Abstract
Objective
Mammalian oocytes undergo a cortical reaction after fertilization, releasing cortical granules and other proteins into the perivitelline space and inhibiting polyspermy. Few studies have evaluated the biological functions and properties of these proteins.
Study design
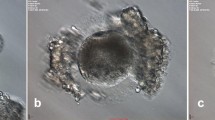
We investigated mouse oocytes in which the zona pellucida (ZP) was present (ZP-intact group) or absent (ZP-free group).
Results
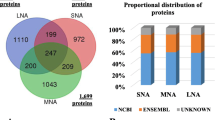
After being activated by Srcl2, secreted proteins are collected from mouse oocytes. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed that identified proteins such as Ldhb, PADi6, Uchl1, Pebp1, Alb, Hsp90aa1, Prss1, trypsinogen 7, trypsin 4, trypsin 10, Sod1, Zp1, Zp2, Zp3, Akap8, Npm2, Pkm2 and Ppia in the ZP-free group. Proteins such as Ldhb, Uchl1, Prss1, trypsin 10, trypsinogen 7, and Ast1 were identified in the ZP-intact groups. The expression of some proteins, including Ldhb, Alb and Sod1, were initially detected following oocyte activation. The finding of four trypsin subtypes, such as Prss1, further support previous observations. Studies investigating the physiological functions and properties of these proteins are ongoing.
Conclusions
Research on these cortical proteins provides a theoretical basis for understanding polyspermy inhibition at the level of ZP and gives technological support for fertilization detection, assessment of oocyte quality and embryonic culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf DP, Hamada M. Induction of zonal and egg plasma membrane blocks to sperm penetration in mouse eggs with cortical granule exudate. Biol Reprod. 1977;17:350–4.
Zhang X, Rutledge J, Khamsi F, Armstrong DT. Release of tissue-type plasminogen activator by activated rat eggs and its possible role in the zona reaction. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992;32:28–32.
Iwahashi K, Kuji N, Fujiwara T, et al. Expression of the exocytotic protein syntaxin in mouse oocytes. Reproduction. 2003;126:73–81.
Liu M, Oh A, Calarco P, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) is a mouse cortical granule protein that plays a role in preimplantation embryonic development. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005;3:42.
Sekiguchi S, Kwon J, Yoshida E, et al. Localization of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 in mouse ova and its function in the plasma membrane to block polyspermy. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:1722–9.
Miller DJ, Gong X, Decker G, Shur BD. Egg cortical granule N-acetylglucosaminidase is required for the mouse zona block to polyspermy. J Cell Biol. 1993;123:1431–40.
Gwatkin RB, Williams DT, Hartmann JF, Kniazuk M. The zona reaction of hamster and mouse eggs: production in vitro by a trypsin-like protease from cortical granules. J Reprod Fertil. 1973;32:259–65.
Liu M, Sims D, Calarco P, Talbot P. Biochemical heterogeneity, migration, and pre-fertilization release of mouse oocyte cortical granules. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003;1:77.
Hoodbhoy T, Carroll EJ, Talbot P. The relationship between p62 and p56, two proteins of the mammalian cortical granule envelope, and Hyalin, the major component of the echinoderm hyaline layer. Biol Reprod. 2000;62:979–87.
Gulyas BJ, Schmell ED. Ovoperoxidase activity in ionophore treated mouse eggs. I. Electron microscopic localization. Gam Res. 1980;3:267–77.
Munoz-Gotera RJ, Hernandez-Gonzalez EO, Mendoza-Hernandez G, Contreras RG, Mujica A. Exocytosis of a 60 kDa protein (calreticulin) from activated hamster oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev. 2001;60:405–13.
Pierce KE, Siebert MC, Kopf GS, Schultz RM, Calarco PG. Characterization and localization of a mouse egg cortical granule antigen prior to and following fertilization or egg activation. Dev Biol. 1990;141:381–92.
Gross VS, Wessel G, Florman HM, Ducibella T. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes mammalian cortical granules and a 32-kilodalton protein in mouse eggs. Biol Reprod. 2000;63:575–81.
Katz-Jaffe MG, Schoolcraft WB, Gardner DK. Analysis of protein expression (secretome) by human and mouse preimplantation embryos. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:678–85.
Beardsley AJ, Li Y, O’Neill C. Characterization of a diverse secretome generated by the mouse preimplantation embryo in vitro. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010;8:71.
Susor A, Liskova L, Toralova T, et al. Role of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-l1 in antipolyspermy defense of mammalian oocytes. Biol Reprod. 2010;82:1151–61.
Wright PW, Bolling LC, Calvert ME, et al. ePAD, an oocyte and early embryo-abundant peptidylarginine deiminase-like protein that localizes to egg cytoplasmic sheets. Dev Biol. 2003;256:73–88.
Esposito G, Vitale AM, Leijten FP, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) 6 is essential for oocyte cytoskeletal sheet formation and female fertility. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;273:25–31.
Lane M, Gardner DK. Lactate regulates pyruvate uptake and metabolism in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Biol Reprod. 2000;62:16–22.
Tawia SA, Lopata A. The fertilization and development of mouse oocytes following cortical granule discharge in the presence of a protease inhibitor. Hum Reprod. 1992;7:1004–9.
Zhang YX, Lai R, Lee WH, Zhang Y. Frog albumin is expressed in skin and characterized as a novel potent trypsin inhibitor. Protein Sci. 2005;14:2469–77.
Hall HG. Hardening of the sea urchin fertilization envelope by peroxidase-catalyzed phenolic coupling of tyrosines. Cell. 1978;15:343–55.
Chen C, Kattera S. Rescue ICSI of oocytes that failed to extrude the second polar body 6 h post-insemination in conventional IVF. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:2118–21.
Fuzzi B, Rizzo R, Criscuoli L, Noci I, Melchiorri L, et al. HLA-G expression in early embryos is a fundamental prerequisite for the obtainment of pregnancy. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(2):311–5.
Rebmann V, Switala M, Eue I, Grosse-Wilde H. Soluble HLA-G is an independent factor for the prediction of pregnancy outcome after ART: a German multi-centre study. Hum Reprod. Epub ahead of print 2010
Borgatti M, Rizzo R, Canto MB, Fumagalli D, et al. Release of sICAM-1 in oocytes and in vitro fertilized human embryos. PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3970.
Hoodbhoy T, Dandekar P, Calarco P, Talbot P. p62/p56 are cortical granule proteins that contribute to formation of the cortical granule envelope and play a role in mammalian preimplantation development. Mol Reprod Dev. 2001;59:78–89.
Moller CC, Wassarman PM. Characterization of a proteinase that cleaves zona pellucida glycoprotein ZP2 following activation of mouse eggs. Dev Biol. 1989;132:103–12.
O’Neill RA, Bhamidipati A, Bi X, et al. Isoelectric focusing technology quantifies protein signaling in 25 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:16153–8.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by Laboratory of Molecular Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (Grant No.09ZR1417000). We thank the Research Centre of Proteome Analysis, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology for the mass spectrometry analysis and Li Peng for her invaluable technical assistance.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Capsule
This study provides a theoretical basis for understanding polyspermy inhibition at the level of the zona pellucida (ZP) and gives technical support for fertilization detection, assessment of oocyte quality, and embryonic culture.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Q., Yang, H., Xue, S. et al. Secretome profile of mouse oocytes after activation using mass spectrum. J Assist Reprod Genet 29, 765–771 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9789-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9789-8