Abstract
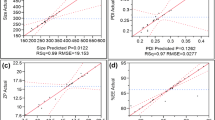
The purpose of the present work was to design and investigate the potential of novel hydroxylpropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) and chitosan nanocarriers (NCs) for effective delivery of model, poorly water soluble drug simvastatin. The prepared system was characterized for particle size, particle size distribution (PDI), zeta potential, differential scanning calorimetery, x-ray diffraction, encapsulation efficiency and drug release studies. The results revealed that among the selected ratios of tripolyphosphate/chitosan, ratio 1:4 and 1:5 proved to be optimum in terms of particle size, particle distribution and drug release profile. The average size of nanoparticles increased from 516 to 617 and 464 to 562 nm for ratio 1:4 and 1:5 with increase in drug/HP-β-CD amount. To assess interactions and whether the simvastatin was incorporated in the NCs in its crystalline or amorphous form DSC and XRD were performed. These results suggest that the encapsulation process produces a marked decrease in crystallinity of simvastatin and/or confers to a nearly amorphous state of drug in NCs. Results reveled that with increase in the amount of HP-β-CD/drug the final loading of the NCs increased due to increased solubilization of simvastatin in the presence of HP-β-CD. The in vitro release profile of prepared NCs showed initial fast release (burst effect) followed by a delayed release pattern. In conclusion, these nanocarriers constitute a novel and efficient system for encapsulation and oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radtke, M.: Nanopure TM: pure drug nanoparticles for the formulation of poorly soluble drugs. New Drugs 3, 62–68 (2001)
Muller, R.H., Bohm, B.H.L.: Nanosuspensions. In: Muller, R.H., Bentia, S., Bohm, B.H.L. (eds.) Emulsions & nanosuspensions for the formulation of poorly soluble drugs, pp. 149–174. Medpharm Scientific Publishers, Stuttgart, Germany (1998)
Muller, R.H., Jacobs, C., Kayser, O.: Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy: rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47(1), 3–19 (2001)
Liversidge, E.M., Liversidge, G.G., Cooper, E.R.: Nanosizing: a formulation approach for poorly water-soluble compounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 18(2), 113–120 (2003)
Rabinow, B.E.: Nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3(9), 785–796 (2004)
Patravale, V.B., Date, A.A., Kulkarni, R.M.: Nanosuspensions: a promising drug delivery strategy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 56(7), 827–840 (2004)
Gref, R., Minamitake, Y., Perracchia, M.T., Trubeskoy, V., Torchilin, V., Langer, R.: Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres. Science 263, 1600–1603 (1994)
Florence, A.T., Hillery, A.M., Hussain, N., Jani, P.U.: Nanoparticles as carriers for oral peptide absorption: studies on particle uptake and fate. J. Control. Release 36, 39–46 (1995)
Allemann, E., Gurny, R., Deolker, E.: Drug loaded nanoparticles: preparation methods and drug targeting issues. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 39, 173–191 (1993)
Tiyaboonchai, W.: Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system for drug delivery. Naresuan Univ. J. 11(3), 51–66 (2003)
Aspden, T.J., Mason, J.D., Jones, N.S.: Chitosan as a nasal delivery system: the effect of chitosan solutions on in vitro and in vivo mucociliary transport rates in human turbinates and volunteers. J. Pharm. Sci. 86, 509–513 (1997)
Lehr, C.M., Bouwstra, J.A., Schacht, E., Junginger, H.E.: In vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of chitosan and some other natural polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 78, 43–48 (1992)
Dumitriu, S., Chornet, E.: Inclusion and release of proteins from polysaccharide-based polyion complexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 31, 223–246 (1998)
Takeuchi, H., Yamamoto, H., Niwa, T., Hino, T., Kawashima, Y.: Enteral absorption of insulin in rats from mucoadhesive chitosan-coated liposomes. Pharm. Res. 13, 896–901 (1996)
