Abstract
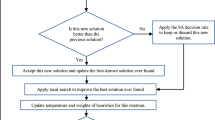
This paper deals with the no-wait job shop scheduling problem resolution. The problem is to find a schedule to minimize the makespan (\(C_{max}\)), that is, the total completeness time of all jobs. The no-wait constraint occurs when two consecutive operations in a job must be processed without any waiting time either on or between machines. For this, we have proposed two different resolution methods, the first is an exact method based on the branch-and-bound algorithm, in which we have defined a new technique of branching. The second is a particular swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, extended from the discrete version of PSO. In the proposed algorithm, we have defined the particle and the velocity structures, and an efficient approach is developed to move a particle to the new position. Moreover, we have adapted the timetabling procedure to find a good solution while respecting the no-wait constraint. Using the PSO method, we have reached good results compared to those in the literature.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AitZai, A., Benmedjdoub, B., & Boudhar, M. (2012). A branch and bound and parallel genetic algorithm for the job shop scheduling problem with blocking. International Journal of Operational Research, 14(3), 343–365.
AitZai, A., & Boudhar, M. (2013). Parallel branch-and-bound and parallel PSO algorithms for job shop scheduling problem with blocking. International Journal of Operational Research, 16(1), 343–365.
Bertolissi, E. (2000). Heuristic algorithm for scheduling in the no-wait fow-hop. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 107, 459–465.
Bouquard, J. L., Billaut, J. C., Kubzin, M. A., & Strusevich, V. A. (2005). Two-machine flowshop scheduling problems with no-wait jobs. Operations Research Letters, 33, 255–262.
Bozejko, W., & Makuchowski, M. (2008). A fast hybrid tabu search algorithm for the no-wait job shop problem. Janiszewskiego 11–17, 50–372 Wrocław, Poland.
Çaliş, B., & Bulkan, S. (2013). A research survey: Review of AI solution strategies of job shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0837-8.
Carlier, J., & Pinson, E. (1989). An algorithm for solving the job-shop problem. Management Science, 35(2), 164–176.
Carlier, J., & Pinson, E. (1994). Adjustment of heads and tails for the job-shop problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 78, 238–251.
Framinan, J. M., & Schuster, C. (2006). An enhancedtimetabling procedure for the no-wait job shop problem: A complete local search approach. Computers and Operations Research, 331, 1200–1213.
Chang, J., Gong, D., & Xiao-ping, M. A. (2007). A heuristic genetic algorithm for no-wait flowshop scheduling problem. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 17(4), 0582–0586.
Gilmor, P., & Gomory, R. (1964). Sequencing a one state-variable machine: A solvable case of the travelling salesman problem. Operations Research, 12, 655–679.
Hall, N. G., & Sriskandarajah, C. (1996). A survey of machine scheduling problems with blocking and no-wait process. Operations Research, 44(3), 510–525.
Kachitvichyanukul, V., & Sitthitham, S. (2011). A two-stage genetic algorithm for multi-objective job shop scheduling problems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22(3), 355–365.
Kalczynski, P. J., & Kamburowski, J. (2007). On no-wait and no-idle flow shops with makespan criterion. European Journal of Operational Research, 178, 677–685.
Kravchenko, S. A. (1998). A polynomial algorithm for a two-machine no-wait job-shop scheduling problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 106, 101–107.
Lawrence, S. (1984). Resource constrained project scheduling: An experimental investigation of heuristic scheduling techniques (Supplement). Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: Graduate School of Industrial Administration.
Lennartz, P. (2006). No-wait job shop scheduling a constraint propagation approach.
Liaw, C. F. (2008). An efficient simple metaheuristic for the makespan in two machines no-wait job shops. Computers and Operations Research, 35(10), 3276–3283.
Mascis, A., & Pacciarelli, D. (2002). Job-shop scheduling with blocking and no-wait constraints. European Journal of Operational Research, 143, 498–517.
Mati, Y., Rezg, N., & Xie, X. (2001). A taboo search approach for deadlock-free scheduling of automated manufacturing systems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 12(5—-6), 535–552.
Meeran, S., & Morshed, M. S. (2012). A hybrid genetic tabu search algorithm for solving job shop scheduling problems: A case study. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(4), 1063–1078.
Pan, J. C. H., & Huang, H. C. (2009). A hybrid genetic algorithm for no-wait job shop scheduling problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 5800–5806.
Pan, Q. K., Wang, L., Tasgetiren, M. F., & Zhao, B. H. (2008). A hybrid discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm for the no-wait flow shop scheduling problem with makespan criterion. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 38(3—-4), 337–347.
Pezhman, R., Meysam, R., & Fariborz, J. (2013). No-wait flexible flowshop with uniform parallel machines and sequence-dependent setup time: A hybrid meta-heuristic approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0830-2.
Qiu, X., & Henry, Y. K. L. (2012). An AIS-based hybrid algorithm for static job shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0701-2.
Sahni, S., & Cho, Y. (1979). Complexity of scheduling shops with no wait in process. Mathematics of Operations Reasearch, 4(4), 448–457.
Samarghandi, H., & ElMekkawy, T. Y. (2013). Two-machine, no-wait job shop problem with separable setup times and single-server constraints. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 65(1—-4), 295–308.
Shuster, C. J. (2006). No-wait job shop scheduling: Tabu search and complexity of sub problems. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 63, 473–491.
Ventura, J. A., & Yoon S. H. (2012). A new genetic algorithm for lot-streaming flow shop scheduling with limited capacity buffers. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0650-9.
Vijay chakaravarthy, G., & Marimuthu, S. (2013). Performance evaluation of proposed differential evolution and particle swarm optimization algorithms for scheduling m-machine flow shops with lot streaming. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(1), 175–191.
Xing, L., Chen, Y., & Yang, K. (2009). An efficient search method for multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling problems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 20(3), 283–293.
Zhu, J., Li, X. & Wang, Q. (2008). Complete local search with limited memory algorithm for job shops to minimize makespan. Key laboratory of Computer Network and Information Integration (Southeast University) Ministry of Education, 210096 Nanjing, PR China.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous referees for their useful comments that have allowed us to improve on the quality of this paper. Thanks are also due to Mr Larbi Benaissa and Prof. Ahmed Guessoum for their contribution to the revision of an earlier version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AitZai, A., Benmedjdoub, B. & Boudhar, M. Branch-and-bound and PSO algorithms for no-wait job shop scheduling. J Intell Manuf 27, 679–688 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0906-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0906-7