Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to analyze the seminal plasma of patients with idiopathic/male factor infertility and healthy controls with proven fertility by NMR spectroscopy, with a hope of establishing difference in biomarker profiles, if any, between the groups.
Methods
A total of 103 subjects visiting the infertility clinic of Manipal University with normozoospermic parameters, oligozoospermia, asthenozoospermia, azoospermia and teratozoospermia were included. Semen characteristics were analysed by standard criteria. Seminal plasma was subjected to NMR spectroscopy at a 700 MHz 1H frequency. The resultant data was analyzed by appropriate software.
Results
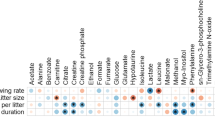
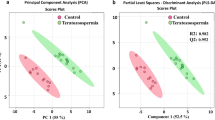
The analysis revealed significant differences between the fertile control group and other forms of male infertility. Interestingly, seminal plasma profile of the idiopathic infertility group showed distinct segregation from the control population as well as other infertile groups. The difference in biomarker profiles between the idiopathic infertility and the rest of the groups combined could originate from either the up-regulation or down regulation of a several compounds, including lysine, arginine, tyrosine, citrate, proline and fructose.
Conclusion
Our data suggests the presence of a metabolic reason behind the origin of idiopathic infertility. 1H NMR based metabonomic profiling based on concentration of biomarker lysine has the potential to aid in the detection and diagnosis of idiopathic infertility in an efficient manner.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson DS, Iman R, Walsh TJ, Kurhanewicz J, Turek PJ. A novel application of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy: non-invasive identification of spermatogenesis in men with non-obstructive azoospermia. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:847–52.
Ahmed Z, Khan MS, Khan MA, Haq A, Rahman J. Seminal fructose in various classes of infertile patients. Pak J Physiol. 2010;6:36–8.
Alexandrino AP, Rodrigues MA, Matsuo T. Evaluation of serum and seminal levels of prostate specific antigen in men with spinal cord injury. J Urol. 2004;171:2230–2.
Alexandrino AP, Rodrigues MA, Matsuo T, Schuquel IT, Costa WF, Santilli JC. Evaluation of seminal citrate level by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in men with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2009;47:878–81.
Ambasudhan R, Singh K, Agarwal JK, Singh SK, Khanna A, Sah RK, et al. Idiopathic cases of male infertility from a region in India show low incidence of Y-chromosome microdeletion. J Biosci. 2003;28:605–12.
Batruch I, Lecker I, Kagedan D, Smith CR, Mullen BJ, Grober E, et al. Proteomic analysis of seminal plasma from normal volunteers and post-vasectomy patients identifies over 2000 proteins and candidate biomarkers of the urogenital system. J Proteome Res. 2011;10:941–53.
Beckonert O, Keun HC, Ebbels TM, Bundy J, Holmes E, Lindon JC, et al. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2692–703.
Botros L, Sakkas D, Seli E. Metabolomics and its application for non-invasive embryo assessment in IVF. Mol Hum Reprod. 2008;14:679–90.
Chaudhury K, Sharma U, Jagannathan NR, Guha SK. Effect of a new injectable male contraceptive on the seminal plasma amino acids studied by proton NMR spectroscopy. Contraception. 2002;66:199–204.
Chew WM, Hricak H, McClure RD, Wendland MF. In vivo human testicular function assessed with P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1990;177:743–7.
Deepinder F, Chowdary HT, Agarwal A. Role of metabolomic analysis of biomarkers in the management of male infertility. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007;7:351–8.
Gonzales GF, Villena A. True corrected seminal fructose level: a better marker of seminal vesicle function in infertile male. Int J Androl. 2001;24:255–60.
Gupta A, Mahdi AA, Ahmad MK, Shukla KK, Jaiswer SP, Shankhwar SN. 1H NMR spectroscopic studies on human seminal plasma: a probative discriminant function analysis classification model. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;54:106–13.
