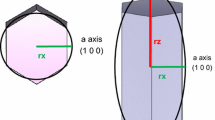
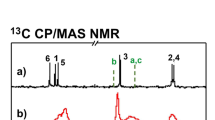
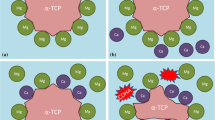
Abstract
New ceramic materials with the ability to set like cement, after mixing a powder phase made of one and/or several of these new reactants and a liquid phase, have been obtained within the ternary system “CaO-P2O5-FeO”. These new reactants have magnetic properties, i.e. cement made from them maintains its magnetic property during the whole setting and hardening. These new materials can be of use, for example, in dental applications, in the treatment of certain types of bone cancer and, in general, in the fields of Biomaterials and Bone Tissue Engineering. In this article, we report on the effect of iron-modified α -tricalcium phosphate, which is the main reactant of commercial calcium phosphate bone cements, on their new setting and hardening properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. E. BROWN and L. C. CHOW, Dental Restorative Cement Pastes, US Patent No.: 4,518,430. Priority Data, May 21, (1985).
Idem., in A New Calcium Phosphate Water-Setting Cement, edited by P. W. Brown, “Cements Research Progress” (American Ceramic Society, Westerville, Ohio, 1986), p. 351.
J. LEMAITRE, A. MIRTCHI and A. MORTIER, Sil. Ind. Ceram. Sci. Tech. 52 (1987) 141.
L. C. CHOW, S. TAKAGI, P. D. CONSTANTINO and C. D. FRIEDMAN, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 179 (1991) 3.
L. C. CHOW, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan (International Edition) 99 (1992) 927.
T. SUGAMA and M. ALLAN, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75(8) (1992) 2076.
J. LEMAITRE, Innov. Tech. Biol. Med. 16(1) (1995) 109.
E. FERNÁndez, F. J. Gil, S. M. Best, M. P. Ginebra, F. C. M. Driessens and J. A. PLANELL, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 10 (1999) 169.
Idem, ibid. 10 (1999) 177.
M. NILSSON, E. FERNÁndez, S. Sarda, L. Lidgren and J. A. PLANELL, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 61(4) (2002) 600.
E. FERNÁndez, F. J. Gil, S. M. Best, M. P. Ginebra, F. C. M. Driessens and J. A. PLANELL, ibid. 41 (1998) 560.
C. KNABE, F. C. M. DRIESSENS, J. A. PLANELL, R. GILDENHAAR, G. BERGER, D. REIF, R. FITZNER, R. J. RADLANSKI and U. GROSS, ibid. 52 (2000) 498.
K. OHURA, M. BOHNER, P. HARDOUIN, J. LEMAITRE, G. PASQUIER, B. FLAUTRE and M. C. BLARY, ibid. 30 (1996) 193.
R. O. C. OREFFO, F. C. M. DRIESSENS, J. A. PLANELL and J. T. TRIFFITT, Biomaterials 19 (1998) 1845.
F. C. M. DRIESSENS, J. A. PLANELL, M. G. BOLTONG, I. KHAIROUN and M. P. GINEBRA, Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. 212H (1998) 427.
E. CHARRIÉRE, J. LEMAITRE and P. H. ZYSSET, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 809.
S. SARDA, M. NILSSON, M. BALCELLS and E. FERNÁndez, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 65A (2003) 215.
J. E. BARRALET, L. GROVER, T. GAUNT, A. J. WRIGHT and I. R. GIBSON, Biomaterials 23 (2002) 3063.
M. BOHNER, Key. Eng. Mater. 192–195 (2001) 765.
Idem., Eur. Spine. J. 10 (2001) S114.
I. KHAIROUN, F. C. M. DRIESSENS, M. G. BOLTONG, J. A. PLANELL and R. WENZ, Biomaterials 20 (1999) 393.
M. P. GINEBRA, F. C. M. DRIESSENS and J. A. PLANELL, ibid. 25 (2004) 3453.
Standard Test Method: ASTM C266-89. Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement Paste by Gillmore Needles, in “Annual Book of ASTM Standards,” Cement, lime, Gypsum (Philadelphia, ASTM, PA, 1993) Vol. 04.01, p. 444.
M. P. GINEBRA, E. FERNÁndez, E. A. P. De Maeyer, R. M. H. Verbeeck, M. G. Boltong, J. GINEBRA, F. C. M. DRIESSENS and J. A. PLANELL, J. Dent. Res. 76(4) (1997) 905.
E. FERNÁndez, M. P. Ginebra, M. G. Boltong, F. C. M.Driessens, J. Ginebra, E. A. P. De Maeyer, R. M. H. Verbeeck and J. A. PLANELL J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 32 (1996) 367.
F. C. M. DRIESSENS, in “Bioceramics of Calcium Phosphate,” edited by K. De Groot (CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Florida, 1993) p. 1.
H. HOSHINO and M. IWASE, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 27B (1996) 595.
E. FERNÁndez Fosfatos de calcio modificados con hierro. Spanish Patent No. P200302342. Universidad Politécnica de Cataluña. Priority Date: 01/10/2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, E., Vlad, M.D., Hamcerencu, M. et al. Effect of iron on the setting properties of α-TCP bone cements. J Mater Sci 40, 3677–3682 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0614-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0614-y