Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the study was to evaluate the correlation between BDNF and oocyte maturation and to verify whether BDNF could predict in vitro fertilization (IVF) outcome.
Methods
The follicle fluid (FF) for BDNF, E2 and P assay were obtained from 59 patients undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The women were divided into two groups by pregnancy outcome and their clinical and lab data were compared. And the correlation of BDNF with E2, P, age, and IVF data were analyzed.
Results
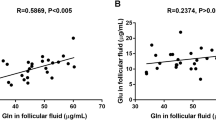
Positive correlation was observed between BDNF and E2 concentration in FF. BDNF was positively correlated with the rate of mature oocytes collected and cleavage rate.
Conclusions
The BDNF in FF could not predict IVF outcome, but BDNF in FF might play an important role in the maturation of oocyte and development of oocyte into preimplantation embryo.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shabankareh HK, Zandi M. Developmental potential of sheep oocytes cultured in different maturation media: effects of epidermal growth factor, insulin-like growth factor I, and cysteamine. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:335–40.
Biswas D, Jung EM, Jeung EB, Hyun SH. Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on porcine preimplantation embryos produced by in vitro fertilization and somatic cell nuclear transfer. Theriogenology. 2011;75:256–67.
Lee GS, Kim HS, Hyun SH, Jeon HY, Nam DH, Jeong YW, et al. Effect of epidermal growth factor in preimplantation development of porcine cloned embryos. Mol Reprod Dev. 2005;71:45–51.
Seifer DB, Feng B, Shelden RM, Chen S, Dreyfus CF. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a novel human ovarian follicular protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:655–9.
Seifer DB, Lambert-Messerlian G, Schneyer AL. Ovarian brain-derived neurotrophic factor is present in follicular fluid from normally cycling women. Fertil Steril. 2003;79:451–2.
Seifer DB, Feng B, Shelden RM. Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence and location of the neurotrophin-Trk receptor family in adult human preovulatory ovarian follicles. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:1129–34.
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Mulders SM, Sollewijn GMD, Hsueh AJ. Ovarian brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes the development of oocytes into preimplantation embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:9206–11.
Martins da Silva SJ, Gardner JO, Taylor JE, Springbett A, De Sousa PA, Anderson RA. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes bovine oocyte cytoplasmic competence for embryo development. Reproduction. 2005;129:423–34.
Lee E, Jeong YI, Park SM, Lee JY, Kim JH, Park SW, et al. Beneficial effects of brain-derived neurotropic factor on in vitro maturation of porcine oocytes. Reproduction. 2007;134:405–14.
Anderson RA, Bayne RA, Gardner J, De Sousa PA. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a regulator of human oocyte maturation and early embryo development. Fertil Steril. 2010;93:1394–406.
Pluchino N, Cubeddu A, Begliuomini S, Merlini S, Giannini A, Bucci F, et al. Daily variation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cortisol in women with normal menstrual cycles, undergoing oral contraception and in postmenopause. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:2303–9.
Buyuk E, Seifer DB. Follicular-fluid neurotrophin levels in women undergoing assisted reproductive technology for different etiologies of infertility. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:1611–5.
Wunder DM, Guibourdenche J, Birkhauser MH, Bersinger NA. Anti-Mullerian hormone and inhibin B as predictors of pregnancy after treatment by in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:2203–10.
Takahashi C, Fujito A, Kazuka M, Sugiyama R, Ito H, Isaka K. Anti-Mullerian hormone substance from follicular fluid is positively associated with success in oocyte fertilization during in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:586–91.
Monteleone P, Artini PG, Simi G, Cela V, Casarosa E, Begliuomini S, et al. Brain derived neurotrophic factor circulating levels in patients undergoing IVF. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2007;24:477–80.
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Fukuda J, Kumagai J, Hsueh AJ, Tanaka T. Regulation of preimplantation embryo development by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev Biol. 2007;311:147–58.
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Sato W, Fukuda J, Kumagai J, Tanaka T. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes implantation and subsequent placental development by stimulating trophoblast cell growth and survival. Endocrinology. 2009;150:3774–82.
Begliuomini S, Casarosa E, Pluchino N, Lenzi E, Centofanti M, Freschi L, et al. Influence of endogenous and exogenous sex hormones on plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:995–1002.
Sohrabji F, Miranda RC, Toran-Allerand CD. Identification of a putative estrogen response element in the gene encoding brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:11110–4.
Chen W, Chen SL, Xing FQ. Brain-derived neurotrophin factor inhibits steroid biosynthesis by human granulosa-lutein cells. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2004;24:1174–6.
Ziegenhorn AA, Schulte-Herbruggen O, Danker-Hopfe H, Malbranc M, Hartung HD, Anders D, et al. Serum neurotrophins—a study on the time course and influencing factors in a large old age sample. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:1436–45.
Conflicts of interest
no
Funds of support
no
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule
BDNF in follicle fluid was assayed. BDNF could not predict IVF outcome, but was important for oocyte maturation and development of oocyte into preimplantation embryo.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Sun, Z., Zhen, J. et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor from follicular fluid is positively associated with rate of mature ooocytes collected and cleavage rate in intracytoplasmic sperm injection patients. J Assist Reprod Genet 28, 1053–1058 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-011-9635-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-011-9635-4