Abstract
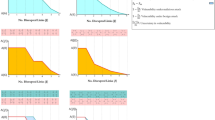
The study of the security and stability of complex networks plays a central role in reducing the risk and consequences of attacks or disfunctions of any type. The concept of vulnerability helps to measure the response of complex networks subjected to attacks on vertices and edges and it allows to spot the critical component of a network in order to improve its security. We introduce an accurate and computable definition of network vulnerability which is directly connected with its topology and we analyze its basic properties. We discuss the relationship of the vulnerability with other parameters of the network and we illustrate this with some examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, R. and Barabási, A. L.: Statistical mechanics of complex networks, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 (2002), 47–97.
Barabási, A. L. and Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks, Science 286 (1999), 509–512.
Bar-Yam, Y.: Dynamics of Complex System, Addison-Wesley, 1997.
Cohen, R., Erez, K., Ben-Avbraham, D. and Havril S.: Resilience of the Internet to random breakdowns, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(21) (2000), 4626–4628.
Cohen, R., Erez, D., Ben-Avbraham, D. and Havril S.: Breakdown of the Internet under international attacks, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86(16) (2001) 3682–3685.
Crucitti, P., Latora, M., Marchiori, M. and Rapisarda, A.: Efficiency of scale-free networks: Error and attack tolerance, Physica, A 320 (2003), 622–642.
Dekker, A. H. and Colbert, B. D.: Network robustness and graph topology, in: Proc. Twenty-Seventh Australasian Computer Science Conference (ACSC2004), Vladimir Estivill-Castro, Ed., ISBN 1-920682-05-8, Dunedin, New Zealand. CRPIT, 26. Estivill-Castro, V., Ed. ACS, (2004), pp. 359–368.
Holme, P., Kim, B. J., Yoon, C. N. and Han, S. H.: Attack vulnerability of complex networks, Phys. Rev., E 65 (2002), art. no. 056109.
Jeong, H., Mason, S., Barabási A. L. and Oltvai, Z. N.: Lethality and centrality in protein networks, Nature 411 (2001), 41–42.
Jeong, H., Tombor, T., Albert, R., Oltvai, Z. N. and Barabási, A. L.: The large-scale organization of metabolic networks, Nature 407 (2000), 651–654.
Latora, V. and Marchiori, M.: Efficient behavior of small-world networks, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(19) (2001), 1-198701-4.
Latora, V. and Marchiori, M.: Economic small-world behavior in weighted networks, Eur. Phys. J., B. 32 (2003), 249–263.
Latora, V. and Marchiori, M.: How the science of complex networks can help developing strategies against terrorism, Chaos, Solitons Fractals 20 (2004) 69–75.
Newman, M. E. J.: The structure and function of complex networks, SIAM Rev. 45 (2003), 167–256.
Strogatz, S. H.: Exploring complex networks, Nature 410 (2001), 268–276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Criado, R., Flores, J., Hernández-Bermejo, B. et al. Effective measurement of network vulnerability under random and intentional attacks. J Math Model Algor 4, 307–316 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10852-005-9006-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10852-005-9006-1