Abstract
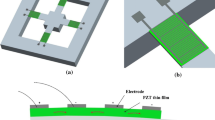
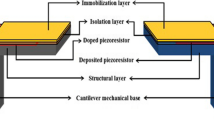
In general, PZT thick films fabricated through screen printing show porosity ranging from 10% to 40%. Unfortunately, these high porosities of thick films greatly affect the electromechanical characteristics of PZT thick film cantilevers. In this paper, we report a systematic analysis on the effect of thick film porosity on the electromechanical characteristics of the PZT thick film cantilevers in order to make the PZT thick film cantilever a highly controllable micro mass sensor or micro self actuator. The theoretical calculations of mass sensitivity and actuating force of the optimal PZT thick film cantilevers are presented with respect to the material properties and geometry of PZT thick films, which are based on experimentally verified material properties and geometrical parameters. The 400 × 300 cantilever with 20% porosity of active material was evaluated to be reliable as an optimal mass sensor and self actuator. The thick film cantilever indicates both high mass sensitivity (~48 pg/Hz), the same as sensitive thin film cantilever sensors, and high actuating force (~1.7 N), similar to strong bulk cantilevers. From the results of the modeling, it was found that the harmonic oscillation response according to material properties including the porosity, and geometry of the fabricated thick film cantilever, is quite controllable and predictable, thus enhancing the actuating force and mass sensitivity. Also, it was confirmed that controlling the porosity of PZT thick films is more efficient than controlling the cantilever geometry to increase the cantilever resonating force. However, optimizing the geometric constituents is more effective than controlling the densification of PZT thick films to increase the mass sensitivity of the cantilevers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Park, T.Y. Kwon, D.S. Yoon, H. Kim, T.S. Kim, Fabrication of microcantilever sensors actuated by piezoelectric Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 thick films and determination of their electromechanical characteristics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 2021–2028 (2005). doi:10.1002/adfm.200500331
J.H. Park, T.Y. Kwon, H.J. Kim, S.R. Kim, D.S. Yoon, C.-I. Chun, H. Kim, T.S. Kim, Resonance properties and mass sensitivity of monolithic microcantilever sensors actuated by piezoelectric PZT thick film. J. Electroceram. 17, 565–572 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10832-006-6290-8
S.P. Beeby, A. Blackburn, N.M. White, Processing of PZT piezoelectric thick films on silicon for microelectromechancial systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 9, 218–229 (1999). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/9/3/302
Y.-B. Jeon, T.-S. Chung, K.-S. No, Fabrication of PZT thick films on silicon substrates for piezoelectric actuator. J. Electroceram. 4(1), 195–199 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1009924113335
R.A. Dorey, S.B. Stringfellow, R.W. Whatmore, Effect of sintering aid and repeated sol infiltrations on the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of a PZT composite thick film. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 2921–2926 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0955-2219(02) 00062-6
S. Le Dren, L. Simon, P. Gonnard, M. Troccaz, A. Nicolas, Investigation of factors affecting the preparation of PZT thick films. Mater. Res. Bull. 35, 2037–2045 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0025-5408(00)00402-5
R.N. Torah, S.P. Beeby, N.M. White, Improving the piezoelectric properties of thick-film PZT: the influence of paste composition, powder milling process and electrode material. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 110, 378–384 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.sna.2003.09.027
J.H. Park, J.H. Son, D.S. Yoon, T.S. Kim, H.-H. Park, H. Kim, Electrical properties of screen printed PZT thick films infiltrated with photo-sensitive sol compared with normal sol for cantilever type biochip. Integr. Ferroelectr. 69, 163–171 (2005). doi:10.1080/10584580590898613
T.Y. Kwon, J.H. Park, Y.B. Kim, D.S. Yoon, C.I. Cheon, H.L. Lee, T.S. Kim, Preparation of piezoelectric 0.1Pb(Zn0.5 W0.5)O3-0.9Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 solid solution and thick films for low temperature firing on a Si-substrate. J. Cryst. Growth 295, 172–178 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.07.005
X. Li, W.Y. Shih, I.A. Aksay, W.-H. Shih, Electromechanical behavior of PZT-brass unimorphs. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 1733–1740 (1999). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb01993.x
W.Y. Shih, X. Li, H. Gu, W.-H. Shih, I.A. Aksay, Simultaneous liquid viscosity and density determination using piezoelectric unimorph cantilevers. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1497–1505 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1287606
J.H. Lee, PZT nanomechanical cantilever studies for protein detection system, PhD Thesis, Yonsei University, 2004, pp. 16–20.
