Abstract
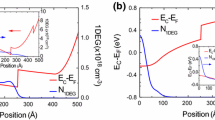
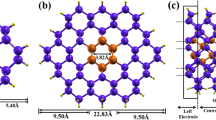
Dopant deactivation in pure Si and pure Ge nanowires (NWs) can compromise the efficiency of the doping process at nanoscale. Quantum confinement, surface segregation and dielectric mismatch, in different ways, strongly reduce the carrier generation induced by intentional addition of dopants. This issue seems to be critical for the fabrication of high-quality electrical devices for various future applications, such as photovoltaics and nanoelectronics. By means of Density Functional Theory simulations, we show how this limit can be rode out in core-shell silicon-germanium NWs (SiGe NWs), playing on the particular energy band alignment that comes out at the Si/Ge interface. We demonstrate how, by choosing the appropriate doping configurations, it is possible to obtain a 1-D electron or hole gas, which has not to be thermally activated and which can furnish carriers also at very low temperatures. Our findings suggest core-shell NWs as possible building blocks for high-speed electronic device and new generation solar cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We take for simplicity the case of Si or any other group-IV semiconductor.
References
Cui, Y., Lieber, C.M.: Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 291(5505), 851–853 (2001)
Xiang, J., Lu, W., Hu, Y., Wu, Y., Yan, H., Lieber, C.M.: Ge/Si nanowire heterostructures as high-performance field-effect transistors. Nature 441(7092), 489 (2006)
Huang, Y., Duan, X., Cui, Y., Lauhon, L.J., Kim, K.H., Lieber, C.M.: Logic gates and computation from assembled nanowire building blocks. Science 294(5545), 1313–1317 (2001)
Duan, X., Huang, Y., Lieber, C.M.: Nonvolatile memory and programmable logic from molecule-gated nanowires. Nano Lett. 2(5), 487–490 (2002)
Cui, Y., Wei, Q., Park, H., Lieber, C.M.: Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 293(5533), 1289–1292 (2001)
Nam, S., Jiang, X., Xiong, Q., Ham, D., Lieber, C.M.: Vertically integrated, three-dimensional nanowire complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor circuits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106(50), 21035–21038 (2009)
Rurali, R.: Colloquium: Structural, electronic, and transport properties of silicon nanowires. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82(1), 427–449 (2010)
Diarra, M., Niquet, Y.M., Delerue, C., Allan, G.: Ionization energy of donor and acceptor impurities in semiconductor nanowires: Importance of dielectric confinement. Phys. Rev. B 75(4), 045301 (2007)
Niquet, Y.M., Genovese, L., Delerue, C., Deutsch, T.: Ab initio calculation of the binding energy of impurities in semiconductors: Application to Si nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 81(16), 161301 (2010)
Björk, M.T., Schmid, H., Knoch, J., Riel, H., Riess, W.: Donor deactivation in silicon nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(2), 103 (2008)
Calderón, M.J., Verduijn, J., Lansbergen, G.P., Tettamanzi, G.C., Rogge, S., Koiller, B.: Heterointerface effects on the charging energy of the shallow D − ground state in silicon: Role of dielectric mismatch. Phys. Rev. B 82(7), 075317 (2010)
Koren, E., Berkovitch, N., Rosenwaks, Y.: Measurement of active dopant distribution and diffusion in individual silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 10(4), 1163–1167 (2010)
Bryant, G.W.: Hydrogenic impurity states in quantum-well wires. Phys. Rev. B 29(12), 6632–6639 (1984)
Rurali, R., Aradi, B., Frauenheim, T., Gali, A.: Donor levels in Si nanowires determined by hybrid-functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 79(11), 115303 (2009)
Niquet, Y.M., Lherbier, A., Quang, N.H., Fernández-Serra, M.V., Blase, X., Delerue, C.: Electronic structure of semiconductor nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 73(16), 165319 (2006)
Peelaers, H., Partoens, B., Peeters, F.M.: Formation and segregation energies of B and P doped and BP codoped silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 6(12), 2781–2784 (2006)
Fernández-Serra, M.V., Adessi, C., Blase, X.: Surface segregation and backscattering in doped silicon nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(16), 166805 (2006)
Cui, Y., Duan, X., Hu, J., Lieber, C.: Doping and electrical transport in silicon nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 104(22), 5213–5216 (2000)
Yu, J.Y., Chung, S.W., Heath, J.R.: Silicon nanowires: Preparation, device fabrication, and transport properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 104(50), 11864–11870 (2000)
Wang, Y., Lew, K.K., Ho, T.T., Pan, L., Novak, S.W., Dickey, E.C., Redwing, J.M., Mayer, T.S.: Use of phosphine as an n-type dopant source for vapor-liquid-solid growth of silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 5(11), 2139–2143 (2005)
