Abstract
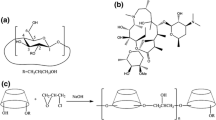
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) on the solubility and dissolution rate of meloxicam. The methods that were employed to prepare meloxicam–β-cyclodextrin complexes were physical mixture, kneaded dispersion, and spray drying. Spray drying method was found to be the best to form a true inclusion complex. Complexes were characterized by thermal analysis, X-ray diffractometry (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. The apparent stability constant of the complex, K c, calculated from the slope and intercept of the AL solubility diagram was found to be 429.73, 259.96, 183.31, and 36.50 L mol−1 at pH 2, 3, 6.5, and 10.3, respectively. The dissolution rate of meloxicam from the complexes was higher than from meloxicam alone. Molecular modeling was also used to investigate the interaction between meloxicam and β-CD. The dominant driving force for the complexation was evidently Van der Waals force with very little electrostatic contribution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekers, O., Uijtendaal, E.V., Beijnen, J.H., Bult, A.W., Underberg, J.M.: Cyclodextrins in the pharmaceutical field. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 17, 1503–1549 (1991). doi:10.3109/03639049109026630
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.E.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1017–1025 (1996). doi:10.1021/js950534b
Li, P., Tabibi, S.E., Yalkowsky, S.H.: Combined effect of complexation and pH on solubilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 87, 1535–1537 (1998). doi:10.1021/js9801889
Chowdary, K.P.R., Nalluri, B.N.: Nimesulide and β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: physicochemical characterization and dissolution rate studies. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 26, 1217–1220 (2000). doi:10.1081/DDC-100100995
Obaidat, A.A., Matalqah, S.M., Najib, N.M.: Improvement and characterization of the in-vitro dissolution behavior of sulindac by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. Acta Pharm. 52, 9–18 (2002)
Oh, I.J., Song, H.M., Lee, K.C.: Effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on the stability of prostaglandin E2 in solution. Int. J. Pharm. 106, 135–140 (1994). doi:10.1016/0378-5173(94)90311-5
Masson, M., Loftsson, T., Jonsdottir, S., Fridriksdottir, H., Petersen, D.S.: Stabilization of ionic drugs through complexation with non-ionic and ionic cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 164, 45–55 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(97)00387-6
Loukas, Y.L., Jayasekera, P., Gregoriadis, G.: Novel liposome-based multicomponent systems for the protection of photolabile agents. Int. J. Pharm. 117, 85–94 (1995). doi:10.1016/0378-5173(94)00320-5
Rajewski, R.A., Stella, V.J.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 2. In vivo drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1142–1169 (1996). doi:10.1021/js960075u
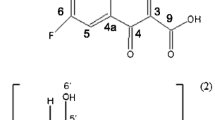
Luger, P., Daneck, K., Engel, W., Trummlitz, G., Wagner, K.: Structure and physicochemical properties of meloxicam, a new NSAID. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 4, 175–187 (1996). doi:10.1016/0928-0987(95)00046-1
Baboota, S., Agarwal, S.P.: Inclusion complexation of meloxicam with β-cyclodextrin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 64, 408–411 (2002)
Baboota, S., Agarwal, S.P.: Meloxicam complexation with β-cyclodextrin: influence on the anti-inflammatory and ulcerogenic activity. Pharmazie 58, 73–74 (2003)
Buchi Naidu, N., Chowadry, K.P.R., Murthy, K.V.R., Satyanarayana, V., Hayman, A.R., Becket, G.: Physicochemical characterization and dissolution properties of meloxicam-cyclodextrin binary systems. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 35, 75–86 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.01.003
Chowdary, K.P.R., Raviprakash, P.: Dissolution kinetics of meloxicam-β-cyclodextrin complex system. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 4, 845–848 (2006)
Abdoh, A.A., El-Barghouthi, M.I., Zughul, M.B., Davies, J.E., Badwan, A.A.: Changes in the conformational structure, microscopic and macroscopic pKas of meloxicam on complexation with natural and modified cyclodextrins. Pharmazie 62, 55–59 (2007)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase solubility techniques. In Reilly, C.N. (ed.) Advances in Analytical Chemistry and Instrumentation, vol. 4, pp. 117–212. Interscience, New York (1965)
Connors, K.A.: Binding Constants: The Measurement of Molecular Complex Stability, pp. 261–281. Wiley, London (1987)
Duchene, D., Vaution, C., Glomot, F.: Cyclodextrins, their value in pharmaceutical technology. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 12, 2193–2215 (1986). doi:10.3109/03639048609042630
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obaidat, A.A., Khanfar, R.A. & Khawam, M.N. The effect of β-cyclodextrin on the solubility and dissolution rate of meloxicam and investigation of the driving force for complexation using molecular modeling. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 63, 273–279 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-008-9517-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-008-9517-2