Abstract
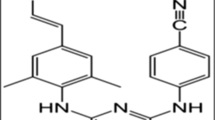
Pirodavir, 4-[2-[1-(6-Methyl-3-pyridazinyl)-4-piperidinyl]ethoxy]benzoic acid ethyl ester, is an antiviral compound which has low aqueous solubility (<0.01 mg/ml). The compound is a weak base (pKa 5.8) with high lipophicity (logP 4.44). Ionization of the compound increases the solubility in acidic medium to 2.3 mg/ml at pH 2.4. However, a low pH is not acceptable for nasal application as this would induce irritation.
Extensive solubility studies were performed using different types of substituted cyclodextrins in order to select an appropriate derivate capable of increasing solubility to an acceptable level for formulations for nasal application. Aqueous solubility of pirodavir increased in a linear fashion with increasing concentration of most of the substituted cyclodextrins. However, using 2-hydropropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) the solubility increased in a non-linear fashion. Based on these studies HPBCD was selected as the most appropriate excipient.
To support a clinical study on the treatment of rhinovirus cold by intranasal Pirodavir formulations were developed containing up to 5 mg/ml of pirodavir and up to 10% of HPBCD. Stability of the formulations was studied and found to be acceptable.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayden F.G., Andries K., Janssen P.A.J.: Safety and efficacy of intranasal pirodavir (R77975) in experimental Rhinovirus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36, 727–732 (1992) and Hayden F.G., Hipskind G.J., Woerner D.H., Eisen G.F., Janssen M., Janssen P.A.J., Andries K., Intranasal pirodavir (R77975) treatment of rhinovirus colds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39, 290–294 (1995)
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1017–1025 (1966)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: In: Reilly, C.N. (ed.) Advances in Analytical Chemistry and Instrumentation, vol. 4. New York: Wiley-Interscience, pp. 117–212 (1965)
Higuchi, T., Kristiansen, H.: Binding specificity between small organic solutes in aqueous solution: Classification of some solutes into two groups according to binding tendencies. J. Pharm. Sci 59, 1601–1608 (1970)
Merkus, F.W.H.M., Verhoef, J.C., Marttin, E., Romeijn, S.G., van der Kuy, P.H.M., Hermens, W.A.J.J., Schipper, N.G.M.: Cyclodextrins in nasal drug delivery, Adv. Drug Del. Rev 36, 41–57 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peeters, J., Neeskens, P. & Brewster, M.E. Development of a formulation of Pirodavir using 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 57, 137–139 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-006-9205-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-006-9205-z