Janes, K.A., Calvo, P., Alonso, M.J.: Polysaccharide colloidal particles as delivery systems for macromolecules. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47, 83–97 (2001)
Bhumkar, D.R., Pokharkar, V.B.: Studies on effect of PH on cross-linking of chitosan with sodium tripolyphosphate: a technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech. 7(2), E1–E6 (2006)
Aral, C., Akbug˘ a, J.: Alternative approach to the preparation of chitosan beads. Int. J. Pharm. 168, 9–15 (1998)
Mi, F.L., Shyu, S.S., Chen, C.T., Schoung, J.Y.: Porous chitosan microsphere for controlling the antigen release of Newcastle disease vaccine: preparation of antigen-adsorbed microsphere and in vitro release. Biomaterials 20, 1603–1612 (1999)
Shu, X.Z., Zhu, K.J.: A novel approach to prepare tripolyphosphate/chitosan complex beads for controlled drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 201, 51–58 (2000)
Ducheˆ ne, D., Ponchel, G., Wouassindjewe, D.: Cyclodextrins in targeting- Application to nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 36(1), 29–40 (1999)
Vyas, A., Saraf, S., Saraf, S.: Cyclodextrin based novel drug delivery systems. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 62(1–2), 23–42 (2008)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007)
Shu, X.Z., Zhu, K.J.: Chitosan/gelatin microspheres prepared by modified emulsification and ionotropic gelation. J. Microencapsul. 18, 237–245 (2001)
Calvo, P., Remun˜a′n-Lo′ pez, C., Vila-Jato, J.L., Alonso, M.J.: Novel hydrophilic chitosan–polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as protein carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 63, 125–132 (1997)
Calvo, P., Vila-Jato, J.L., Alonso, M.J.: Evaluation of cationic polymer-coated nanocapsules as ocular drug carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 153, 41–50 (1997)
Bodmeier, R., Chen, H., Paeratakul, O.: A novel approach to the oral delivery of micro- or nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 6, 413–417 (1989)
Ambike, A.A., Mahadik, K.R., Paradkar, A.: Spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions of simvastatin a low Tg drug: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Pharm. Res. 22, 990–998 (2005)
Kang, B.K., Lee, J.S., Chon, S.K., Jeong, S.Y., Yuk, S.H., Khang, G., Lee, H.B., Cho, S.H.: Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) for oral bioavailability enhancement of simvastatin in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 274, 65–73 (2004)
Rajput, S.J., Raj, H.A.: Simultaneous spectroscopic estimation of ezetimibe and simvastatin in tablet dosage forms. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 69, 759–762 (2007)
Arayne, M.S., Sultana, N., Hussain, F., Ali, S.A.: Validated spectrophotometric method for quantitative determination of simvastatinin pharmaceutical formulations and human serum. J. Anal. Chem. 62, 536–541 (2007)
Bhatia, N.M., Deshmukh, D.D., Kokil, S.U., Bhatia, M.S.: (2009) Simultaneous spectrophotometric estimation of simvastatin and ezetimibe in tablet formulation. J. Chem. 6(2), 541–544. http://www.e-journals.in/
Zerrouk, N., Corti, G., Ancillotti, S., Maestrelli, F., Cirri, M., Mura, P.: Influence of cyclodextrins and chitosan, separately or in combination, on glyburide solubility and permeability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 62, 241–246 (2006)
Maestrelli, F., Garcia-Fuentes, M., Mura, P., Jose′ Alonso, M.: A new drug nanocarrier consisting of chitosan and hydoxypropylcyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 63, 79–86 (2006)
Patel, A.R., Vavia, P.R.: Effect of hydrophilic polymer on solubilization of fenofibrate by cyclodextrin complexation. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 56, 247–251 (2006)
Chowdary, K.P.R., Srinivas, S.V. Influence of hydrophilic polymers on celecoxib complexation with hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 7(3), E-1–E-6 (2006)
