Abstract
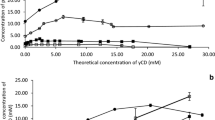
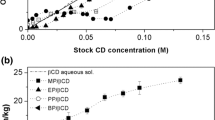
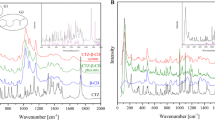
Due to their antimicrobial activity, parabens (i.e. alkyl esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid) are widely used as preservatives in several industries (pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic). Although being extremely effective, their usage is hampered by their low aqueous solubility. Several formulation strategies can be applied to enhance their solubility, one of which is formation of water-soluble cyclodextrin (CD) complexes. Formation of inclusion complexes has been proved to be a good approach to increase solubility of lipophilic drugs and other active ingredients. Some research has been done in this field. However, a complete and comprehensive study on how the alkyl chain length of parabens influences the complex formation, aggregation and formation of insoluble complexes is still lacking. Phase-solubility studies showed that all the very water-soluble hydroxypropylated CDs form linear (AL) type phase-solubility profiles with all tested parabens. The poorly soluble βCD did also form AL-type profiles with methyl and ethyl paraben while the βCD complexes of propyl and butyl paraben have limited solubility in water and, thus displayed B-type profiles. The paraben complexes of αCD and γCD all had limited solubility in water and, thus, displayed B-type phase-solubility profiles. Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy, Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray powder diffraction were applied to elucidate the nature of the solid phases from the phase-solubility studies. They consistently showed the presence of solid pure paraben over the CD concentration range studied when AL-type profiles were observed, and precipitation of poorly soluble paraben/CD complexes when B-type were observed (i.e. during and after the B-type plateau region). These studies demonstrate that the composition of solid phases is related to the type of phase-solubility profile. It was also shown that in aqueous CD solutions, paraben solubilization increase with increasing side chain length (i.e. methyl < ethyl < propyl < butyl), as well as, with increasing size of the CD cavity (i.e. αCD < βCD < γCD). This statement is valid for linear region of phase-solubility diagrams (i.e. A- and B-type).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giordano, F., Bettini, R., Donini, C., Gazzaniga, A., Caira, M.R., Zhang, G.G.Z., Grant, D.J.W.: Physical properties of parabens and their mixtures: solubility in water, thermal behavior, and crystal structures. J. Pharm. Sci. 88(11), 1210–1216 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1021/js9900452
Ma, M., Lee, T., Kwong, E.: Interaction of methylparaben preservative with selected sugars and sugar alcohols. J. Pharm. Sci. 91(7), 1715–1723 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.10167
Jude Jenita, M., Thulasidhasan, J., Rajendiran, N.: Encapsulation of alkylparabens with natural and modified α- and β-cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 79(3), 365–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-013-0360-8
Stappaerts, J., Do Thi, T., Dominguez-Vega, E., Somsen, G.W., Van den Mooter, G., Augustijns, P.: The impact of guest compounds on cyclodextrin aggregation behavior: a series of structurally related parabens. Int. J. Pharm. 529(1), 442–450 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.026
Saokham, P., Do, T.T., Van den Mooter, G., Loftsson, T.: Inclusion complexes of p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters and γ-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 90(1), 111–122 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-017-0776-7
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59(7), 645–666 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012
Crini, G.: Review: a history of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 114(21), 10940–10975 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500081p
Loftsson, T., Duchene, D.: Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 329(1–2), 1–11 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.10.044
Loftsson, T., Masson, M., Brewster, M.E.: Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 93(5), 1091–1099 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20047
Sá Couto, A.R., Salústio, P., Cabral-Marques, H.: Cyclodextrins. In: Kishan Gopal Ramawat, J.-M.M. (ed.) Polysaccharides, Bioactivity and Biotechnology, vol. 1. pp. 247–288. Springer International Publishing, Berlin (2015)
Schonbeck, C., Madsen, T.L., Peters, G.H., Holm, R., Loftsson, T.: Soluble 1:1 complexes and insoluble 3:2 complexes—understanding the phase-solubility diagram of hydrocortisone and gamma-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 531(2), 504–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.024
Cohen, J., Lach, J.L.: Interaction of pharmaceuticals with Schardinger dextrins. I. Interaction with hydroxybenzoic acids and p-hydroxybenzoates. J. Pharm. Sci. 52, 132–136 (1963)
Caira, M.R., de Vries, E.J.C., Nassimbeni, L.R.: Cyclodextrin inclusion of p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 73(2), 647–651 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1025446617121
Chan, L.W., Kurup, T.R.R., Muthaiah, A., Thenmozhiyal, J.C.: Interaction of p-hydroxybenzoic esters with beta-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 195(1), 71–79 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(99)00393-2