Nah, J., Varahramyan, K., Liu, E.S., Banerjee, S.K., Tutuc, E.: Doping of Ge-Si x Ge1−x core-shell nanowires using low energy ion implantation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(20), 203108 (2008)
Nah, J., Liu, E.S., Shahrjerdi, D., Varahramyan, K.M., Banerjee, S.K., Tutuc, E.: Realization of dual-gated Ge-Si x Ge1−x core-shell nanowire field effect transistors with highly doped source and drain. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(6), 063117 (2009)
Lauhon, L.J., Gudiksen, M.S., Wang, D., Lieber, C.M.: Epitaxial core-shell and core-multishell nanowire heterostructures. Nature 420(6911), 57 (2002)
Amato, M., Ossicini, S., Rurali, R.: Band-offset driven efficiency of the doping of SiGe core-shell nanowires. Nano Lett. 11(2), 594–598 (2011)
Lu, W., Xiang, J., Timko, B.P., Wu, Y., Lieber, C.M.: One-dimensional hole gas in germanium/silicon nanowire heterostructures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102(29), 10046 (2005)
Dayeh, S.A., Gin, A.V., Picraux, S.T.: Advanced core/multishell germanium/silicon nanowire heterostructures: Morphology and transport. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(16), 163112 (2011)
Ossicini, S., Amato, M., Guerra, R., Palummo, M., Pulci, O.: Silicon and germanium nanostructures for photovoltaic applications: Ab-initio results. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5(10), 1637–1649 (2010)
Joshi, G., Lee, H., Lan, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, G., Wang, D., Gould, R.W., Cuff, D.C., Tang, M.Y., Dresselhaus, M.S., Chen, G., Ren, Z.: Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in nanostructured p-type silicon germanium bulk alloys. Nano Lett. 8(12), 4670–4674 (2008)
Gudiksen, M.S., Lauhon, L.J., Wang, J., Smith, D.C., Lieber, C.M.: Growth of nanowire superlattice structures for nanoscale photonics and electronics. Nature 415(6872), 617–620 (2002)
Hohenberg, P., Kohn, W.: Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 136(3B) (1964)
Kohn, W., Sham, L.J.: Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 140(4A) (1965)
Perdew, J.P., Kurt, S.: Primer in Density Functional Theory. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Perdew, J.P., Zunger, A.: Self-interaction correction to density-functional approximations for many-electron systems. Phys. Rev. B 23(10), 5048–5079 (1981)
Onida, G., Reining, L., Rubio, A.: Electronic excitations: density-functional versus many-body Green’s-function approaches. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74(2), 601–659 (2002)
Runge, E., Gross, E.K.U.: Density-functional theory for time-dependent systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52(12), 997 (1984)
Soler, J.M., Artacho, E., Gale, J.D., García, A., Junquera, J., Ordejón, P., Sánchez-Portal, D.: The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys., Condens. Matter 14(11), 2745–2779 (2002)
Amato, M., Palummo, M., Ossicini, S.: SiGe nanowires: Structural stability, quantum confinement, and electronic properties. Phys. Rev. B 80(23), 235333 (2009)
Amato, M., Palummo, M., Ossicini, S.: Reduced quantum confinement effect and electron-hole separation in SiGe nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 79(20), 201302(R) (2009)
Palummo, M., Amato, M., Ossicini, S.: Ab initio optoelectronic properties of SiGe nanowires: Role of many-body effects. Phys. Rev. B 82(7), 073305 (2010)
Amato, M., Palummo, M., Ossicini, S.: Segregation, quantum confinement effect and band offset for [110] SiGe NWs. Phys. Status Solidi B 247(8), 2096 (2010)
Wu, Y., Cui, Y., Huynh, L., Barrelet, C.J., Bell, D.C., Lieber, C.M.: Controlled growth and structures of molecular-scale silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 4(3), 433–436 (2004)
Tutuc, E., Chu, J., Ott, J., Guha, S.: Doping of germanium nanowires grown in presence of PH3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(26), 263101 (2006)
Peelaers, H., Partoens, B., Peeters, F.M.: Properties of B and P doped Ge nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(26), 263103 (2007)
Nduwimana, A., Wang, X.Q.: Charge carrier separation in modulation doped coaxial semiconductor nanowires. Nano Lett. 9(1), 283–286 (2009)
Park, J.S., Ryu, B., Chang, K.J.: Stability of donor-pair defects in Si1−x Ge x alloy nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(21), 10345–10350 (2011)
Zhang, S.B., Northrup, J.E.: Chemical potential dependence of defect formation energies in GaAs: Application to Ga self-diffusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2339–2342 (1991)
Derycke, V., Soukiassian, P.G., Amy, F., Chabal, Y.J., D’angelo, M.D., Enriquez, H.B., Silly, M.G.: Nanochemistry at the atomic scale revealed in hydrogen-induced semiconductor surface metallization. Nat. Mater. 2(4), 253–258 (2003)
