Abstract
Purpose
The vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) is crucial for normal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis during pregnancy, and alterations in the VEGFA gene expression were detected in women with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion (IRSA) and spontaneously aborted conceptuses. Our aim was to evaluate whether there is an association between the functional −2549 insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene and IRSA in reproductive couples.
Methods
We performed a case-control study involving 149 women and their 140 partners with three or more IRSA and 149 control women and men. Allele-specific polymerase chain reaction was used for genotyping.
Results
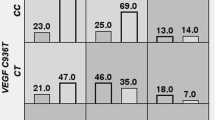
We found no association of the −2549 I/D polymorphism with IRSA in women. However, men with the DD genotype have a 1.75-fold increased risk of IRSA compared with men carrying the ID and II genotypes (95 % confidence interval (CI) = 1.05–2.93, P = 0.032). In addition, the D allele in men contributes to a 1.42-fold increased risk of IRSA (95 % CI = 1.02–1.97, P = 0.036) compared to men carrying the I allele.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the −2549 I/D polymorphism in the VEGFA gene in men might be associated with IRSA. Additional genetic association studies including both partners, as well as expression studies, are needed to elucidate the role of this polymorphism in IRSA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jauniaux E, Farquharson RG, Christiansen OB, Exalto N. Evidence-based guidelines for the investigation and medical treatment of recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod. 2006;21:2216–22.
Rull K, Nagirnaja L, Laan M. Genetics of recurrent miscarriage: challenges, current knowledge, future directions. Front Genet. 2012;3:34.
Burton GJ, Charnock-Jones DS, Jauniaux E. Regulation of vascular growth and function in the human placenta. Reproduction. 2009;138:895–902.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Van Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:549–80.
Andraweera PH, Dekker GA, Roberts CT. The vascular endothelial growth factor family in adverse pregnancy outcomes. Hum Reprod Update. 2012;18:436–57.
Rogers MS, D’Amato RJ. The effect of genetic diversity on angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:561–74.
Su MT, Lin SH, Chen YC. Genetic association studies of angiogenesis- and vasoconstriction-related genes in women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2011;17:803–12.
Zhang B, Dai B, Zhang X, Wang Z. Vascular endothelial growth factor and recurrent spontaneous abortion: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2012;507:1–8.
Xu X, Du C, Li H, Du J, Yan X, Peng L, et al. Association of VEGF genetic polymorphisms with recurrent spontaneous abortion risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0123696.
Chuzhanova NA, Anassis EJ, Ball EV, Krawczak M, Cooper DN. Meta-analysis of indels causing human genetic disease: mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of local DNA sequence complexity. Hum Mutat. 2003;21:28–44.
Mills RE, Luttig CT, Larkins CE, Beauchamp A, Tsui C, Pittard WS, et al. An initial map of insertion and deletion (INDEL) variation in the human genome. Genome Res. 2006;16:1182–90.
Brogan IJ, Khan N, Isaac K, Hutchinson JA, Pravica V, Hutchinson IV. Novel polymorphisms in the promoter and 5′ UTR regions of the human vascular endothelial growth factor gene. Hum Immunol. 1999;60:1245–9.
Yang B, Cross DF, Ollerenshaw M, Millward BA, Demaine AG. Polymorphisms of the vascular endothelial growth factor and susceptibility to diabetic microvascular complications in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2003;17:1–6.
Pereza N, Ostojić S, Volk M, Kapović M, Peterlin B. Matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 3 and 9 functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms in idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;24:567–75.
Atzeni F, Boiardi L, Vaglio A, Nicoli D, Farnetti E, Palmisano A, et al. TLR-4 and VEGF polymorphisms in chronic periaortitis. PLoS One. 2013;8, e62330.
Kapahi R, Manjari M, Uppal MS, Singh NR, Sambyal V, Guleria K. Association of -2549 insertion/deletion polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor with breast cancer in North Indian patients. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2013;17:242–8.
Buraczynska M, Ksiazek P, Baranowicz-Gaszczyk I, Jozwiak L. Association of the VEGF gene polymorphism with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:827–32.