Bibby, D.C., Davies, N.M., Tucker, I.G.: Mechanisms by which cyclodextrins modify drug release from polymeric drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 197, 1–11 (2000)
Loftsson, T., Frioriksdottir, H., Siguroardottir, A.M., Ueda, H.: The effect of water-soluble polymers on drug–cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 110, 169–177 (1994)
Ammar, H.O., Salama, H.A., Ghorab, M., Mahmoud, A.A.: Formulation and biological evaluation of glimepiride–cyclodextrin–polymer systems. Int. J. Pharm. 309, 129–138 (2006)
Pan, Y., Li, Y.J., Zhao, H.Y., Zheng, J.M., Xu, H., Wei, G., et al.: Int. J. Pharm. 349, 139–147 (2002)
Papadimitriou, S., Bikiaris, D., Avgoustakis, K., Karavas, E., Georgarakis, M.: Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with dorzolamide and pramipexole. Carbohydr. Polym. 73, 44–54 (2008)
Zhang, H., Oh, M., Allen, C., Kumacheva, E.: Monodisperse chitosan nanoparticles for mucosal drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 5(6), 2461–2468 (2004)
Fernandez-Urrusuno, R., Calvo, P., Remunan-Lopez, C., Vila-Jato, J.L., Alonso, M.J.: Enhancement of nasal absorption of insulin using chitosan Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 16, 1576–1581 (1999)
Kim, D.G., Jeong, Y.I., Choi, C., Roh, S.H., Kang, S.K., Jang, M.K., Nah, J.W.: Retinol-encapsulated low molecular water-soluble chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 319, 130–138 (2006)
Dhawan, S., Singla, A.K.: Nifedipine loaded chitosan microspheres prepared by emulsification phase separation. Biotech. Histochem. 78, 243–254 (2003)
Gupta, P., Bansal, A.K.: Devitrification of amorphous celecoxib. AAPS PharmSciTech. 6, E223–E230 (2005)
Kausbal, A.M., Gupta, P., Bansal, A.K.: Amorphous drug delivery systems: molecular aspects, design, and performance. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 21(3), 133–193 (2004)
Karavas, E., Georgarakis, E., Sigalas, M.P., Avgoustakis, K., Bikiaris, D.: Investigation of the release mechanism of a sparingly water-soluble drug from solid dispersions in hydrophilic carriers based on physical state of drug, particle size distribution and drug-polymer interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 66(3), 334–347 (2007)
Karavas, E., Georgarakis, E., Docoslis, A., Bikiaris, D.: Combining SEM, TEM, and micro-Raman techniques to differentiate between the amorphous molecular level dispersions and nanodispersions of a poorly water-soluble drug within a polymer matrix. Int. J. Pharm. 340, 76–83 (2007)
Shah, B., Kakumanu, V.K., Bansal, A.K.: Analytical techniques for quantification of amorphous/crystalline phases in pharmaceutical solids. J. Pharm. Sci. 95, 1641–1665 (2006)
Jun, S.W., Kim, M.S., Kim, J.S., Park, H.J., Lee, S., Woo, J.S., Hwang, S.J.: Preparation and characterization of simvastatin/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 66(3), 413–421 (2007)
Boonsongrit, Y., Mitrevej, A., Mueller, B.W.: Chitosan drug binding by ionic interaction. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 62(3), 267–274 (2006)
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to AICTE [F.No.: 8023/BOR/RPS-153/2006-07] New Delhi for financial assistance. Authors are thankful to Ranbaxy, India for providing pure drug and Dr. Denis Simon and Emilie Van- Oudendycke of Roquette, Lestrem, France for providing hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Authors also extend their gratitude to Head, University Institute of pharmacy, Pt., Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India for providing facilities to carry out research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas, A., Saraf, S. & Saraf, S. Encapsulation of cyclodextrin complexed simvastatin in chitosan nanocarriers: A novel technique for oral delivery. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 66, 251–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-009-9605-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-009-9605-y