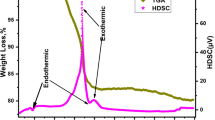
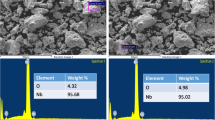
Abstract
Effect of calcination conditions on phase formation and particle size of lead zirconate (PbZrO3) powders synthesized by a solid-state reaction with different vibro-milling times was investigated. A combination of the milling time and calcination conditions was found to have a pronounced effect on both the phase formation and particle size of the calcined PbZrO3 powders. The calcination temperature for the formation of single-phase perovskite lead zirconate was lower when longer milling times were applied. The optimal combination of the milling time and calcination condition for the production of the smallest nanosized (∼28 nm) high purity PbZrO3 powders is 35 h and 750 °C for 4 h with heating/cooling rates of 30 °C/min, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe B, Cook WR, Jaffe H (1971) Piezoelectric ceramics Academic Press, New York
Moulson AJ, Herbert JM (2003) Electroceramics, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Haertling GH (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:797
Rao YS, Sunandana CS (1992) J Mater Sci Lett 11:595
Ibrahim DM, Hennicke HW (1981) Trans J Br Ceram Soc 80:18
Oren EE, Taspinar E, Tas AC (1997) J Am Ceram Soc 80:2714
Rujiwatra A, Tapala S, Luachan S, Khamman O, Ananta S (2006) Mater Lett 60:2893
Lanagan MT, Kim JH, Jang S, Newnham RE (1988) J Am Ceram Soc 71:311
Lee SE, Xue JM, Wan DM, Wang J (1999) Acta Mater 47:2633
Xue JM, Wan DM, Lee SE, Wang J (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:1687
Ngamjarurojana A, Khamman O, Yimnirun R, Ananta S (2006) Mater Lett 60:2867
Wongmaneerung R, Yimnirun R, Ananta S (2006) Mater Lett 60:1447
Chaisan W, Khamman O, Yimnirun R, Ananta S J Mater Sci (to be published)
Ananta S, Thomas NW (1999) J Eur Ceram Soc 19:155
Klug H, Alexander L (1974) X-Ray diffraction procedures for polycrystalline and amorphous materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Puchmark C, Rujijanagul G, Jiansirisomboon S, Tunkasiri T (2004) Ferroelectric Lett 31:1
Powder Diffraction File No. 35–0739. International Centre for Diffraction Data, Newtown Square, PA, 2000
Wongmaneerung R, Yimnirun R, Ananta S (2006) Mater Lett 60:2666
Revesz A, Ungar T, Borbely A, Lendvai J (1996) Nanostruct Mater 7:779
Reed JS (1995) Principles of ceramic processing, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Chattopadhyay S, Ayyub P, Palkar VR, Multani M (1995) Phys Rev B 52:13177
Powder Diffraction File No. 77-1971. International Centre for Diffraction Data, Newtown Square, PA, 2000
Chattopadhyay S, Ayyub P, Palkar VR, Gurjar AV, Wankar RM, Multani M (1997) J Phys: Condens Matter 9:8135
Chattopadhyay S (1997) NanoStructured Mater 9:551
Leonard MR, Safari A (1996) IEEE ISAF 2:1003
Uchino K, Sadanaga E, Hirose T (1989) J Am Ceram Soc 72:1555
Begg BD, Vance ER, Nowotny J (1994) J Am Ceram Soc 77:3186
Saegusa K, Rhine WE, Bowen HK (1993) J Am Ceram Soc 76:1505
Li X, Shih WH (1997) J Am Ceram Soc 80:2844
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC), NSTDA, Ministry of Science and Technology, the Thailand Research Fund (TRF), the Commission on Higher Education (CHE), Faculty of Science, and the Graduate School of Chiang Mai University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khamman, O., Sarakonsri, T., Rujiwatra, A. et al. Effects of milling time and calcination condition on phase formation and particle size of lead zirconate nanopowders prepared by vibro-milling. J Mater Sci 42, 8438–8446 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1776-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1776-6