Amle D, Mir R, Khaneja A, Agarwal S, Ahlawat R, Ray PC, et al. Association of 18 bp insertion/deletion polymorphism, at -2549 position of VEGF gene, with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients of North Indian population. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015;14:19.
Breunis WB, Biezeveld MH, Geissler J, Ottenkamp J, Kuipers IM, Lam J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene haplotypes in Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1588–94.
Allanore Y, Borderie D, Airo P, Guiducci S, Czirják L, Nasonov EL, et al. Lack of association between three vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms and systemic sclerosis: results from a multicenter EUSTAR study of European Caucasian patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:257–9.
Aggarwal S, Parveen F, Faridi RM, Phadke S, Borkar M, Agrawal S. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms in North Indian patients with recurrent miscarriages. Reprod Biomed Online. 2011;22:59–64.
Dekker G, Robillard PY, Roberts C. The etiology of preeclampsia: the role of the father. J Reprod Immunol. 2011;89:126–32.
Udry S, Aranda FM, Latino JO, de Larrañaga GF. Paternal factor V Leiden and recurrent pregnancy loss: a new concept behind fetal genetics? J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:666–9.
Asadpor U, Totonchi M, Sabbaghian M, Hoseinifar H, Akhound MR, Zari Moradi S, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease (USP26) gene alterations associated with male infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) in Iranian infertile patients. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30:923–31.
Andraweera P, Thompson S, Zhang V, Nowak R, Dekker G, Roberts C. Maternal, paternal and fetal single nucleotide polymorphisms in vascular endothelial growth factor family genes associate with pregnancy complications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:S13.
Pang L, Wei Z, Li O, Huang R, Qin J, Chen H, et al. An increase in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF soluble receptor-1 (sFlt-1) are associated with early recurrent spontaneous abortion. PLoS One. 2013;8, e75759.
Vuorela P, Carpén O, Tulppala M, Halmesmäki E. VEGF, its receptors and the tie receptors in recurrent miscarriage. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:276–82.
Choi HK, Choi BC, Lee SH, Kim JW, Cha KY, Baek KH. Expression of angiogenesis- and apoptosis-related genes in chorionic villi derived from recurrent pregnancy loss patients. Mol Reprod Dev. 2003;66:24–31.
Amirchaghmaghi E, Rezaei A, Moini A, Roghaei MA, Hafezi M, Aflatoonian R. Gene expression analysis of VEGF and its receptors and assessment of its serum level in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Cell J. 2015;16:538–45.
Banerjee P, Ghosh S, Dutta M, Subramani E, Khalpada J, Roychoudhury S, et al. Identification of key contributory factors responsible for vascular dysfunction in idiopathic recurrent spontaneous miscarriage. PLoS One. 2013;8, e80940.
Banerjee P, Jana SK, Pasricha P, Ghosh S, Chakravarty B, Chaudhury K. Proinflammatory cytokines induced altered expression of cyclooxygenase-2 gene results in unreceptive endometrium in women with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous miscarriage. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:179–87.
Lash GE, Innes BA, Drury JA, Robson SC, Quenby S, Bulmer JN. Localization of angiogenic growth factors and their receptors in the human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle and in recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:183–95.
Eller AG, Branch DW, Nelson L, Porter TF, Silver RM. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A gene polymorphisms in women with recurrent pregnancy loss. J Reprod Immunol. 2011;88:48–52.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants “Genetic factors in the etiology of idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion” (University of Rijeka, Croatia, number 13.06.1.3.32) and “Gynecology and reproduction: genomics and stem cells” (Slovenia, number P3—0326).
Ethical approval
All procedures involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The study was approved by Slovenian and Croatian National Ethics’ Committees and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as described in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Capsule
The −2549 insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene in men might be associated with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereza, N., Ostojić, S., Smirčić, A. et al. The −2549 insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene in couples with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion. J Assist Reprod Genet 32, 1789–1794 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0593-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0593-0