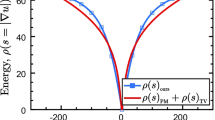
Abstract
Speckle reduction is a prerequisite for many image processing tasks in synthetic aperture radar images, as well as all coherent images. In recent years, predominant state-of-the-art approaches for despeckling are usually based on nonlocal methods which mainly concentrate on achieving utmost image restoration quality, with relatively low computational efficiency. Therefore, in this study we aim to propose an efficient despeckling model with both high computational efficiency and high recovery quality. To this end, we exploit a newly developed trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion (TNRD) framework which has proven a simple and effective model for various image restoration problems. In the original TNRD applications, the diffusion network is usually derived based on the direct gradient descent scheme. However, this approach will encounter some problem for the task of multiplicative noise reduction exploited in this study. To solve this problem, we employed a new architecture derived from the proximal gradient descent method. Taking into account the speckle noise statistics, the diffusion process for the despeckling task is derived. We then retrain all the model parameters in the presence of speckle noise. Finally, optimized nonlinear diffusion filtering models are obtained, which are specialized for despeckling with various noise levels. Experimental results substantiate that the trained filtering models provide comparable or even better results than state-of-the-art nonlocal approaches. Meanwhile, our proposed model merely contains convolution of linear filters with an image, which offers high-level parallelism on GPUs. As a consequence, for images of size \(512 \times 512\), our GPU implementation takes less than 0.1 s to produce state-of-the-art despeckling performance.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achim, A., Kuruoğlu, E.E., Zerubia, J.: SAR image filtering based on the heavy-tailed rayleigh model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(9), 2686–2693 (2006)
Achim, A., Tsakalides, P., Bezerianos, A.: SAR image denoising via Bayesian wavelet shrinkage based on heavy-tailed modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 41(8), 1773–1784 (2003)
Aja-Fernández, S., Alberola-López, C.: On the estimation of the coefficient of variation for anisotropic diffusion speckle filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(9), 2694–2701 (2006)
Alparone, L., Baronti, S., Garzelli, A., Nencini, F.: Landsat ETM+ and SAR image fusion based on generalized intensity modulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 42(12), 2832–2839 (2004)
Argenti, F., Bianchi, T., Lapini, A., Alparone, L.: Fast map despeckling based on Laplacian–Gaussian modeling of wavelet coefficients. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 9(1), 13–17 (2012)
Argenti, F., Lapini, A., Bianchi, T., Alparone, L.: A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 1(3), 6–35 (2013)
Aubert, G., Aujol, J.-F.: A variational approach to removing multiplicative noise. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 68(4), 925–946 (2008)
Bianchi, T., Argenti, F., Alparone, L.: Segmentation-based map despeckling of SAR images in the undecimated wavelet domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46(9), 2728–2742 (2008)
Bredies, K., Kunisch, K., Pock, T.: Total generalized variation. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3(3), 492–526 (2010)
Buades, A., Coll, B., Morel, J.-M.: A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4(2), 490–530 (2005)
Chen, L., Liu, X., Wang, X., Zhu, P.: Multiplicative noise removal via nonlocal similarity-based sparse representation. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 54(2), 199–215 (2016)
Chen, Y., Feng, W., Ranftl, R., Qiao, H., Pock, T.: A higher-order MRF based variational model for multiplicative noise reduction. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(11), 1370–1374 (2014)
Chen, Y., Pock, T.: Trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion: a flexible framework for fast and effective image restoration. IEEE TPAMI (2016). http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7527621/
Chen, Y., Yu, W., Pock, T.: On learning optimized reaction diffusion processes for effective image restoration. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015)
Cozzolino, D., Parrilli, S., Scarpa, G., Poggi, G., Verdoliva, L.: Fast adaptive nonlocal SAR despeckling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 11(2), 524–528 (2014)
Csiszár, I.: Why least squares and maximum entropy? An axiomatic approach to inference for linear inverse problems. Ann. Stat. 19(4), 2032–2066 (1991)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007)
Deledalle, C.-A., Denis, L., Tupin, F.: Iterative weighted maximum likelihood denoising with probabilistic patch-based weights. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(12), 2661–2672 (2009)
Deledalle, C.-A., Denis, L., Tupin, F.: How to compare noisy patches? Patch similarity beyond Gaussian noise. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 99(1), 86–102 (2012)
Di Martino, G., Poderico, M., Poggi, G., Riccio, D., Verdoliva, L.: Benchmarking framework for SAR despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(3), 1596–1615 (2014)
