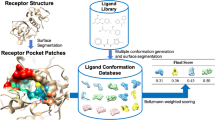
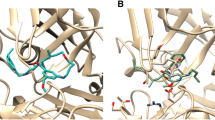
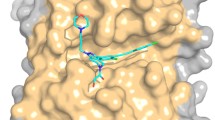
Abstract
Using the D3R Grand Challenge 4 dataset containing Beta-secretase 1 (BACE) and Cathepsin S (CatS) inhibitors, we have evaluated the performance of our in-house docking workflow that involves in the first step the selection of the most suitable docking software for the system of interest based on structural and functional information available in public databases, followed by the docking of the dataset to predict the binding modes and ranking of ligands. The macrocyclic nature of the BACE ligands brought additional challenges, which were dealt with by a careful preparation of the three-dimensional input structures for ligands. This provided top-performing predictions for BACE, in contrast with CatS, where the predictions in the absence of guiding constraints provided poor results. These results highlight the importance of previous structural knowledge that is needed for correct predictions on some challenging targets. After the end of the challenge, we also carried out free energy calculations (i.e. in a non-blinded manner) for CatS using the pmx software and several force fields (AMBER, Charmm). Using knowledge-based starting pose construction allowed reaching remarkable accuracy for the CatS free energy estimates. Interestingly, we show that the use of a consensus result, by averaging the results from different force fields, increases the prediction accuracy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy VB, Sun S, Azimi E, Elmariah SB, Dong X, Lerner EA (2015) Redefining the concept of protease-activated receptors: cathepsin S evokes itch via activation of Mrgprs. Nat Commun 6:7864. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8864
Ainscough JS, Macleod T, McGonagle D, Brakefield R, Baron JM, Alase A, Wittmann M, Stacey M (2017) Cathepsin S is the major activator of the psoriasis-associated proinflammatory cytokine IL-36\(\gamma\). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(13):E2748–E2757. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1620954114
Elmariah SB, Reddy VB, Lerner EA (2014) Cathepsin S signals via PAR2 and generates a novel tethered ligand receptor agonist. PLoS ONE 9(6):e99702. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099702
Xu J, Wang H, Ding K, Lu X, Li T, Wang J, Wang C (2013) Inhibition of cathepsin S produces neuroprotective effects after traumatic brain injury in mice. Mediat Inflamm 187:873. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/187873
Thurmond RL, Sun S, Karlsson L, Edwards JP (2005) Cathepsin S inhibitors as novel immunomodulators. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 6(5):473–482
Link JO, Zipfel S (2006) Advances in cathepsin S inhibitor design. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 9(4):471–482
Wiener JJM, Sun S, Thurmond RL (2010) Recent advances in the design of cathepsin S inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 10(7):717–732. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802610791113432
Lee-Dutra A, Wiener DK, Sun S (2011) Cathepsin S inhibitors: 2004–2010. Expert Opin Ther Pat 21(3):311–337. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543776.2011.553800
Wilkinson RDA, Williams R, Scott CJ, Burden RE (2015) Cathepsin S: therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic potential. Biol Chem 396(8):867–882. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2015-0114
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S, Mendiaz EA, Denis P, Teplow DB, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, Luo Y, Fisher S, Fuller J, Edenson S, Lile J, Jarosinski MA, Biere AL, Curran E, Burgess T, Louis JC, Collins F, Treanor J, Rogers G, Citron M (1999) Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286(5440):735–741. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5440.735
Willem M, Garratt AN, Novak B, Citron M, Kaufmann S, Rittger A, DeStrooper B, Saftig P, Birchmeier C, Haass C (2006) Control of peripheral nerve myelination by the beta-secretase BACE1. Science 314(5799):664–666. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1132341
Jonsson T, Atwal JK, Steinberg S, Snaedal J, Jonsson PV, Bjornsson S, Stefansson H, Sulem P, Gudbjartsson D, Maloney J, Hoyte K, Gustafson A, Liu Y, Lu Y, Bhangale T, Graham RR, Huttenlocher J, Bjornsdottir G, Andreassen OA, Jönsson EG, Palotie A, Behrens TW, Magnusson OT, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Watts RJ, Stefansson K (2012) A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. Nature 488(7409):96–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11283
Baxter EW, Conway KA, Kennis L, Bischoff F, Mercken MH, Winter HLD, Reynolds CH, Tounge BA, Luo C, Scott MK, Huang Y, Braeken M, Pieters SMA, Berthelot DJC, Masure S, Bruinzeel WD, Jordan AD, Parker MH, Boyd RE, Qu J, Alexander RS, Brenneman DE, Reitz AB (2007) 2-Amino-3,4-dihydroquinazolines as inhibitors of BACE-1 (beta-site APP cleaving enzyme): use of structure based design to convert a micromolar hit into a nanomolar lead. J Med Chem 50(18):4261–4264. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0705408
