Abstract
Purpose
Intracardiac echocardiographic (ICE) imaging might be useful for integrating three-dimensional computed tomographic (CT) images for left atrial (LA) catheter navigation during atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. However, the optimal CT image integration method using ICE has not been established.
Methods
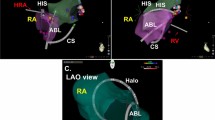
This study included 52 AF patients who underwent successful circumferential pulmonary vein isolation (CPVI). In all patients, CT image integration was performed after the CPVI with the following two methods: (1) using ICE images of the LA derived from the right atrium and right ventricular outflow tract (RA-merge) and (2) using ICE images of the LA directly derived from the LA added to the image for the RA-merge (LA-merge). The accuracy of these two methods was assessed by the distances between the integrated CT image and ICE image (ICE-to-CT distance), and between the CT image and actual ablated sites for the CPVI (CT-to-ABL distance).
Results
The mean ICE-to-CT distance was comparable between the two methods (RA-merge = 1.6 ± 0.5 mm, LA-merge = 1.7 ± 0.4 mm; p = 0.33). However, the mean CT-to-ABL distance was shorter for the LA-merge (2.1 ± 0.6 mm) than RA-merge (2.5 ± 0.8 mm; p < 0.01). The LA, especially the left-sided PVs and LA roof, was more sharply delineated by direct LA imaging, and whereas the greatest CT-to-ABL distance was observed at the roof portion of the left superior PV (3.7 ± 2.8 mm) after the RA-merge, it improved to 2.6 ± 1.9 mm after the LA-merge (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
Additional ICE images of the LA directly acquired from the LA might lead to a greater accuracy of the CT image integration for the CVPI.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kistler PM, Earley MJ, Harris S, Abrams D, Ellis S, Sporton SC, et al. Validation of three-dimensional cardiac image integration: use of integrated CT image into electroanatomic mapping system to perform catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17:341–8.
Martinek M, Nesser HJ, Aichinger J, Boehm G, Purerfellner H. Impact of integration of multislice computed tomography imaging into three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping on clinical outcomes, safety, and efficacy using radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007;30:1215–23.
Rossillo A, Indiani S, Bonso A, Themistoclakis S, Corrado A, Raviele A. Novel ICE-guided registration strategy for integration of electroanatomical mapping with three-dimensional CT/MR images to guide catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009;20:374–8.
Kimura M, Sasaki S, Owada S, Horiuchi D, Sasaki K, Itoh T, et al. Validation of accuracy of three-dimensional left atrial CartoSound™ and CT image integration: influence of respiratory phase and cardiac cycle. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24:1002–7.
Deftereos S, Giannopoulos G, Kossyvakis C, Panagopoulou V, Raisakis K, Kaoukis A, et al. Integration of intracardiac echocardiographic imaging of the left atrium with electroanatomic mapping data for pulmonary vein isolation: first-in-Greece experience with the CartoSound™ system and brief literature review. Hell J Cardiol. 2012;53:10–6.
Schwartzman D, Zhong H. On the use of CartoSound for left atrial navigation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21:656–64.
Brooks AG, Wilson L, Chia NH, Lau DH, Alasady M, Leong DP, et al. Accuracy and clinical outcomes of CT image integration with Carto-sound compared to electro-anatomical mapping for atrial fibrillation ablation: a randomized controlled study. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:2774–82.
Kaseno K, Tada H, Koyama K, Jingu M, Hiramatsu S, Yokokawa M, et al. Prevalence and characterization of pulmonary vein variants in patients with atrial fibrillation determined using 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101:1638–42.
Yamasaki H, Tada H, Sekiguchi Y, Igarashi M, Arimoto T, Machino T, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of asymptomatic excessive transmural injury after radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8:826–32.
Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, Schwab M, Sunsaneewitayakul B, Vasavakul T, et al. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:2044–53.
Oral H, Chugh A, Good E, Wimmer A, Dey S, Gadeela N, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation guided by complex electrograms. Circulation. 2007;115:2606–12.
Haïssaguerre M, Hocini M, Sanders P, Sacher F, Rotter M, Takahashi Y, et al. Catheter ablation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: clinical outcome and mechanisms of subsequent arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16:1138–47.
Singh SM, Heist EK, Donaldson DM, Collins RM, Chevalier J, Mela T, et al. Image integration using intracardiac ultrasound to guide catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5:1548–55.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. John Martin for his help in the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaseno, K., Hisazaki, K., Nakamura, K. et al. The impact of the CartoSound® image directly acquired from the left atrium for integration in atrial fibrillation ablation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 53, 301–308 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0368-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0368-5