Gupta A, Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, Ahmad MK, Bansal N, Sankhwar P, et al. Efficacy of Withania somnifera on seminal plasma metabolites of infertile males: a proton NMR study at 800 MHz. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;149:208–14.
Hafez B, Goff L, Hafez S. Recent advances in andrology research: physiopathology and clinical application to fertility and infertility. Arch Androl. 1997;39:173–95.
Hamamah S, Seguin F, Barthelemy C, Akoka S, Le Pape A, Lansac J, et al. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance studies of seminal plasma from fertile and infertile men. J Reprod Fertil. 1993;97:51–5.
Hung Y, Huang M. A multi-class IC package type classifier based on kernel-based nonlinear LS-SVM method. J Comput Intell Electron Syst. 2014;7:472–80.
Jonsson M, Linse S, Frohm B, Lundwall A, Malm J. Semenogelins I and II bind zinc and regulate the activity of prostate-specific antigen. Biochem J. 2005;387:447–53.
Kovac JR, Lipshultz LI. The significance of insulin-like factor 3 as a marker of intratesticular testosterone. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:66–7.
Kussmann M, Raymond F, Affolter M. Omics-driven biomarker discovery in nutrition and health. J Biotechnol. 2006;124:758–87.
Lamb DJ. A look towards the future: advances in andrology expected to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of the infertile male. In: Lipshultz L, Howards S, Niederberger C, editors. Infertility in the male. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2009. p. 642–53.
Lynch MJ, Masters J, Pryor JP, Lindon JC, Spraul M, Foxall PJ, et al. Ultra high field NMR spectroscopic studies on human seminal fluid, seminal vesicle and prostatic secretions. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1994;12:5–19.
Maher AD, Cloarec O, Patki P, Craggs M, Holmes E, Lindon JC, et al. Dynamic biochemical information recovery in spontaneous human seminal fluid reactions via 1H NMR kinetic statistical total correlation spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2009;81:288–95.
Maher AD, Patki P, Lindon JC, Want EJ, Holmes E, Craggs M, et al. Seminal oligouridinosis: low uridine secretion as a biomarker for infertility in spinal neurotrauma. Clin Chem. 2008;54:2063–6.
Mallidis C, Agbaje IM, Rogers DA, Glenn JV, Pringle R, Atkinson AB, et al. Advanced glycation end products accumulate in the reproductive tract of men with diabetes. Int J Androl. 2009;32:295–305.
Mallidis C, Green BD, Rogers D, Agbaje IM, Hollis J, Migaud M, et al. Metabolic profile changes in the testes of mice with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int J Androl. 2009;32:156–65.
Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Human anatomy and physiology. 7th ed. Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings; 2007.
Mendes P. Emerging bioinformatics for the metabolome. Brief Bioinform. 2002;3:134–45.
Nobeli I, Thornton JM. A bioinformatician’s view of the metabolome. Bioessays. 2006;28:534–45.
Pampalakis G, Sotiropoulou G. Tissue kallikrein proteolytic cascade pathways in normal physiology and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1776:22–31.
Pauling L, Robinson AB, Teranishi R, Cary P. Quantitative analysis of urine vapor and breath by gas–liquid partition chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971;68:2374–6.
Pilch B, Mann M. Large-scale and high-confidence proteomic analysis of human seminal plasma. Genome Biol. 2006;7:R40.
Ponglowhapan S, Essen- Gustavsson B, Linde Forsberg C. Influence of glucose and fructose in the extender during long term storage of chilled canine semen. Theriogentology. 2004;62:1498–517.
Rhee SY, Dickerson J, Xu D. Bioinformatics and its applications in plant biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:335–60.
Rohr G, Eggert-Kruse W, Kalbitzer HR. NMR spectroscopy in andrology: research uses and possible clinical applications. Int J Androl. 1995;18:12–9.