F.G. Brath, J.A.C. Humphrey, Sensing in Biological Engineering (Spronger Wien, NewYork, 2002)
D. Sarid, Scanning force microscopy (Oxford University Press, New York, 1994)
J.W. Yi, W.Y. Shih, W.-H. Shih, Effect of length, width, and mode on the mass detection sensitivity of piezoelectric unimorph cantilevers. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 1680–1686 (2002). doi:10.1063/1.1427403
J.W. Yi, W.Y. Shih, R. Mutharasan, W.-H. Shih, In situ cell detection using piezoelectric PZT-stainless steel cantilevers. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 619–625 (2003). doi:10.1063/1.1524022
J. Merhaut, Theory of Electroacoustics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1981), p. 100
M.D. Ward, D.A. Butty, In situ interfacial mass detection with piezoelectric transducers. Science 249, 1000–1007 (1990). doi:10.1126/science.249.4972.1000
G.Y. Chen, R.J. Warmack, T. Thundat, D.P. Allison, A. Huang, Resonance response of scanning force microscopy cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 65, 2532–2537 (1994). doi:10.1063/1.1144647
P.I. Oden, G.Y. Chen, R.A. Steele, R.J. Warmack, T. Thundat, Viscous drag measurements utilizing microfabricated cantilevers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 3814–3816 (1996). doi:10.1063/1.116626
R. Sandberg, K. Molhave, A. Boisen, W. Svendsen, Effect of gold coating on the Q-factor of a resonant cantilever. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 2249–2253 (2005). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/12/006
K.Y. Yasumura, T.D. Stowe, E.M. Chow, T. Pfafman, T.W. Kenny, B.C. Stipe, D. Rugar, Quality factors in micron- and submicron- thick cantilevers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 9, 117–125 (2000). doi:10.1109/84.825786
T.B. Gabrielson, Mechanical-thermal noise in micromachined acoustic and vibration sensors. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 40, 903–909 (1993). doi:10.1109/16.210197
Q.-M. Wang, Q. Zhang, B. Xu, R. Liu, L.E. Cross, Nonlinear piezoelectric behavior of ceramic bending mode actuators under strong electric fields. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 3352–3306 (1999). doi:10.1063/1.371213
J.G. Smith, W.-S. Choi, The constituent equations of piezoelectric heterogeneous bimorphs. IEEE Trans. Ultra. Ferro. Freq. Contr. 38, 256–270 (1991). doi:10.1109/58.79611
B. Krause, G.-H. Koops, N.F.A. van der Vegt, M. Wessling, M. Wubbenhorst, J. van Turnhout, Ultralow-k dielectrics made by supercritical foaming of thin polymer films. Adv. Mater. 14, 1041–1046 (2002). doi:10.1002/1521-4095(20020805) 14:15<1041::AID-ADMA1041>3.0.CO;2-A
J.H. Lee, K.H. Yoon, T.S. Kim, Characterization of resonant behavior and sensitivity using micromachined PZT cantilever. Integr. Ferroelectr. 50, 43–52 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Intelligent Microsystem Center sponsored by the Korea Ministry of Science and Technology as a part of the 21st Century’s Frontier R&D Projects (Grant MS-01-133-01) and National Core Research Center for Nanomedical Technology sponsored by KOSEF (Grant R15-2004-024-00000-0). Also, this work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD), (Grant Number: KRF-2006-351-D00002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Kim, H., Yoon, D.S. et al. Effects of the material properties on piezoelectric PZT thick film micro cantilevers as sensors and self actuators. J Electroceram 25, 1–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-009-9581-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-009-9581-z