Summary
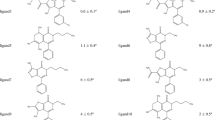
The usefulness of free-energy calculations in non-academic environments, in general, and in the pharmaceutical industry, in particular, is a long-time debated issue, often considered from the angle of cost/performance criteria. In the context of the rational drug design of low-affinity, non-peptide inhibitors to the SH2 domain of the pp60src tyrosine kinase, the continuing difficulties encountered in an attempt to obtain accurate free-energy estimates are addressed. free-energy calculations can provide a convincing answer, assuming that two key-requirements are fulfilled: (i) thorough sampling of the configurational space is necessary to minimize the statistical error, hence raising the question: to which extent can we sacrifice the computational effort, yet without jeopardizing the precision of the free-energy calculation? (ii) the sensitivity of binding free-energies to the parameters utilized imposes an appropriate parametrization of the potential energy function, especially for non-peptide molecules that are usually poorly described by multipurpose macromolecular force fields. Employing the free-energy perturbation method, accurate ranking, within ±0.7 kcal/mol, is obtained in the case of four non-peptide mimes of a sequence recognized by the pp60src SH2 domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soriano P., Montgomery C., Geske R., Bradley A.(1991). Targeted disruption of the c-src proto-oncogene leads to osteopetrosis in mice. Cell 64: 693702
Lange G., Lesuisse D., Deprez P., Schoot B., Loenze P., Benard D., Marquette J.P., Broto P., Sarubbi E., Mandine E.(2002). Principles governing the binding of a class of non- peptidic inhibitors to the SH2 domain of src studied by X-ray analysis. J. Med. Chem. 45: 2915–2922
Lange G., Lesuisse D., Deprez P., Schoot B., Loenze P., Benard D., Marquette J.P., Broto P., Sarubbi E., Mandine E.(2003). Requirements for specific binding of low affinity inhibitor fragments to the SH2 domain of pp60Src are identical to those for high affinity binding of full length inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 46: 5184–5195
Gao J., Kuczera K., Tidor B., Karplus M.(1989). Hidden thermodynamics of mutant proteins: A molecular dynamics analysis. Science 244: 1069–1072
Zwanzig R.W.(1954). High-temperature equation of state by a perturbation method. I. Nonpolar gases. J. Chem. Phys. 22: 1420–1426
Hénin J., Pohorille A., Chipot C.(2005). Insights into the recognition and association of transmembrane α-helices. The free-energy of α-helix dimerization in glycophorin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127: 8478–8484
Mark A.E. (1998). free-energy Perturbation Calculations. In: Schleyer P.v.R., Allinger N.L., Clark T., Gasteiger J., Kollman P.A., Schaefer H.F.,III, Schreiner P.R. (eds), Encyclopedia of computational chemistry vol. 2. Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp. 1070–1083
Widom B.(1963). Some topics in the theory of fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 39: 2808–2812
Tembe B.L., McCammon J.A.(1984). Ligand-receptor interactions. Comp. Chem. 8: 281–283
Jorgensen W.L., Chandrasekhar J., Madura J.D., Impey R.W., Klein M.L.(1983). Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79: 926–935
Chipot C.(2003). Rational determination of charge distributions for free-energy calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 24: 409–15
Kalé L., Skeel R., Bhandarkar M., Brunner R., Gursoy A., Krawetz N., Phillips J., Shinozaki A., Varadarajan K., Schulten K.(1999). NAMD2: Greater scalability for parallel molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 151: 283–312
Bhandarkar, M., Brunner, R., Chipot, C., Dalke, A., Dixit, S., Grayson, P., Gullingsrud, J., Gursoy, A., Humphrey,W., Hurwitz, D., Krawetz, N., Nelson, M., Phillips, J., Shinozaki, A., Zheng, G., Zhu, F., NAMD users guide, Version 2.5. Theoretical Biophysics Group, University of Illinois and Beckman Institute, 405 North Mathews, Urbana, Illinois 61801, September 2003.
Feller S.E., Zhang Y.H., Pastor R.W., Brooks B.R.(1995). Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulations– The Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 103: 4613–4621
Darden T.A., York D.M., Pedersen L.G.(1993). Particle mesh Ewald: An NlogN method for ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 98: 10089–10092
Essman U., Perera L., Berkowitz M., Darden T., Lee H., Pedersen L.G.(1995). A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 103: 8577–8593
Brandsdal B.O., Österberg F., Almlöf M., Feierberg I., Luzhkov V.B., Åqvist J. (2003). free-energy calculations and ligand binding, Adv. Protein Chem. 66:123–158
Acknowledgments
Jérôme Hénin and Bernard Maigret are gratefully acknowledged for fruitful and motivating discussions. The authors are indebted to Robert Gilli (Université d’Aix-Marseille) for sharing the experimental micro-calorimetry data prior to publication. The Centre Informatique National de l’Enseignement Supérieur (CINES) and the centre de Calcul Réseaux et Visualisation Haute Performance (CRVHP) is acknowledged for generous provision of CPU time on their SGI Origin 3000 architectures. This work was funded in part by a Hoechst Marion Roussel sponsorship (GIP FR98 CHM 032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chipot, C., Rozanska, X. & Dixit, S.B. Can free energy calculations be fast and accurate at the same time? Binding of low-affinity, non-peptide inhibitors to the SH2 domain of the src protein. J Comput Aided Mol Des 19, 765–770 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-005-9021-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-005-9021-3