Abstract
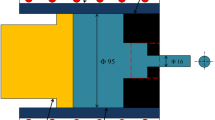
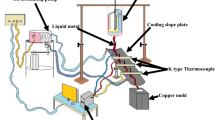
The effects of melt temperature and mold preheating temperature on the fluidity of Ca containing AZ31 alloys were evaluated under various casting conditions. The flow lengths of AZ31-xCa alloy melt increased with increasing the melt temperature due to lower viscosity and longer time to fill the mold cavity. The increment of the flow lengths of AZ31-xCa alloy melt with increasing the mold preheating temperature was not large due to large diameter of circular cross section of mold cavity. The fluidity of AZ31-xCa alloy melts was affected more forcefully by melt temperature than by mold preheating temperature under casting conditions used in this study. Also, the flow lengths of AZ31-xCa alloy melt were affected by grain size of primary solid particles solidified during filling mold cavity and surface oxide film due to addition of Ca.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. CASHION and N. RICKETTS, in Magnesium Technology 2000, Nashville, March 2000, edited by H. I. Kaplan, J. N. Hryn and B. B. Clow (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000) p. 77.
N. RICKETTS and S. CASHION, in Magnesium Technology 2001, New Orleans, February 2001, edited by J. Hryn (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2001) p. 31.
M. SAKAMOTO, S. AKIYAMA, T. HAGIO and K. OGI, J. Jpn. Foundry Eng. Soc. 69 (1997) 227.
S. Y. CHANG and J. C. CHOI, Metals and Materials Int. 4 (1998) 165.
M. H. KIM, W. W. PARK, B. S. YOU, Y. B. HUANG and W. C. KIM, Mater Sci Forum 419–422 (2003) 575.
B. S. YOU, M. H. KIM, W. W. PARK and I. S. CHUNG, ibid. 419–422 (2003) 581.
B. H. CHOI, B. S. YOU, W. W. PARK, Y. B. HUANG and I. M. PARK, Metals and Materials Int. 9 (2003) 395.
Y. B. HUANG, I. S. CHUNG, B. S. YOU, W. W. PARK and B. H. CHOI, ibid., 10 (2004) 7.
B. H. CHOI, B. S. YOU, W. W. PARK and I. M. PARK, J. Kor. Met. Mater. 42 (2004) 674.
B. H. CHOI, B. S. YOU, C. D. YIM, W. W. PARK and I. M. PARK, Mater Sci Forum 475–479 (2005) 2477.
M. C. FLEMINGS, in “Solidification Processing” (McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, 1974) p. 220.
S. L. SIN and D. DUBE, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 386 (2004) 34.
G. H. GEIGER and D. R. POIRIER, in “Transport Phenomena in Metallurgy” (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company; Reading, MA, 1973) p. 15.
Y. C. LEE, K. DAHLE and D. H. STJOHN, Metall. Mater. Trans.A 31A (2000) 2895.
Y.-D. KWON, Z.-H. LEE and K.-H. KIM, J. Kor. Foundrymen’s Soc. 22 (2002) 109.
Idem, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 360 (2003) 372.
W. QUDONG, L. YIZHEN, Z. XIAOQIN, D. WENJIANG, Z. YANPING, L. QINGHUA and L. JIE, ibid 271 (1999) 109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yim, C.D., You, B.S., Jang, R.S. et al. Effects of melt temperature and mold preheating temperature on the fluidity of Ca containing AZ31 alloys. J Mater Sci 41, 2347–2350 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-4498-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-4498-2