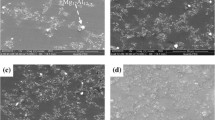
Abstract
In the present study, hybrid magnesium based composites reinforced with an equivalent of 5 vol.% of micron and nano-sized Al2O3 particulates were synthesized using powder metallurgy technique incorporating an innovative microwave assisted rapid sintering technique. Microstructural characterization revealed near equiaxed grain morphology and the presence of minimal porosity in all the samples. Mechanical characterization studies revealed that the coupled addition of micron and nano-sized particulate reinforcements in magnesium matrix leads to a significant increase in hardness, elastic modulus, 0.2% yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and a decrease in ductility when compared to pure magnesium. Tensile testing results further revealed an increase in elastic modulus and ductility with no apparent change in the 0.2% yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of the hybrid composites upon the addition of nano-sized alumina particulates from 0.5 to 0.75 volume percent. With an increase in nano-sized alumina particulates from 0.75 to 1%, the overall mechanical properties of the hybrid composites were enhanced with an increase being observed in the elastic modulus, 0.2% yield strength and ductility of the composites. An attempt is made in this study to investigate the feasibility of the processing methodology and to study the effects of the addition of particulate reinforcements of different sizes on the microstructure, physical and mechanical properties of magnesium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. LLYOD, Int. Mater. Rev. 39 (1994) 1.
A. LUO, Metal. Mater. A 26 (1995) 2445.
M. GUPTA, M. O. LAI and D. SARAVANARANGANTHAN, J. Mater. Sci. 35 (2000) 2155.
B. L. MORDIKE and K. U. KAINER, in “Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications” (Werkstoff-Insformations gesellschaft, Frankfu, Germany, 1998).
R. OAKLEY, R. F. COCHRANE and R. STEVENS, Key. Eng. Mater. 104 (1995) 387.
I. A. IBRAHIM, F. A. MOHAMED and E. J. LAVERNIA, J. Mat. Sci. 26 (1991) 1137.
R. M. GERMAN, in “Sintering Theory and Practice” (John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, 1996) p. 2, 404.
R. M. GERMAN, in “Powder Metallurgy Science” (Metal Powder Industries Federation, USA, 1984).
J. P. SCHAFFER, A. SAXENA, S. D. ANTOLOVICH, T. H. SANDERS J. R. and S. B. WARNER, in “The Science and Design of Engineering Materials,” 2nd ed. (McGraw Hill, 1999).
R. ROY, D. AGRAWAL, J. CHENG and S. GEDEVANISHVILI, Nature 399 (1999) 668.
D. AGRAWAL, Mater. World 7 (1999) 672.
R. ROY, J. CHENG, and D. K. AGRAWAL, US Patent No. 6,365,885 B1, April 2, 2002.
S. F. HASSAN and M. GUPTA, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct.in press (2004).
S. F. HASSAN and M. GUPTA, J. Alloy. Compd. 345 (2002) 246.
S. F. HASSAN and M. GUPTA, J. Alloy. Compd. 335 (2002) L10.
S. F. HASSAN and M. GUPTA, Mat. Res. Bull. 37 (2002) 377.
J. SCHRÖDER and K. U. KAINER, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct 135 (1991) 33.
X. N. ZHANG and R. J. WU, Key. Eng. Mater. 249 (2003) 217.
S. K. THAKUR, B. K. DHINDAW, N. HORT and K. U. KAINER, Mater. Sci. Forum. 426–432 (2003) 2027.
M. GUPTA, C. LANE and E. J. LAVERNIA, Scr. Metall. Mater. 26 (1992) 825.
M. R. KRISHNADEV, R. ANGERS, C. G. KRISHNADAS NAIR and G. J. HUARD, J. Met. 45 (1993) 52.
A. BUCH, in “Pure Metals Properties” (ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, USA, 1999) p. 20.
Website: http://www.ceramics.nist.gov/srd/summary/scdaos.htm, last accessed Oct 2004.
A. L. GEIGER and M. JACKSON, Adv. Mat. Proc. 136(7) (1989) 23.
S. F. HASSAN and M. GUPTA, Mat. Sci. Tech. in press (2004).
M. GUPTA and M. K. SURAPPA, Key. Eng. Mat. 104–107 (1995) 259.
A. R. BOCCACINI, G. ONDRACEK, P. MAZILU and D. WINDELBEG, J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 4 (1993) 11 9.
G. E. FOUGERE, L. RIESTER, M. FERBER, J. R. WEERTMAN and R. W. SIEGEL, Mat. Sci. Eng. A—Struct 204 (1995) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, W.L.E., Karthik, S. & Gupta, M. Development of hybrid Mg/Al2O3 composites with improved properties using microwave assisted rapid sintering route. J Mater Sci 40, 3395–3402 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0419-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0419-z