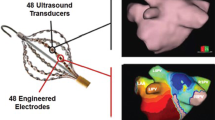
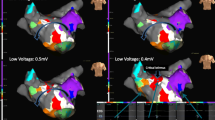
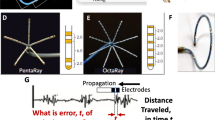
Abstract
Over the past 5 years, catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) has evolved from an experimental procedure to one that is now performed throughout the world. The rapid and widespread acceptance of this procedure reflects encouraging reports of the safety and efficacy of catheter ablation of AF. The improved outcomes of catheter ablation of AF have resulted from a combination of increasing clinical experience, but also several important technological advances. One of the most important of these has been the development and widespread utilization of three dimensional mapping systems during AF ablation The purpose of this article is to briefly review the current status and clinical role of three dimensional mapping systems in catheter ablation of AF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre M, Shah DC, Jais P, et al. Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation 2000;102:2463–2465.
Marrouche NF, Martin DO, Wazni O, et al. Phased-array intracardiac echocardiography monitoring during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: Impact on outcome and complications. Circulation 2003;107:2710–2716.
Vasamreddy CR, Lickfett L, Jayam VK, et al. Predictors of recurrence following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using an irrigated-tip ablation catheter. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004;15:692–697.
Oral H, Knight BP, Tada H, et al. Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002;105:1077–1081.
Pappone C, Oreto G, Rosanio S, et al. Atrial electroanatomic remodeling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein ablation: efficacy of an anatomic approach in a large cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2001;104:2539–2544.
Ouyang F, Bansch D, Ernst S, et al. Complete isolation of the left atrium surrounding the pulmonary veins: new insights from the double-lasso technique in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004;110:2090–2096.
Oral H, Scharf C, Chugh A, et al. Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: segmental pulmonary vein ostial ablation versus left atrial ablation. Circulation 2003;108:2355–2360.
Vasamreddy CR, Dalal D, Eldadah Z, Dickfeld T, Jayam VK, Henrikson CA, Meininger C, Dong J, Lickfett L, Berger R, Calkins H. Safety and efficacy of circumferential pulmonary vein catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2005;2:42–48.
Gepstein L, Hayam G, Ben-Haim SA. A novel method for nonfluoroscopic catheter-based electroanatomical mapping of the heart. In vitro and in vivo accuracy results. Circulation 1997;95(6):1611–1622.
De Groot N, Bootsma M, Van Der Velde E, Schalij M. Three-Dimensional catheter positioning during radiofrequency ablation in patients: first application of a real-time position management system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2000;11:1183–1192.
Peters NS, Jackman WM, Schilling RJ, Beatty G, Davies DW. Human left ventricular endocardial activation mapping using a novel noncontact catheter. Circulation 1997;95:1658–1660.
Novak P, Guerra P, Thibault B, Macle L. Utility of a nonfluoroscopic navigation system for pulmonary vein isolation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004;15:967.
Jais P, Haissaguerre M, Shah DC, et al. A focal source of atrial fibrillation treated by discrete radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1997;95:572–576.
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998;339:659–666.
Chen SA, Hsieh MH, Tai CT, et al. Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins: electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological responses, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1999;100:1879–1886.
Robbins IM, Colvin EV, Doyle TP, Kemp WE, Loyd JE, McMahon WS, Kay GN. Pulmonary vein stenosis after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 1998;98(17):1769–1775.
Kato R, Lickfett L, Meininger G, Dickfeld T, Wu R, Juang G, Angkeow P, LaCorte J, Bluemke D, Berger R, Halperin H, Calkins H. Pulmonary vein anatomy in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Lessons learned by use of the magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 2003;107:2004–2010.
Pappone C, Rosanio S, Augello G, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and quality of life after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation for atrial fibrillation: outcomes from a controlled nonrandomized long-term study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42:185–197.
Mansour M, Ruskin J, Keane D. Efficacy and safety of segmental ostial versus circumferential extra-ostial pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004;15:532–537.
Kottkamp H, Tanner H, Kobza R, et al. Time courses and quantitative analysis of atrial fibrillation episode number and duration after circular plus linear left atrial lesions: trigger elimination or substrate modification: early or delayed cure? J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;44:869–877.
Pappone C, Oral H, Santinelli V, et al. Atrio-esophageal fistula as a complication of percutaneous transcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004;109:2724–2726.
Scanavacca MI, D’Avila A, Parga J, et al. Left Atrial-Esophageal Fistula Following Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004;15:960–962.
Page RL, Wilkinson WE, Clair WK, et al. Asymptomatic arrhythmias in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Circulation 1994;89:224–227.
Tse HF, Reek S, Timmermans C, et al. Pulmonary vein isolation using transvenous catheter cryoablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation without risk of pulmonary vein stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42:752–758.
Meininger GR, Calkins H, Lickfett L, et al. Initial experience with a novel focused ultrasound ablation system for ring ablation outside the pulmonary vein. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2003;8:141–148.
Faddis MN, Blume W, Finney J, et al. Novel, magnetically guided catheter for endocardial mapping and radiofrequency catheter ablation. Circulation 2002;106:2980–2985.
Solomon SB, Dickfield T, Calkins H. Real-time cardiac catheter navigation on three-dimensional CT images. J Interv Card Electrphysiol 2003;8:27–36.
Sra J, Krum D, Hare J, Okerlund D, Thompson H, Vass M, Schweitzer J, Olson E, Foley WD, Akhtar M. Feasibility and validation of registration of three-dimensional left atrial models derived from computed tomography with a contact cardiac mapping system. Heart Rhythm 2005;2:55–63.
Pappone C, Santinelli V, Manguso F, et al. Pulmonary vein denervation enhances long-term benefit after circumferential ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004;109:327–334.
Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, et al. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:2044–2053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calkins, H. Three Dimensional Mapping of Atrial Fibrillation: Techniques and Necessity. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 13 (Suppl 1), 53–59 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-005-2624-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-005-2624-8