Roth MY, Lin K, Bay K, Amory JK, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, et al. Serum insulin-like factor 3 is highly correlated with intratesticular testosterone in normal men with acute, experimental gonadotropin deficiency stimulated with low-dose human chorionic gonadotropin: a randomized, controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:132–9.
Schiller J, Arnhold J, Glander HJ, Arnold K. Lipid analysis of human spermatozoa and seminal plasma by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy - effects of freezing and thawing. Chem Phys Lipids. 2000;106:145–56.
Scott R, Seli E, Miller K, Sakkas D, Scott K, Burns DH. Noninvasive metabolomic profiling of human embryo culture media using Raman spectroscopy predicts embryonic reproductive potential: a prospective blinded pilot study. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:77–83.
Segalen J, de Certaines JD, Le Calvé M, Colleu D, Bansard JY, Rio M. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance of human seminal plasma in in vitro fertilization attempts: use of automatic spectrum analysis. J Reprod Fertil. 1995;103:181–7.
Seli E, Botros L, Sakkas D, Burns DH. Noninvasive metabolomic profiling of embryo culture media using proton nuclear magnetic resonance correlates with reproductive potential of embryos in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:2183–9.
Seli E, Sakkas D, Scott R, Kwok SC, Rosendahl SM, Burns DH. Noninvasive metabolomic profiling of embryo culture media using Raman and near-infrared spectroscopy correlates with reproductive potential of embryos in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2007;88:1350–7.
Seli E, Vergouw CG, Morita H, Botros L, Roos P, Lambalk CB, et al. Noninvasive metabolomic profiling as an adjunct to morphology for noninvasive embryo assessment in women undergoing single embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:535–42.
Sharma RK, Agarwal A. Role of reactive oxygen species in male infertility. Urology. 1996;48:835–50.
Singh R, Sinclair KD. Metabolomics: approaches to assessing oocyte and embryo quality. Theriogenology. 2007;68:S56–62.
Thonneau P, Spira A. Prevalence of infertility: international data and problems of measurement. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1991;38:43–52.
Tomlins AM, Foxall PJ, Lynch MJ, Parkinson J, Everett JR, Nicholson JK. High resolution 1H NMR spectroscopic studies on dynamic biochemical processes in incubated human seminal fluid samples. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1379:367–80.
Vergouw CG, Botros LL, Roos P, Lens JW, Schats R, Hompes PG, et al. Metabolomic profiling by near-infrared spectroscopy as a tool to assess embryo viability: a novel, non-invasive method for embryo selection. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:1499–504.
World Health Organization. WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and semen cervical mucus interaction. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1987.
World Health Organization. WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm-cervical mucus interaction. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1999.
Worley B, Powers R. Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr Metabolomics. 2013;1:92–107.
Yatsenko AN, Roy A, Chen R, Ma L, Murthy LJ, Yan W, et al. Non-invasive genetic diagnosis of male infertility using spermatozoal RNA: KLHL10 mutations in oligozoospermic patients impair homodimerization. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:3411–9.
Yoshida K, Yamasaki T, Yoshiike M, Takano S, Sato I, Iwamoto T. Quantification of seminal plasma motility inhibitor/semenogelin in human seminal plasma. J Androl. 2003;24:878–84.
Acknowledgments
The guidance by Dr. Satish Kumar Adiga, Professor and Clinical Embryologist, Division of Reproductive Medicine, Department of OBG, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, India is gratefully acknowledged by the authors. The help of National Facility for High Field NMR in TIFR is greatly acknowledged. AS acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India, for providing SPM Fellowship.
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Soumita Ghosh and Arjun Sengupta these authors contributed equally to this work.
Capsule NMR spectroscopy on seminal plasma of fertile and infertile men revealed significant differences in biomarker profile between idiopathic and other forms of infertility.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayaraman, V., Ghosh, S., Sengupta, A. et al. Identification of biochemical differences between different forms of male infertility by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. J Assist Reprod Genet 31, 1195–1204 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0282-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0282-4