Abstract
Purpose
Men are exposed to various doses of ionizing radiation due to living in regions with high natural background radiation, accidentally, occupationally or for cancer treatment. To study genomic instability of AZFc region to gamma radiation, blood samples from normal, oligozoospermia, and azoospermia individuals were irradiated by a Co-60 source.
Methods
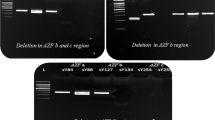
Irradiated cells were kept for 48 h in order to repair initial DNA damages. Real time PCR was performed for three markers (SY 1206, SY 1197, SY 579) for testing copy number variation before and after irradiation. Copy number variations were compared by calculation of cycle threshold comparative method.
Results
Copy number variations of studied markers in AZFc region (microdeletion and duplication) in all samples after exposure to radiation increased with a dose dependent fashion. The frequency of instability was significantly higher in samples from infertile men in comparison with fertile ones (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
No significant difference was seen between the two infertile groups (p > 0.05). This observation might be a possible explanation for induction of azoospermia and oligozoospermia after radiotherapy. Increased frequency of induced microdeletion and duplication in infertile men compared with normal might be attributed to the deficiency in repair systems and the genetic factors involved in incomplete spermatogenesis of infertile men.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howell SJ, Shalet SM. Spermatogenesis after cancer treatment: damage and recovery. J Natl Canc Inst Monogr. 2005;34:12–7.
Gagetia GC, Krishnamurthy H. Effect of low doses of gamma-radiation on the steady-state spermatogenesis of mouse: a flow-cytometric study. Mutat Res. 1995;332:97–107.
Ash P. The influence of radiation on fertility in man. Br J Radiol. 1980;53:271–8.
Meirow D, Schenker JG. Cancer and male infertility. Hum Reprod. 1995;10:2017–22.
Kuczyk M, Machtens S, Bokemeyer C, Schultheiss D, Jonas U. Sexual function and fertility after treatment of testicular cancer. Curr Opin Urol. 2000;10:473–7.
Deepali P, Snjay P, Jyoti S, Sebastian PC, Sher A. Genomic instability of the DYZ1 repeat in patient with Y chromosome anomalies and males exposed to natural background radiation. DNA Res. 2006;13:103–9.
Snjay P, Jyoti S, Sebastian PC, Ahamd J, Sher A. Tandem duplication and copy number polymorphism of the SRY gene in patients with sex chromosome anomalies and males exposed to natural background radiation. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006;12:113–21.
Snjay P, Jyoti S, Sebastian PC, Sher A. AZFc somatic microdeletions and copy number polymorphism of the DAZ genes in human males exposed to natural background radiation. Hum Genet. 2007;121:337–46.
Arruda JT, Silva DM, Silva CC, Moura KKVO, da-Cruz AD. Homologous recombination between HERVs causes duplications in the AZFa region of men accidentally exposed to cesium-137 in Goiânia. Genet Mol Res. 2008;7:1063–9.
Arruda JT. Occurrence of mutations in loci linked to Y chromosome in the offspring born to individuals exposed to ionizing radiation. Genet Mol Res. 2009;8:938.
Reijo R, Algappan RK, Patrizio P, Page DC. Severe oligospermia resulting from deletion of azoospermia factor gene on Y chromosome. Lancet. 1996;347:1290–3.
McElreavey K, Krausz C, Bishop CE. The human Y chromosome and male infertility. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2000;28:2211–32.
Hughes CM, Lewis SE, McKelvey-Martin VJ, Thompson W. A comparison of baseline and induced DNA damage in human spermatozoa from fertile and infertile men, using a modified comet assay. Mol Hum Reprod. 1996;2:613–9.
Pasqualotto FF, Sharma RK, Kobayashi H, Nelson DR, Thomas AJ, Jr-Agarwal A. Oxidative stress in normospermic men undergoing infertility evaluation. J Androl. 2001;22:316–22.
Papachristou F, Simopoulou M, Touloupidis S. DNA damage and chromosomal aberrations in various types of male factor infertility. Fertil Steril. 2008;9:1774–81.
Hall EJ. Radiobiology for the radiologist. 5th ed. New York: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2000.
Mozdarani H, Salimi M. Numerical chromosome abnormalities in 8-cell embryos generated from gamma-irradiated male mice in the absence and presence of vitamin E. Int J Radiat Biol. 2006;82:817–22.
Mozdarani H, Nazari E. Cytogenetic damage in preimplantation mouse embryos generated after paternal and parental gamma-irradiation and the influence of vitamin C. Reproduction. 2009;137:35–43.