Panza F, Lozupone M, Solfrizzi V, Sardone R, Piccininni C, Dibello V, Stallone R, Giannelli G, Bellomo A, Greco A, Daniele A, Seripa D, Logroscino G, Imbimbo BP (2018) BACE inhibitors in clinical development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 18(11):847–857. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1531706
Burki T (2018) Alzheimer’s disease research: the future of BACE inhibitors. Lancet 391(10139):2486. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31425-9
Lerchner A, Machauer R, Betschart C, Veenstra S, Rueeger H, McCarthy C, Tintelnot-Blomley M, Jaton AL, Rabe S, Desrayaud S, Enz A, Staufenbiel M, Paganetti P, Rondeau JM, Neumann U (2010) Macrocyclic BACE-1 inhibitors acutely reduce Abeta in brain after po application. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(2):603–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.11.092
Turkenburg JP, Lamers MBAC, Brzozowski AM, Wright LM, Hubbard RE, Sturt SL, Williams DH (2002) Structure of a Cys25->Ser mutant of human cathepsin S. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58(Pt 3):451–455. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444901021825
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):235–242. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Hong L, Turner RT 3rd, Koelsch G, Shin D, Ghosh AK, Tang J (2002) Crystal structure of memapsin 2 (beta-secretase) in complex with an inhibitor OM00-3. Biochemistry 41(36):963–967. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi026232n
Hattori Y, Kobayashi K, Deguchi A, Nohara Y, Akiyama T, Teruya K, Sanjoh A, Nakagawa A, Yamashita E, Akaji K (2015) Evaluation of transition-state mimics in a superior BACE1 cleavage sequence as peptide-mimetic BACE1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 23(17):5626–5640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.07.023
Neumann U, Ufer M, Jacobson LH, Rouzade-Dominguez ML, Huledal G, Kolly C, Lüönd RM, Machauer R, Veenstra SJ, Hurth K, Rueeger H, Tintelnot-Blomley M, Staufenbiel M, Shimshek DR, Perrot L, Frieauff W, Dubost V, Schiller H, Vogg B, Beltz K, Avrameas A, Kretz S, Pezous N, Rondeau JM, Beckmann N, Hartmann A, Vormfelde S, David OJ, Galli B, Ramos R, Graf A, Lopez Lopez C (2018) The BACE-1 inhibitor CNP520 for prevention trials in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 10(11):e9316. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201809316
van Zundert GCP, Hudson BM, de Oliveira SHP, Keedy DA, Fonseca R, Heliou A, Suresh P, Borrelli K, Day T, Fraser JS, van den Bedem H (2018) qFit-ligand reveals widespread conformational heterogeneity of drug-like molecules in X-ray electron density maps. J Med Chem 61(24):183–198. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01292
Shiba T, Kametaka S, Kawasaki M, Shibata M, Waguri S, Uchiyama Y, Wakatsuki S (2004) Insights into the phosphoregulation of beta-secretase sorting signal by the VHS domain of GGA1. Traffic 5(6):437–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00188.x
Hong L, Tang J (2004) Flap position of free memapsin 2 (beta-secretase), a model for flap opening in aspartic protease catalysis. Biochemistry 43(16):4689–4695. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0498252
Clarke B, Demont E, Dingwall C, Dunsdon R, Faller A, Hawkins J, Hussain I, MacPherson D, Maile G, Matico R, Milner P, Mosley J, Naylor A, O’Brien A, Redshaw S, Riddell D, Rowland P, Soleil V, Smith KJ, Stanway S, Stemp G, Sweitzer S, Theobald P, Vesey D, Walter DS, Ward J, Wayne G (2008) BACE-1 inhibitors part 1: identification of novel hydroxy ethylamines (HEAs). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(3):1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.12.017
Beswick P, Charrier N, Clarke B, Demont E, Dingwall C, Dunsdon R, Faller A, Gleave R, Hawkins J, Hussain I, Johnson CN, MacPherson D, Maile G, Matico R, Milner P, Mosley J, Naylor A, O’Brien A, Redshaw S, Riddell D, Rowland P, Skidmore J, Soleil V, Smith KJ, Stanway S, Stemp G, Stuart A, Sweitzer S, Theobald P, Vesey D, Walter DS, Ward J, Wayne G (2008) BACE-1 inhibitors part 3: identification of hydroxy ethylamines (HEAs) with nanomolar potency in cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(3):1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.12.020
Chaput L, Selwa E, Elisée E, Iorga BI (2019) Blinded evaluation of cathepsin S inhibitors from the D3RGC3 dataset using molecular docking and free energy calculations. J Comput Aided Mol Des 33(1):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-018-0161-7
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Liu T, Lin Y, Wen X, Jorissen RN, Gilson MK (2007) BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D198–D201. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl999
Machauer R, Laumen K, Veenstra S, Rondeau JM, Tintelnot-Blomley M, Betschart C, Jaton AL, Desrayaud S, Staufenbiel M, Rabe S, Paganetti P, Neumann U (2009) Macrocyclic peptidomimetic beta-secretase (BACE-1) inhibitors with activity in vivo. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(5):1366–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.01.055
