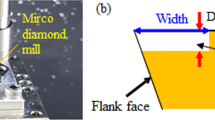
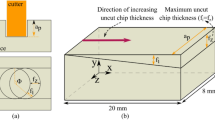
Abstract
The experimental investigation on cutting tool wear and a model for tool wear estimation is reported in this paper. The changes in the values of cutting forces, vibrations and acoustic emissions with cutting tool wear are recoded and analyzed. On the basis of experimental results a model is developed for tool wear estimation in turning operations using Adaptive Neuro fuzzy Inference system (ANFIS). Acoustic emission (Ring down count), vibrations (acceleration) and cutting forces along with time have been used to formulate model. This model is capable of estimating the wear rate of the cutting tool. The wear estimation results obtained by the model are compared with the practical results and are presented. The model performed quite satisfactory results with the actual and predicted tool wear values. The model can also be used for estimating tool wear on-line but the accuracy of the model depends upon the proper training and section of data points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhard S. (2002). On line and indirect tool wear monitoring in turning with artificial neural networks: A review of more than a decade of research. Mechanical Systems and Signal processing, 16(4): 487–546
Dimla D.E. Sr., Lister P.M. (2000). On-line metal cutting tool condition monitoring I: Force and vibration analyses. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 40, 739–768
Dimla D.E. Jr., Lister P.M., Leighton N.J. (1998). Automatic tool state identification in a metal turning operation using MLP Neural networks and multivariate process parameters. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 38(4): 343–352
Fang X.D. (1995). Expert system supported Fuzzy diagnosis of finish-turning process states. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 35(6): 913–924
Jang, J. S. R., & Sun, C. T. (1995). Neuro-Fizzy modeling and control. Proceedings of the IEEE, 83(3) (March 1995).
Li S., Elbestawi M.A. (1996). Fuzzy clustering for automated tool condition monitoring in machining. Mechanical Systems and Signal processing, 10(5): 533–550
Mamdani E.H., Assilian S. (1975). An experiment in linguistic synthesis with fuzzy logic controller. International Journal of Man–Machine Studies, 7(1): 1–13
Miller, R., & Hill, E. (2000). Non destructive testing handbook (3rd ed., pp. 1–19). ASNT publications.
Moriwaki T., Okushima K. (1980). Detection for cutting tool fracture by Acoustic emission measurement. Annals of the CIRP, 29, 35–40
Pandit S.M., Kashov S. (1983). Variation in friction coefficient with tool wear. Wear, 84, 65–79
Rao S.B. (1986). Tool wear monitoring through the dynamics of stable turning. ASME Journal of Engineering for Industry, 108, 183–190
Ravindra H.V., Krishanamurthy R. (1983). Tool wear monitoring in turning using a pattern recognition technique. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 37, 731–740
Ravindra H.V., Srinivasa Y.G. (1993). Modeling of tool wear based on cutting forces in turning. Wear, 49, 25–32
Selvam M.S. (1975). Tool vibration and its influence on surface roughness in turning. Wear, 35, 29–37
Sugeno, M. (1985). Industrial applications of fuzzy control (pp. 1–150). Elsevier Science Pub. Co.
Xiaoli L. (2002). A brief review: Acoustic emission method for tool wear monitoring during turning. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 42, 157–165
Zadeh L.A. (1973). Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes. IEEE Transactions on systems, Man and Cybernetics, 3(1): 28–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, V.S., Sharma, S.K. & Sharma, A.K. Cutting tool wear estimation for turning. J Intell Manuf 19, 99–108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-007-0048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-007-0048-2