Lach, J.L., Cohen, J.: Interaction of pharmaceuticals with schardinger dextrins II: interaction with selected compounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 52(2), 137–142 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600520207
de Vries, E.J.C., Caira, M.R., Bogdan, M., Farcas, S.I., Bogdan, D.: Inclusion of parabens in β-cyclodextrin: a solution NMR and X-ray structural investigation. Supramol. Sci. 21(5), 358–366 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/10610270801956202
Holm, R., Olesen, N.E., Alexandersen, S.D., Dahlgaard, B.N., Westh, P., Mu, H.: Thermodynamic investigation of the interaction between cyclodextrins and preservatives—application and verification in a mathematical model to determine the needed preservative surplus in aqueous cyclodextrin formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 87, 22–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2015.09.011
Lehner, S.J., Müller, B.W., Seydel, J.K.: Interactions between p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and their antimicrobial effect against Candida albicans. Int. J. Pharm. 93(1), 201–208 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(93)90178-I
Malaekeh-Nikouei, B., Bazzaz, F., Soheili, B.S., Mohammadian, V.: K.: Problems in ophthalmic drug delivery: evaluation of the interaction between preservatives and cyclodextrins. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 6(5), e6333 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.6333
Matsuda, H., Ito, K., Sato, Y., Yoshizawa, D., Tanaka, M., Taki, A., Sumiyoshi, H., Utsuki, T., Hirayama, F., Uekama, K.: Inclusion complexation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters with 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrins. On changes in solubility and antimicrobial activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 41(8), 1448–1452 (1993)
Loftsson, T., Stefánsdóttir, Ó, Friôriksdóttir, H., Guômundsson, Ö: Interactions between preservatives and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 18(13), 1477–1484 (1992). https://doi.org/10.3109/03639049209040853
Tanaka, M., Iwata, Y., Kouzuki, Y., Taniguchi, K., Matsuda, H., Arima, H., Tsuchiya, S.: Effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on percutaneous absorption of methyl paraben. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47(11), 897–900 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1995.tb03267.x
Saokham, P., Sa Couto, A., Ryzhakov, A., Loftsson, T.: The self-assemble of natural cyclodextrins in aqueous solutions: application of miniature permeation studies for critical aggregation concentration (cac) determinations. Int. J. Pharm. 505(1–2), 187–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.03.049
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Loftsson, T., Hreinsdóttir, D., Másson, M.: Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 302(1), 18–28 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.05.042
Coleman, A.W., Nicolis, I., Keller, N., Dalbiez, J.P.: Aggregation of cyclodextrins: an explanation of the abnormal solubility ofβ-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 13(2), 139–143 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01053637
Wu, A., Shen, X., He, Y.: Investigation on gamma-cyclodextrin nanotube induced by N,N′-diphenylbenzidine molecule. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 297(2), 525–533 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.11.014
McDonald, C., Palmer, L., Boddy, M.: The solubilities of esters of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, determined separately and together, in aqueous solutions of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 22(9–10), 1025–1029 (1996). https://doi.org/10.3109/03639049609065936
Narayanan, G., Boy, R., Gupta, B.S., Tonelli, A.E.: Analytical techniques for characterizing cyclodextrins and their inclusion complexes with large and small molecular weight guest molecules. Polym. Test. 62, 402–439 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.07.023
Dibbern, H.W.: UV- and IR spectra of some important drugs: classified in therapeutic groups including tables of characteristic UV absorption data and examples for the UV spectrocognostic identification of drugs. vol. 2. Editio Cantor, (1978)
Muankaew, C., Jansook, P., Sigurđsson, H.H., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrin-based telmisartan ophthalmic suspension: formulation development for water-insoluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 507(1), 21–31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.04.071
Jansook, P., Ritthidej, G.C., Ueda, H., Stefansson, E., Loftsson, T.: yCD/HPyCD mixtures as solubilizer: solid-state characterization and sample dexamethasone eye drop suspension. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 13(3), 336–350 (2010)
Cirri, M., Maestrelli, F., Furlanetto, S., Mura, P.: Solid-state characterization of glyburide-cyclodextrin co-ground products. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 77(2), 413–422 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000038982.40315.8f
Acknowledgements
The financial support received from the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT) (Grant No. 135040) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couto, A.R.S., Aguiar, S., Ryzhakov, A. et al. Interaction of native cyclodextrins and their hydroxypropylated derivatives with parabens in aqueous solutions. Part 1: evaluation of inclusion complexes. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 93, 309–321 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-00876-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-00876-5