. Almaz Press, Ontario
Smolenskii GA (1970) J Phys Soc Jpn 28(Suppl):26
Cross LE (1994) Ferroelectrics 151:305
Chen J, Chan HM, Harmer MP (1989) J Am Ceram Soc 72:593. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb06180.x
Davis PK, Akbas MA (2000) J Phys Chem Solids 61:159. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00275-9
Zhao XH, Qu WG, He H, Vittayakorn N, Tan X (2006) J Am Ceram Soc 89:202. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00675.x
Setter N, Cross LE (1980) J Appl Phys 51:4356. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.328296
Zaslavskii AI, Bryzhina MF (1963) Sov Phys Crystallogr 7:577
Baba-Kishi KZ, Cressey G, Cernik RJ (1992) J Appl Cryst 25:477. doi:https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889892001110
Baldinozzi G, Sciau P, Buffat PA (1993) Solid State Commun 86:541. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(93)90135-A
Choo WK, Kim HJ, Yang JH, Lim H, Lee JY, Kwon JR et al (1993) Jpn J Appl Phys 32:4249. doi:https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.32.4249
Baldinozzi G, Sciau P, Pinot M, Grebille D (1995) Acta Crystallogr B 51:668. doi:https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768194014047
Yasuda N, Fujimoto S, Yoshimura T (1986) J Phys C Solid State Phys 19:1055. doi:https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3719/19/7/016
Baldinozzi G, Sciau P, Bulou A (1995) J Phys Condens Matter 7:8109. doi:https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/7/42/008
Ardelean I, Barbur I, Timar V, Borodi Gh (2003) Mod Phys Lett B 17:1135. doi:https://doi.org/10.1142/S021798490300613X
Akbas MA, Davies PK (1997) J Am Ceram Soc 80:2933. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1997.tb03214.x
Juhas P, Davies PK (2004) J Am Ceram Soc 87:2086
Jaffe B, Cook WR, Jaffe H (1971) Piezoelectric ceramics. Academic Press, London
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Crystallogr A 32:751. doi:https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
Uchino K, Nomura S (1982) Ferroelectr Lett 44:55. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/07315178208201875
Vittayakorn N, Rujijanagul G, Tan X, Marquardt MA, Cann DP (2004) J Appl Phys 96:5103. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1796511
Chen IW (2000) J Phys Chem Solids 61:197. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00282-6
Lu CH (1996) J Mater Sci 31:699. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00367888
Stringer CJ, Randall CA (2007) J Am Ceram Soc 90:1802. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.01640.x
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation through the CAREER grant DMR-0346819.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, D., Zhao, X., Besser, M.F. et al. Structure and properties of (1 − x)Pb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3 − xPb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 solid solution ceramics. J Mater Sci 43, 5258–5264 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2772-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2772-1