Rurali, R., Cartoixà, X.: Theory of defects in one-dimensional systems: Application to Al-catalyzed Si nanowires. Nano Lett. 9(3), 975–979 (2009)
Peressi, M., Binggeli, N., Baldereschi, A.: Band engineering at interfaces: theory and numerical experiments. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 31(11), 1273 (1998)
Zunger, A.: Theoretical predictions of electronic materials and their properties. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 3(1), 32–37 (1998)
Ciraci, S., Batra, I.P.: Strained Si/Ge superlattices: Structural stability, growth, and electronic properties. Phys. Rev. B 38(3), 1835–1848 (1988)
Van de Walle, C., Martin, R.: Theoretical study of band offsets at semiconductor interfaces. Phys. Rev. B 35(15), 8154–8165 (1987)
Van de Walle, C.G., Martin, R.M.: Theoretical study of Si/Ge interfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 3(4), 1256–1259 (1985)
Peköz, R., Raty, J.Y.: From bare Ge nanowire to Ge/Si core/shell nanowires: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 80(15), 155432 (2009)
Musin, R.N., Wang, X.Q.: Structural and electronic properties of epitaxial core-shell nanowire heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 71(15), 155318 (2005)
Migas, D.B., Borisenko, V.E.: Structural, electronic, and optical properties of 〈001〉-oriented SiGe nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 76(3), 035440 (2007)
Musin, R.N., Wang, X.Q.: Quantum size effect in core-shell structured silicon-germanium nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 74(16), 165308 (2006)
Peng, X., Logan, P.: Electronic properties of strained Si/Ge core-shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 143119 (2010)
Yang, L., Musin, R.N., Wang, X.Q., Chou, M.Y.: Quantum confinement effect in Si/Ge core-shell nanowires: First-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 77(19), 195325 (2008)
Nduwimana, A., Musin, R.N., Smith, A.M., Wang, X.Q.: Spatial carrier confinement in core-shell and multishell nanowire heterostructures. Nano Lett. 8(10), 3341–3344 (2008)
Liu, N., Li, Y.R., Lu, N., Yao, Y.X., Fang, X.W., Wang, C.Z., Ho, K.M.: Charge localization in [112] Si/Ge and Ge/Si core-shell nanowires. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 43(27), 275404 (2010)
Peköz, R., Malcığlu, O.B., Raty, J.Y.: First-principles design of efficient solar cells using two-dimensional arrays of core-shell and layered SiGe nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 83(3), 035317 (2011)
Peng, X., Tang, F., Logan, P.: Band structure of Si/Ge core-shell nanowires along the [110] direction modulated by external uniaxial strain. J. Phys., Condens. Matter 23(11), 115502 (2011)
Kagimura, R., Nunes, R.W., Chacham, H.: Surface dangling-bond states and band lineups in hydrogen-terminated Si, Ge, and Ge/Si nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(2), 026801 (2007)
Peelaers, H., Partoens, B., Peeters, F.M.: Electronic and dynamical properties of Si/Ge core-shell nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 82(11), 113411 (2010)
Huang, S., Yang, L.: Strain engineering of band offsets in Si/Ge core-shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(9), 093114 (2011)
Yan, B., Frauenheim, T., Gali, A.: Gate-controlled donor activation in silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 10(9), 3791–3795 (2010)
Zhang, S., Lopez, F.J., Hyun, J.K., Lauhon, L.J.: Direct detection of Hole Gas in Ge-Si Core-Shell nanowires by enhanced Raman scattering. Nano Lett. 10(11), 4483–4487 (2010)
Li, L., Smith, D.J., Dailey, E., Madras, P., Drucker, J., McCartney, M.R.: Observation of hole accumulation in Ge/Si Core/Shell nanowires using off-axis electron holography. Nano Lett. 11(2), 493–497 (2011)
Peng, K.Q., Lee, S.T.: Silicon nanowires for photovoltaic solar energy conversion. Adv. Mater. 23(2), 198–215 (2011)
Acknowledgements
M. Amato and S. Ossicini greatly acknowledge the Transnational Access Programme of the HPC-EUROPA2 Project and the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement 245977, Ministero Affari Esteri, Direzione Generale per la Promozione and Cooperazione Culturale. Funding under Contract Nos. TEC2009-06986, FIS2009-12721-C04-03, and CSD2007-00041 are greatly acknowledged. The authors thankfully acknowledge the computer resources, technical expertise and assistance provided by the Res Española de Supercomputaciòn and the CINECA award under the ISCRA initiative (No. HP10BQNB3U), for the availability of high performance computing resources and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amato, M., Rurali, R. & Ossicini, S. Doping of SiGe core-shell nanowires. J Comput Electron 11, 272–279 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-012-0394-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-012-0394-y