Repping S, de-Vries JW, Van-Daalen SK, Korver CM, Leschot NJ, Van-Der-Veen F. The use of sperm HALO-FISH to determine DAZ gene copy number. Mol Hum Reprod. 2003;9:183–8.
De-Vries JW, Hoffer MJV, Repping S, Hoovers JMN, Leschot NJ, Van-Der-Veen F. Reduced copy number of DAZ genes in subfertile and infertile men. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:68–75.
Fernandes S, Huellen K, Goncalves J, Dukal H, Zeisler J, Rajpert-De-Meyts E, et al. High frequency of DAZ1/DAZ2 gene deletions in patients with severe oligozoospermia. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002;8:286–98.
Rozé V, Bresson J, Luc-Fellmann F. Quantitative PCR technique for the identification of microrearrangements of the AZFc region. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2007;24:241–8.
World Health Organization. WHO manual for the standardized investigation and diagnosis of the infertile couple. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2000.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Neel JV, Lewis SE. The comparative radiation genetics of humans and mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:327–62.
Meistrich ML. Male gonadal toxicity. Pediatr Blood Canc. 2009;53:261–6.
Colpi GM, Contalbi GF, Nerva F, Sagone P, Piediferro G. Testicular function following chemo–radiotherapy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;113S:S2–6.
Hermann RM, Henkel K, Christiansen H, Vorwerk H, Hille A. Testicular dose and hormonal changes after radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2005;75:83–8.
Papachristou F, Lialiaris T, Touloupidis S, Kalaitzis C, Simopoulos C, Sofikitis N. Evidence of increased chromosomal instability in infertile males after exposure to mitomycin C and caffeine. Asian J Androl. 2006;8:199–204.
Yamada K, Fujita K, Quan J, Sekine M, Kashima K, Yahata T, et al. Increased apoptosis of germ cells in patients with AZFc deletions. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2010;27:293–7.
Crow JF. The origins, patterns and implications of human spontaneous mutation. Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:40–7.
Wyman C, Kanaar R. DNA double-strand break repair: all’s well that ends well. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:363–83.
Gasior SL, Wakeman TP, Xu B, Deininger PL. The human LINE-1 retrotransposon creates DNA double-strand breaks. J Mol Biol. 2006;357:1383–93.
Mahowald GK, Baron JM, Sleckman BP. Collateral damage from antigen receptor gene diversification. Cell. 2008;135:1009–12.
Nili HA, Mozdarani H, Aleyasin A. Correlation of sperm DNA damage with protamine deficiency in Iranian subfertile men. Reprod BioMedicine Online. 2009;184:479–85.
Falk M, Lukasova E, Kozubek S. Higher-order chromatin structure in DSB induction repair and misrepair. Mutat Res. 2010;704:88–100.
Moskovtsev SI, Mullen JB, Lecker I, Jarvi K, White J, Roberts M. Frequency and severity of sperm DNA damage in patient with confirmed cases of male infertility of different etiology. Reprod BioMedicine Online. 2010;20:759–63.
Bryant PE. The signal model a possible explanation for the conversion of DNA double strand breaks in to chromatid breaks. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998;73:243–51.
Bryant PE, Mozdarani H. Mechanisms underlying the conversion of DNA double strand breaks in to chromatid breaks. Int J Low Radiat. 2004;1:223–30.
Sankaranarayanan K, Wassom JS. Ionizing radiation and genetic risks XIV. Potential research directions in the post-genome era based on knowledge of repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian somatic cells and the origin of deletions associated with human genomic disorders. Mutat Res. 2005;578:333–70.
Baker S, Plug A, Prolla T, Bronner C, Harris A, Yao X, et al. Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat Genet. 1996;13:336–42.
Mark S, Renee A, Reijo P. Male infertility, genetic analysis of the DAZ on Y chromosome and genetic analysis of DNA repair. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;184:41–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Research Department of the Faculty of Medical Sciences of Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran. The authors wish to express their sincere thanks to all patients and healthy individuals for their blood donation and kind contribution and Ms Zahra Tizmaghz for irradiation of samples.
Conflict of Interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule
Lymphocytes from infertile individuals showed higher frequency of genome instability in AZFc region on Y chromosome after gamma irradiation compared to normal controls.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghbeli-Nejad, S., Mozdarani, H., Behmanesh, M. et al. Genome instability in AZFc region on Y chromosome in leukocytes of fertile and infertile individuals following exposure to gamma radiation. J Assist Reprod Genet 29, 53–61 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-011-9626-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-011-9626-5