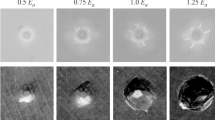
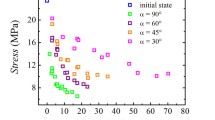
Abstract
Solid-particle erosion tests were carried out to study the effect of matrix material, impact angle, and impact velocity on the erosion behavior of seven types of thermoplastic neat polymers (i.e., polyetherimide, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketone, polyphenylene sulfide, polyethersulfone, polysulfone, and ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene). Steady-state erosion rates of these polymers have been evaluated at different impact angles (15–90°) and impact velocities (25–66 m/s). Silica sand of particle size 200 ± 50 μm was used as the erodent. These polymers have exhibited maximum erosion rate (E max) at 30° impact angle indicating ductile erosion behavior. Some of these polymers have shown an incubation behavior at lower impact velocities for an impact angle of 90°. Correlations among steady-state erosion rate and mechanical properties and glass transition temperature (T g) were established. Morphology of eroded surfaces was examined using scanning electron microscopy and possible wear mechanisms were discussed.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PEI, PEEK, PEK, and PPS were cleaned with acetone, whereas PES, PSU, and UHMWPE were cleaned with cotton because these polymers react with acetone.
Abbreviations
- ABS :
-
Acrylonitryl-butyldiene styrene
- PA:
-
Polyamide
- PB :
-
Polybutadine
- PC:
-
Polycarbonate
- PE:
-
Polyethylene
- PEI:
-
Polyetherimide
- PEEK:
-
Polyetheretherketone
- PEK:
-
Polyetherketone
- PES:
-
Polyethersulfone
- PMMA:
-
Polymetyl methacrylate
- PP:
-
Polypropylene
- PPS:
-
Polyphenylene sulfide
- PS:
-
Polystyrene
- PSU:
-
Polysulfone
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- TPI:
-
Thermoplastic polyimide
- UHMWPE:
-
Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene
References
Johnston NJ, Towell TW, Hergenrother PM (1991) Thermoplastic composite materials. Elsevier Science Publishers, BV, p 27
Barkoula N-M, Karger-Kocsis J (2002) J Mater Sci 37:3807
Hutchings IM (2002) Tribology: friction and wear of engineering materials. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, p 174
Arjula S, Harsha AP (2006) Polym Test 26:188
Tilly GP (1969) Wear 14:63
Smeltzer CE, Gulden ME, Campton WA (1970) J Basic Eng 92:639
Ratner SB, Styller EE (1981) Wear 73:213
Rajesh JJ, Bijwe J, Tewari US, Venkataraman B (2001) Wear 249:702
Barkoula NM, Gremmels J, Karger-Kocsis J (2001) Wear 247:100
Thai CM, Tsuda K, Hojo H (1981) J Test Eval 9:359
Walley SM, Field JE Yennadhiou P (1984) Wear 100:263
Friedrich K (1986) J Mater Sci 21:3317
Walley SM, Field JE (1987) Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 321:277
Walley SM, Field JE, Scullion IM, Heukensfeldt Jansen FPM, Bell D (1984) In: Field JE, Dear JP (eds) Proceedings of seventh international conference on erosion by liquid and solid impact. Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, UK, p 58
Walley SM, Field JE, Greengrass M (1987) Wear 114:59
Wang YQ, Huang LP, Liu WL, Li J (1998) Wear 218:128
Rao PV, Buckley DH (1984) ASLE Trans 27:373
Rao PV, Buckley DH (1986) ASLE Trans 29:283
Böhm H, Betz S, Ball A (1990) Tribol Int 23:399
Brandstädter A, Goretta KC, Routbort JL, Groppi DP, Karasek KR (1991) Wear 147:155
Kayser W (1967) In: Fyall AA, King RB (eds) Proceedings of 2nd Meersburg conference on rain erosion and allied phenomena. Royal Aircraft Establishment, Farnborough, UK, p 427
Marei AI, Izvozchikov PV (1967) Abrasion of rubber. MacLaren, London, p 274
Hutchings IM, Deuchar DWT, Muhr AH (1987) J Mater Sci 22:4071
Arnold JC, Hutchings IM (1989) J Mater Sci 24:833
Li J, Hutchings IM (1990) Wear 135:293
Besztercey G, Karger-Kocsis J, Szaplonczay P (1999) Polym Bull 42:717
Tilly GP, Sage W (1970) Wear 16:447
Williams JH Jr, Lau EK (1974) Wear 29:219
Häger A, Friedrich K, Dzenis YA, Paipetis SA (1995) In: Street K, Whistler BC (eds) Proceedings of ICCM-10, Canada 1995. Woodhead Publishing Ltd, Cambridge, p 155
Miyazaki N, Takeda N (1993) J Compos Mater 27:21
Miyazaki N, Hamao T (1994) J Compos Mater 28:871
Harsha AP, Tewari US, Venkataraman B (2003) Wear 254:693
Harsha AP, Thakre AA (2007) Wear 262:807
Pool KV, Dharan CKH, Finnie I (1986) Wear 107:1
Zahavi J, Schimitt GF Jr (1981) Wear 71:179
Mathias PJ, Wu W, Goretta KC, Routbort JL, Groppi DP, Karasek KR (1989) Wear 135:161
Roy M, Vishwanathan B, Sundararajan G (1994) Wear 171:149
Miyazaki N, Funakura S (1998) J Compos Mater 32:1295
Barkoula N-M, Karger-Kocsis J (2002) Wear 252:80
Tewari US, Harsha AP, Häger AM, Friedrich K (2002) Wear 252:992
Tewari US, Harsha AP, Häger AM, Friedrich K (2003) Compos Sci Technol 63:549
Moss E, Karger-Kocsis J (1999) Adv Compos Lett 8:59
Rattan R, Bijwe J (2006) Wear 262:568
Bull SJ (1997) Mater Sci Forum 246:105
Ruff AW, Ives LK (1975) Wear 35:195
Lamy B (1984) Tribol Int 17:35
Wiederhorn SM, Hockey BJ (1983) J Mater Sci 18:766
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arjula, S., Harsha, A.P. & Ghosh, M.K. Solid-particle erosion behavior of high-performance thermoplastic polymers. J Mater Sci 43, 1757–1768 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2405-0