Dong, Y., Zeng, T.: A convex variational model for restoring blurred images with multiplicative. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6(3), 1598–1625 (2013)
Durand, S., Fadili, J., Nikolova, M.: Multiplicative noise removal using l1 fidelity on frame coefficients. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 36(3), 201–226 (2010)
Elad, M., Aharon, M.: Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(12), 3736–3745 (2006)
Escande, P., Weiss, P., Zhang, W.: A variational model for multiplicative structured noise removal. J. Math. Imaging Vis. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10851-016-0667-3
Feng, W., Lei, H., Gao, Y.: Speckle reduction via higher order total variation approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(4), 1831–1843 (2014)
Frost, V., Shanmugan, K., Holtzman, J.: A model for radar images and its applications to adaptive digital filtering of multiplicative noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 4(2), 157–166 (1982)
Goodman, J.W.: Statistical properties of laser speckle patterns. In: Laser Speckle and Related Phenomena, pp. 9–75. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1975). http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-662-43205-1_23
Huang, Y.-M., Lu, D.-Y., Zeng, T.: Two-step approach for the restoration of images corrupted by multiplicative noise. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(6), A2856–A2873 (2013)
Huang, Y.-M., Moisan, L., Ng, M.K., Zeng, T.: Multiplicative noise removal via a learned dictionary. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(11), 4534–4543 (2012)
Jin, Z., Yang, X.: A variational model to remove the multiplicative noise in ultrasound images. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 39(1), 62–74 (2011)
Kuan, D.T., Sawchuk, A., Strand, T.C., Chavel, P.: Adaptive restoration of images with speckle. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 35(3), 373–383 (1987)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Lee, J.-S.: Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2, 165–168 (1980)
Lee, J.-S.: Refined filtering of image noise using local statistics. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 15(4), 380–389 (1981)
Liu, D.C., Nocedal, J.: On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Math. Program. 45(1), 503–528 (1989)
Lopes, A., Nezry, E., Touzi, R., Laur, H.: Maximum a posteriori speckle filtering and first order texture models in SAR images. In: Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 1990, pp. 2409–2412 (1990)
Lopes, A., Nezry, E., Touzi, R., Laur, H.: Structure detection and statistical adaptive speckle filtering in SAR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 14(9), 1735–1758 (1993)
Martin, D., Fowlkes, C., Tal, D., Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Computer Vision (2001)
Nesterov, Y.: Introductory Lectures on Convex Optimization, volume 87 of Applied Optimization. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (2004). A basic course
Ochs, P., Chen, Y., Brox, T., Pock, T.: iPiano: inertial proximal algorithm for nonconvex optimization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7(2), 1388–1419 (2014)
Oliver, C., Quegan, S.: Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. SciTech Publishing, Rayleigh (2004)
Parrilli, S., Poderico, M., Angelino, C.V., Verdoliva, L.: A nonlocal SAR image denoising algorithm based on LLMMSE wavelet shrinkage. IEEE Trans. Geosc. Remote Sens. 50(2), 606–616 (2012)
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(7), 629–639 (1990)
Ranjani, J., Thiruvengadam, S.J.: Dual-tree complex wavelet transform based SAR despeckling using interscale dependence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 48(6), 2723–2731 (2010)
Ranjani, J.J., Thiruvengadam, S.: Generalized SAR despeckling based on dtcwt exploiting interscale and intrascale dependences. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 8(3), 552–556 (2011)
Roth, S., Black, M.J.: Fields of experts. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 82(2), 205–229 (2009)
Sattar, F., Floreby, L., Salomonsson, G., Lovstrom, B.: Image enhancement based on a nonlinear multiscale method. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(6), 888–895 (1997)
Steidl, G., Teuber, T.: Removing multiplicative noise by Douglas–Rachford splitting methods. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 36(2), 168–184 (2010)
Teuber, T., Lang, A.: A new similarity measure for nonlocal filtering in the presence of multiplicative noise. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 56(12), 3821–3842 (2012)
Teuber, T., Lang, A.: Nonlocal filters for removing multiplicative noise. Scale Space Var. Methods Comput. Vis. 6667, 50–61 (2012)
Touzi, R.: A review of speckle filtering in the context of estimation theory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 40(11), 2392–2404 (2002)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Yu, Y., Acton, S.T.: Speckle reducing anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 11(11), 1260–1270 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, W., Chen, Y. Speckle Reduction with Trained Nonlinear Diffusion Filtering. J Math Imaging Vis 58, 162–178 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-016-0697-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-016-0697-x