Clarke B, Demont E, Dingwall C, Dunsdon R, Faller A, Hawkins J, Hussain I, MacPherson D, Maile G, Matico R, Milner P, Mosley J, Naylor A, O’Brien A, Redshaw S, Riddell D, Rowland P, Soleil V, Smith KJ, Stanway S, Stemp G, Sweitzer S, Theobald P, Vesey D, Walter DS, Ward J, Wayne G (2008) BACE-1 inhibitors part 2: identification of hydroxy ethylamines (HEAs) with reduced peptidic character. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(3):1017–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.12.019
Charrier N, Clarke B, Cutler L, Demont E, Dingwall C, Dunsdon R, East P, Hawkins J, Howes C, Hussain I, Jeffrey P, Maile G, Matico R, Mosley J, Naylor A, O’Brien A, Redshaw S, Rowland P, Soleil V, Smith KJ, Sweitzer S, Theobald P, Vesey D, Walter DS, Wayne G (2008) Second generation of hydroxyethylamine BACE-1 inhibitors: optimizing potency and oral bioavailability. J Med Chem 51(11):3313–3317. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm800138h
Sandgren V, Agback T, Johansson PO, Lindberg J, Kvarnström I, Samuelsson B, Belda O, Dahlgren A (2012) Highly potent macrocyclic BACE-1 inhibitors incorporating a hydroxyethylamine core: design, synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of enzyme inhibitor complexes. Bioorg Med Chem 20(14):4377–4389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.05.039
Hanessian S, Shao Z, Betschart C, Rondeau JM, Neumann U, Tintelnot-Blomley M (2010) Structure-based design and synthesis of novel P2/P3 modified, non-peptidic beta-secretase (BACE-1) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(6):1924–1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.139
Sealy JM, Truong AP, Tso L, Probst GD, Aquino J, Hom RK, Jagodzinska BM, Dressen D, Wone DWG, Brogley L, John V, Tung JS, Pleiss MA, Tucker JA, Konradi AW, Dappen MS, Toth G, Pan H, Ruslim L, Miller J, Bova MP, Sinha S, Quinn KP, Sauer JM (2009) Design and synthesis of cell potent BACE-1 inhibitors: structure-activity relationship of P1’ substituents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(22):6386–6391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.09.061
Verdonk ML, Cole JC, Hartshorn MJ, Murray CW, Taylor RD (2003) Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 52(4):609–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.10465
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Pennington LD, Whittington DA, Bartberger MD, Jordan SR, Monenschein H, Nguyen TT, Yang BH, Xue QM, Vounatsos F, Wahl RC, Chen K, Wood S, Citron M, Patel VF, Hitchcock SA, Zhong W (2013) Hydroxyethylamine-based inhibitors of BACE1: P1–P3 macrocyclization can improve potency, selectivity, and cell activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(15):4459–4464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.05.028
Gapsys V, Michielssens S, Peters JH, de Groot BL, Leonov H (2015) Calculation of binding free energies. In: Kukol A (eds) Molecular modeling of proteins. Methods in molecular biology (Methods and protocols), vol 1215. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 173–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1465-4_9
Wang L, Deng Y, Knight JL, Wu Y, Kim B, Sherman W, Shelley JC, Lin T, Abel R (2013) Modeling local structural rearrangements using FEP/REST: application to relative binding affinity predictions of CDK2 inhibitors. J Chem Theory Comput 9(2):1282–1293. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct300911a
Gapsys V, Michielssens S, Seeliger D, de Groot BL (2015) Pmx: automated protein structure and topology generation for alchemical perturbations. J Comput Chem 36(5):348–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23804
Crooks GE (1999) Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences. Phys Rev E 60(3):2721–2726. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.60.2721
Shirts MR, Bair E, Hooker G, Pande VS (2003) Equilibrium free energies from nonequilibrium measurements using maximum-likelihood methods. Phys Rev Lett 91(14):140601. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.140601
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E (2015) GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
Hornak V, Abel R, Okur A, Strockbine B, Roitberg A, Simmerling C (2006) Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 65(3):712–725. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21123
Best RB, Hummer G (2009) Optimized molecular dynamics force fields applied to the helix-coil transition of polypeptides. J Phys Chem B 113(26):9004–9015. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp901540t
Lindorff-Larsen K, Piana S, Palmo K, Maragakis P, Klepeis JL, Dror RO, Shaw DE (2010) Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 78(8):1950–1958. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22711
Huang J, Rauscher S, Nawrocki G, Ran T, Feig M, de Groot BL, Grubmüller H, MacKerell AD Jr (2017) CHARMM36m: an improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins. Nat Methods 14:71–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4067
