Abstract
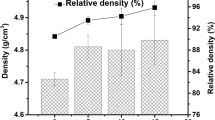
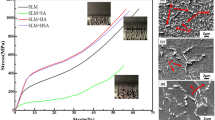
This study examines the effect of heating mode, sintering temperature, and varying yttria alumina garnet (YAG) addition (5 and 10 wt%) on the densification and properties of ferritic (434L) stainless steel. The straight 434L stainless steel and 434L–YAG composites were sintered in a conventional and a 2.45 GHz microwave furnace. The composites were sintered to solid-state as well as supersolidus sintering temperature at 1200 and 1400 °C, respectively. Both 434L and 434L–YAG compacts coupled with microwaves and underwent rapid heating (∼45 °C/min). This resulted in about 85% reduction in the processing time. For all compositions microwave sintering results in greater densification. As compared to conventional sintering, microwave sintered compacts exhibit a more refined microstructure, thereby, resulting in higher bulk hardness. The mechanical properties and sliding wear resistance of 434L stainless steel is shown to be sensitive both to the sintering condition as well as YAG addition and has been correlated to the effect of heating mode on the pore morphology.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis JR (1994) In: Stainless steels. ASM International, Materials Park, OH, USA
Dyke DL, Ambs HD (1983) In: Klar E (ed) American society for metals, powder metallurgy applications, advantages and limitations. ASM, Materials Park, OH, USA, p 123
German RM (ed) (1998) Powder metallurgy of iron and steel. John Wiley, New York, NY, USA
German RM (ed) (1996) Sintering theory and practice. John Wiley, New York, NY, USA
Madan DS (1991) Int J Powder Metall 27:339
Lei G, German RM, Nayar HS (1983) Powder Metall Int 15:70
Chatterjee SK, Warwick ME (1985) In: Modern developments in powder metallurgy, vol 16 MPIF, Princeton, NJ, USA, p 277
Wang W, Su Y (1986) Powder Metall 29:177
Molinari A, Strafelini G, Kazior J, Pieczonka T (1998) Int J Powder Metall 34:21
Reinshagen JH, Mason RP (1994) Int J Powder Metall 30:165
Cambal L, Lund JA (1972) Int J Powder Metall 8:131
German RM (1997) Metall Mater Trans A 28:1553
German RM (1997) Int J Powder Metall 33:49
Pagounis E, Lindroos VK (1998) Mater Sci Eng A 246:221
Velasco F, Anton N, Torralba JM, Ruiz-Prieto JM (1997) Mater Sci Tech 13:847
Patankar SN, Tan MJ (2000) Powder Metall 43:350
Datta P, Upadhyaya GS (2003) Sci Sintering 32:109
Vardavoulias M, Jeandin M, Velasco F, Torralba JM (1996) Tribol Int 29:499
Mukherjee SK, Upadhyaya GS (1983) Int J Powder Metall Powder Tech 19:289
Shankar J, Upadhyaya A, Balasubramaniam R (2004) Corr Sci 46:487
Jain J, Kar AM, Upadhyaya A (2004) Mater Lett 58:2037
Rao KJ, Ramesh PD (1995) Bull Mater Sci 18:447
Clark DE, Sutton WH (1996) Ann Rev Mater Sci 26:299
Pozar DM (ed) (2001) Microwave engineering, 2nd edn. John Wiley, Toronto, Canada
Gerdes T, Willert-Porada M, Rödiger K, Dreyer K (1996) Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 430:175
Roy R, Agrawal DK, Cheng JP, Gedevanishvili S (1999) Nature 399:668
Willert-Porada M, Park HS (2001) In: Clark DE, Binner JGP, Lewis DA (eds) Microwaves: theory and application in materials processing IV. The American Ceramic Society, Westerville, OH, USA, p 459
Anklekar RM, Agrawal DK, Roy R (2001) Powder Metall 44:355
Sethi G, Upadhyaya A, Agrawal D (2003) Sci Sintering 35:49
Willert-Porada M (1997) In: Clark DE, Sutton WH, Lewis DA (eds) Microwaves: theory and application in materials processing IV. The American Ceramic Society, Westerville, OH, USA, p 153
Standard Test Methods For Metal Powders and Powder Metallurgy Products (1991) Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, USA
Pert E, Carmel Y, Birnboim A, Olorunyolemi T, Gershon D, Calame J, Lloyd IK, Wilson Jr OC (2001) J Am Ceram Soc 84:1981
Lide DR (ed) (1998) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, 79th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Nayer A (ed) (1997) The metals data book. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, USA
Howard RT, Cohen M (1947) Trans AIME 172:413
Mishra P, Sethi G, Upadhyaya A (2006) Metall Mater Trans B 37B:839
Kang SJL (ed) (2005) Sintering: densification, grain growth & microstructure. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, London, UK
Sahay SS, Krishan K (2004) Physica B 348:310
Sahay SS, Krishnan K (2005) Thermochim Acta 430:23
Peelamedu RD, Roy R, Agrawal D (2001) Mater Res Bull 36:2723
Anklekar RM, Bauer K, Agrawal DK, Roy R (2005) Powder Metall 48:39
Iglesias FAC, Roman JMR, Cambronero LEG, Prieto JMR, Lopez ERM, Lopez FA (1998) In: Proc of PM World Congress: high alloy steel, vol. 3. EPMA, Shrewsbury, UK, p 471
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Department of Science & Technology (DST) and Ministry of Human Resource and Development (MHRD), India. The microwave sintering experiments were conducted at the Microwave Research Center at Penn Sate University through partial financial support from DOE (grant no. DE-FC26-02NT41662). Assistance provided by Vintee Singh in experiments is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S.S., Upadhyaya, A. & Agrawal, D. Effect of heating mode and temperature on sintering of YAG dispersed 434L ferritic stainless steel. J Mater Sci 42, 966–978 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0006-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0006-y