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general Amber force field. J Comput Chem 25(9):1157–1174. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20035
Yesselman JD, Price DJ, Knight JL, Brooks CL III (2012) MATCH: an atom-typing toolset for molecular mechanics force fields. J Comput Chem 33(2):189–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21963
Vanommeslaeghe K, Hatcher E, Acharya C, Kundu S, Zhong S, Shim J, Darian E, Guvench O, Lopes P, Vorobyov I, Mackerell D (2010) CHARMM general force field: a force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J Comput Chem 31(4):671–690. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21367
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79(2):926–935. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.445869
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: an Nlog(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.464397
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.470117
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18(12):1463–1472. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199709)18:12%3C1463::AID-JCC4%3E3.0.CO;2-H
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M (2007) Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys 126(014):101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2408420
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52(12):7182–7190. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.328693
Gapsys V, Michielssens S, Seeliger D, de Groot BL (2016) Accurate and rigorous prediction of the changes in protein free energies in a large-scale mutation scan. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:7364–7368. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201510054
Gathiaka S, Liu S, Chiu M, Yang H, Stuckey JA, Kang YN, Delproposto J, Kubish G, Dunbar JB, Carlson HA, Burley SK, Walters WP, Amaro RE, Feher VA, Gilson MK (2016) D3R grand challenge 2015: evaluation of protein-ligand pose and affinity predictions. J Comput Aided Mol Des 30(9):651–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-016-9946-8
Schrödinger LLC (2015) The PyMOL molecular graphics system, version 1.8.0.3
Hagberg A, Swart P, Schult DA (2008) Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. Tech. rep., Los Alamos National Lab.(LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
Hunter JD (2007) Matplotlib: a 2D graphics environment. Comput Sci Eng 9(3):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCSE.2007.55
Surpateanu G, Iorga BI (2012) Evaluation of docking performance in a blinded virtual screening of fragment-like trypsin inhibitors. J Comput Aided Mol Des 26(5):595–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-011-9526-x
Colas C, Iorga BI (2014) Virtual screening of the SAMPL4 blinded HIV integrase inhibitors dataset. J Comput Aided Mol Des 28(4):455–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-014-9707-5
Martiny VY, Martz F, Selwa E, Iorga BI (2016) Blind pose prediction, scoring, and affinity ranking of the CSAR 2014 dataset. J Chem Inf Model 56(6):996–1003. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00337
Selwa E, Martiny VY, Iorga BI (2016) Molecular docking performance evaluated on the D3R Grand Challenge 2015 drug-like ligand datasets. J Comput Aided Mol Des 30(9):829–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-016-9983-3
Selwa E, Elisée E, Zavala A, Iorga BI (2018) Blinded evaluation of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) ligands binding using molecular docking and free energy calculations. J Comput Aided Mol Des 32(1):273–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-017-0054-1
Gapsys V, de Groot BL (2017) Alchemical free energy calculations for nucleotide mutations in protein-DNA complexes. J Chem Theory Comput 13(12):6275–6289. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00849
Aldeghi M, Gapsys V, de Groot BL (2018) Accurate estimation of ligand binding affinity changes upon protein mutation. ACS Central Sci 4(12):1708–1718. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.8b00717
Funding
The funding was provided by Agence Nationale de la Recherche (FR) (Grant Nos. ANR-10-LABX-33, ANR-14-JAMR-0002); Conseil Régional, Île-de-France (DIM Malinf); Université Paris-Saclay (Globetalkers 2019); H2020 European Research Council (ERC-2012-ADG_20120314, Grant Agreement 322947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research reported in this publication was supported by grants ANR-10-LABX-33 (LabEx LERMIT) and ANR-14-JAMR-0002 (JPIAMR) from the French National Research Agency (ANR), by the Région Ile-de-France (DIM Malinf), by the Université Paris-Saclay (Globetalkers 2019) and by European Research Council grant ERC-2012-ADG_20120314 (Grant Agreement 322947).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elisée, E., Gapsys, V., Mele, N. et al. Performance evaluation of molecular docking and free energy calculations protocols using the D3R Grand Challenge 4 dataset. J Comput Aided Mol Des 33, 1031–1043 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-019-00232-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-019-00232-w